Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 1: ANOVA - A Dependence Technique
Table 1: ANOVA - A Dependence Technique
Uploaded by
Abhijit Paikaray0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
Anova Note
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageTable 1: ANOVA - A Dependence Technique
Table 1: ANOVA - A Dependence Technique
Uploaded by
Abhijit PaikarayCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT BANGALORE
RMD; PGP – IV (2021-2022)
Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
Basic concept
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a dependence technique. It is used to check the
differences in the mean values of dependent variable associated with the effect of
controlled independent variables, after taking into account the influence/impact of the
controlled independent variables. Essentially, ANOVA is used as a test of means for two or
more populations. The null hypothesis, typically, is that all means are equal (Ho= µ1 = µ2 = µ3)
and the alternative hypothesis is at least one pair of means is unequal. For example, suppose
a marketing research consultant is interested to examine whether heavy, medium, light, and
nonusers of cold drink differ in their preference for cold drink Coca-Cola, measured in a 7-
point Likert-type scale. The null hypothesis that the four groups are not different in
preference, whereas alternative is that at least one pair of groups is different.
ANOVA must have a dependent variable (DV) that is metric and one or more
independent variables that are nonmetric. The nonmetric independent variable (IV) is called
factor. When an ANOVA involves in only ONE metric DV and ONE nonmetric IV, it is
called One-way ANOVA. If two or more IVs are involved, the analysis is termed as n-way
ANOVA. See Table 1 for different types of ANOVA.
Table 1: ANOVA – a dependence technique
No. & Nature of IV No. & Nature of DV Types of test
One categorical One metric One-way ANOVA
Two Categorical One metric Two-way ANOVA
One categorical and one non-categorical (covariate) One metric ANCOVA
One or more categorical Two or more metric MANOVA
Application of ANOVA
Marketing managers are often interested in examining the differences in the mean
values of the dependent variable for several categories of single independent variable. For
example:
Do the various segments differ in terms of their volume of product
consumptions?
Do the brand evaluations of groups exposed to different commercials vary?
Do retailers, wholesalers, and agents differ in their attitudes toward the firm’s
distribution systems?
How does consumers’ intention to buy a brand vary with different price
levels?
The answer to these and similar questions can be determined by conducting one-way
ANOVA.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The History of Money - From Barter To Bitcoin - TelegraphDocument3 pagesThe History of Money - From Barter To Bitcoin - TelegraphAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Answer Key Consumption and InvestmentDocument4 pagesMacroeconomics Answer Key Consumption and InvestmentAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Cons InvDocument75 pagesCons InvAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- DataDocument58 pagesDataAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Questions Module2Document3 pagesQuestions Module2Abhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Lecture Material On MoodleDocument10 pagesSupply Chain Management: Lecture Material On MoodleAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Fashion Industry Faces Disruption From Outside and From Within FT May 2016Document4 pagesFashion Industry Faces Disruption From Outside and From Within FT May 2016Abhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
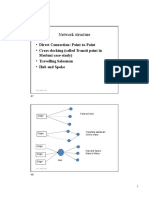
- Hub and SpokeDocument2 pagesHub and SpokeAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Single Period Inventory (Or Newsvendor) Model: Recap From I Year and ExtensionDocument16 pagesSingle Period Inventory (Or Newsvendor) Model: Recap From I Year and ExtensionAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Inventory Allocation ProblemDocument1 pageInventory Allocation ProblemAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Post Hoc Test Write UpDocument1 pagePost Hoc Test Write UpAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Digital PsychologyDocument53 pagesDigital PsychologyAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Foods: Profiling Individual Di Beverage Preference and Consumption: New Insights From A Large-Scale StudyDocument17 pagesFoods: Profiling Individual Di Beverage Preference and Consumption: New Insights From A Large-Scale StudyAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- DS II Tutorial 2-SecB, E, FDocument6 pagesDS II Tutorial 2-SecB, E, FAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- A Company Makes Two Products A and B, Using A Single Resource Pool. The Resource Is Available For 900Document7 pagesA Company Makes Two Products A and B, Using A Single Resource Pool. The Resource Is Available For 900Abhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Covid Vaccine Distribution (Prepared by Shourya) ProcurementDocument9 pagesCovid Vaccine Distribution (Prepared by Shourya) ProcurementAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Strategically Valuable Resources Have Five CharacteristicsDocument1 pageStrategically Valuable Resources Have Five CharacteristicsAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Bajaj CNSDocument3 pagesBajaj CNSAbhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- What'S Your Negotiation Strategy?Document3 pagesWhat'S Your Negotiation Strategy?Abhijit PaikarayNo ratings yet
- Science Process SkillsIntegratedDocument42 pagesScience Process SkillsIntegratedblurrmieNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii FinalDocument8 pagesChapter Iii Finalshellamaebutangon20No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ChiSquareDocument13 pagesChapter 8 ChiSquareYii Phin JongNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Kompetensi, Kompleksitas Tugas, Skeptisme Profesional Terhadap Kualitas Audit Pada BPKP Provinsi Sumatera UtaraDocument11 pagesPengaruh Kompetensi, Kompleksitas Tugas, Skeptisme Profesional Terhadap Kualitas Audit Pada BPKP Provinsi Sumatera UtaraRadina AngganisNo ratings yet
- 1year Syllabus 300716 PDFDocument45 pages1year Syllabus 300716 PDFshaili VermaNo ratings yet
- Biology 8e - Raven - Chapter 1: A. Inductive ReasoningDocument15 pagesBiology 8e - Raven - Chapter 1: A. Inductive Reasoningmafaldina1No ratings yet
- CC 2Document12 pagesCC 2PojangNo ratings yet
- Real Statistics Using ExcelprintDocument7 pagesReal Statistics Using Excelprintamin jamalNo ratings yet
- CMG WorksheetDocument6 pagesCMG Worksheet2057010260No ratings yet
- Information Gathering: Unobtrusive Methods: Kendall & Kendall Systems Analysis and Design, Global Edition, 9eDocument51 pagesInformation Gathering: Unobtrusive Methods: Kendall & Kendall Systems Analysis and Design, Global Edition, 9eBrodyNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument1 pageDocxRAoNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Q 1 M2 & M3Document20 pagesPhilosophy Q 1 M2 & M3Stephanie AriasNo ratings yet
- MB0044 Slides Unit 04Document18 pagesMB0044 Slides Unit 04Saagar KarandeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Political ScienceDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Political ScienceMary Gwyneth Nicomedez100% (2)
- BRM Queation PaperDocument7 pagesBRM Queation PaperAf UsmanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MAT1004 Stat NewDocument7 pagesSyllabus MAT1004 Stat NewTrường XuânNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument2 pagesResearch MethodsJanti Undari0% (1)
- 1.automation Testing OverviewDocument11 pages1.automation Testing OverviewPAVANONLINETRAININGS.COMNo ratings yet
- Exer 3Document8 pagesExer 3deusleanNo ratings yet
- COMPSTAT 2004 - Proceedings in Computational Statistics - Jaromir Antoch (2004) PDFDocument578 pagesCOMPSTAT 2004 - Proceedings in Computational Statistics - Jaromir Antoch (2004) PDFHaojie LiangNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques - Ii: Dr. Pritha GuhaDocument27 pagesQuantitative Techniques - Ii: Dr. Pritha GuhaPradnya Nikam bj21158No ratings yet
- اسئلة مراجعة لطرق البحث وتصميم الابحاث للمعتقلDocument29 pagesاسئلة مراجعة لطرق البحث وتصميم الابحاث للمعتقلAtamnaHelloNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Permasalahan Infrastruktur Drainase Di Kampus Universitas Hasanuddin, Kecamatan Tamalanrea Kota MakassarDocument11 pagesIdentifikasi Permasalahan Infrastruktur Drainase Di Kampus Universitas Hasanuddin, Kecamatan Tamalanrea Kota MakassarShohifah ShafNo ratings yet
- XD AT.06.10 - Selecting Items For Testing and Audit SamplingDocument5 pagesXD AT.06.10 - Selecting Items For Testing and Audit SamplingMaydet MalapitNo ratings yet
- The Casimir Effect and The Quantum VacuumDocument9 pagesThe Casimir Effect and The Quantum VacuumAgris NelietisNo ratings yet
- SPSS Analysis Social ChangeDocument4 pagesSPSS Analysis Social Changevgadamba1No ratings yet
- CANARI Guidelines No. 4 - Guidelines For Participatory PlanningDocument44 pagesCANARI Guidelines No. 4 - Guidelines For Participatory PlanningCaribbean Natural Resources InstituteNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Take Home ExaminationDocument9 pagesBiostatistics Take Home ExaminationUsran Ali BubinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biology Now With Physiology 2nd Edition by Anne Houtman Megan Scudellari Cindy MaloneDocument20 pagesTest Bank For Biology Now With Physiology 2nd Edition by Anne Houtman Megan Scudellari Cindy MaloneJoseph Mattews100% (40)
- Quarter 1Document64 pagesQuarter 1Val LaborNo ratings yet