Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OBGYN Trans
Uploaded by
anonymousCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OBGYN Trans
Uploaded by
anonymousCopyright:
Available Formats
Oral Revalida Review 2019
OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
Lecturer: Ana Katrina Rubin-Siton, MD
*NOTE: Please study the trans together with the
lecture slides
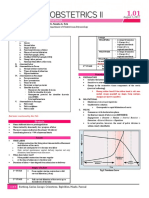
PART 1: OBSTETRICS High Risk Pregnancy:
I. General Reminders 1. Extremes of Ages
1. Before doing the complete History and PE, a. Young primigravidas
GET THE VITAL SIGNS FIRST. b. Elderly primigravidas
(pelvic exam cannot be done in a patient with 2. Medical Complications (HTN, DM, CVD,
elevated BP) Asthma, Infection, Malignancies, etc.)
2. Always obtain consent from the patient and 3. Poor Obstetrical History
explain that you are going to do a pelvic a. 2 consecutive abortions
examination. b. 3 or more repeated abortions
3. Assure that the patient has already urinated c. History of preterm delivery
prior to doing the pelvic examination. d. History of term/preterm fetal death in utero
e. History of term/preterm neonatal death
II. FIRST PRE-NATAL CHECK UP f. Previous baby with congenital anomaly
4. Placenta previa
A. HISTORY TAKING
5. Gynecologic tumors
Must Knows! 6. With coexisting trophoblastic disease or has
had one in the last year
1. Get the accurate AOG by computation of the 7. Patients with problems with fetal aging,
LMP structure, and size
NOTE: a. AOG ≥ 41 weeks
b. Fetal macrosomia or IUGR
*Ultrasound is the most reliable tool to detect c. Unsure fetal aging
AOG <12 weeks (early ultrasound) d. Multiple gestation
*If the disparity between the computed AOG by e. Fetal congenital anomalies
LMP and Early UTZ is 2 WEEKS OR MORE, USE 8. Polyhydramnios/Oligohydramnios
THE AOG BY EARLY ULTRASOUND
2. Ask and know whether the cycle is ovulatory
or not 10 DANGER SIGNS OF PREGNANCY
3. Compute for the Estimated Date of Delivery 1. Persistent headache
(EDD): 2. Blurring of vision
Naegele’s Rule: add 7 days to the date of the 3. Nausea and vomiting
first day of the last normal menstrual period 4. Fever and chills
and counting back 3 months 5. Epigastric Pain/Hypogastric Pain
6. Dysuria
4. Classify if the patient is HIGH RISK or NOT 7. Decreased fetal movement
8. Watery Vaginal Discharge
Oral Revalida Review 2019
9. Bloody Vaginal Discharge
10. Nondependent edema/ Swelling of the POSITIVE SIGNS OF PREGNANCY
hands and feet that is non-resolving
Definitive signs that the pregnancy has really
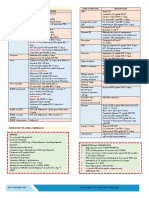
PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS OF PREGNANCY occurred
• Fetal Heart Tones
Signs and symptoms that may resemble
pregnancy but may be attributable to something
TVS 6-8 WEEKS
else
DOPPLER 10-12 WEEKS
• Amenorrhea STETHOSCOPE 18 WEEKS
• Nausea & vomiting
• Fatigue • Perception of active fetal movement by the
• Urinary frequency examiner
• Quickening • Recognition of embryo or fetus by ultrasound
• Uterine enlargement
• Pigmentation changes EXPECTED FINDINGS AGE OF GESTATION
ON UTZ
Gestational Sac 4-5 weeks
Yolk Sac 5-6 weeks
PROBABLE SIGNS OF PREGNANCY Fetal heart beat 6-8 weeks
Crown Rump Length Predictive of
Signs and symptoms that are noted by the
Gestational Age up
examiner, and are more certain implications
to 12 weeks
that the woman is pregnant
• Abdominal enlargement B. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
• Changes in uterus and cervix 1. Weight
*HEGAR’s sign – softening of the
uterine isthmus Weight Gain: (recorded in pounds)
*GOODELL’s sign –Softening of the
cervix (6-8 weeks)
*CHADWICK’S sign- Vaginal mucosa
usually appears dark bluish red and congested
• Palpation of fetal outline
• Braxton Hicks contractions
• Ballotement (20th week)
*uterus is pushed with a finger to feel
whether a fetus moves away and returns again
• (+) Pregnancy test – β HCG
*Onset: 8-9 days after ovulation
*Peak: 60-70 days (10th -11th week)
*Nadir: 14-16 weeks AOG
Oral Revalida Review 2019
*Weight gain is not expected in the first
trimester because of nausea and vomiting
2. Breast Examination
Do not forget to drape the patient properly
during the examination
c. Fetal Heart Tones (be guided by the AOG in
doing the appropriate technique to check for
FHT)
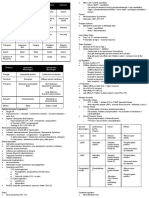
4. Pelvic Examination
3. Abdominal Examination
a. External Genitalia: (done by inspection)
a. Fundic Height: start at 16-18 weeks until 34
Reporting:
weeks
“Hair is distributed in an inverted right triangle
b. Leopold’s Maneuver: Start at 28-30 weeks
pattern, (+) RMLE episiotomy scar measuring
LM1: Fundal grip (what fetal part occupies the ___cm, no gross lesions”
fundus?)
b. Speculum Examination
*Head: ballotable mass, small, hard and round
*Buttocks: wider and softer Technique:
1. Separate the labia using the thumb and pinky
LM2: Umbilical grip (where is the fetal back? of your dominant gloved hand to visualize the
Landmark to check for the heart tones) urethral opening and the vaginal opening.
2. Avoid the urethra.
LM3: Pawlick’s grip (what fetal part is lying at 3. Insert the speculum downwards and
the pelvic inlet?) posteriorly to follow the normal course of the
*Grasp the part of the fetus above the vaginal vault on a dorsal lithotomy position.
symphysis pubis 4. Open the blades of the speculum WITHOUT
*May tell if the presenting part is still floating WITHDRAWING it.
or already engaged 5. Describe the findings.
6. Assess the odor upon withdrawal of the
LM4: Pelvic Grip (what is the presenting part of speculum.
the fetal head?)
Reporting: ‘’cervix is violaceous, smooth, with
*Not usually and routinely done
minimal, whitish, mucoid, non-foul discharge’’
NOTE: In lubricating the speculum, use water if
you are going to do Pap smear; otherwise KY
Jelly may be used.
Oral Revalida Review 2019
c. Internal Examination What Kind of Ultrasound?
1. Transvaginal: if <12 weeks AOG
Technique:
2. Transabdominal: if >12 weeks AOG
1. Separate the labia using the thumb and
pinky. C. Fetal biometry (>13 weeks)
2. Insert the thumb first followed by the middle
2. CBC: to get a baseline values for the patient
finger, palm up.
since physiologic anemia is expected in
3. Palpate
pregnancy (see values for pregnant patients)
Reporting: ‘’cervix is soft, long, closed; uterus
enlarged to 2 months size, no adnexal mass or
tenderness’’
d. Bimanual Examination:
Technique:
Start from the umbilicus going down, palpate
the fundus and observe and feel as the cervix
moves down to your examining finger, that
correlates with level of the fundus.
3. Blood Typing
e. Examination of the Adnexa: not done if >12 4. Urinalysis: to detect asymptomatic
weeks AOG for the uterus already becomes an bacteriuria and to rule out any foci of infection
abdominal organ since infection can precipitate abortion (1st half
Technique: Palpate from the ASIS downwards of pregnancy) and preterm labor (2nd half of
NOTE: Do not do SPECULUM EXAMINATION in a pregnancy)
patient with no sexual contact; only do rectal 5. Hepatitis B Screening
examination if warranted. 6. HIV Screening
7. Vaginal and anal culture for Group B Strep
f. RECTOVAGINAL EXAM (35-37 weeks)
Technique: Insert the pointing finger inside the 3. GDM SCREENING
vagina and the middle finger in the anal canal
Indication: to check for the presence of masses In all Filipino women, we request FBS right
on the cul de sac away on the first prenatal check up
C. PLANS
1. Ultrasound
Uses of Ultrasound:
A. Determine the viability: especially if the AOG
by LMP is <12 weeks wherein Doppler cannot
determine heart tones
B. Disparity between the computed AOG by LMP
and Physical Examination findings (bimanual
examination)
Oral Revalida Review 2019
NOTE: At 24-28 weeks: HPL levels are high b. Treatment:
which can increase glucose levels Sig: Metronidazole 500mg/tab, 1 tab BID for 7
days (avoid taking alcohol within 72 hours of
4. FOLLOW-UP SCHEDULE
the last intake)
Monthly until 28 weeks (7 months)
Every 2 weeks until 36 weeks (9 NOTE: Trichomoniasis is a sexually transimitted
months) disease therefore, TREAT THE SEXUAL PARTNER
Weekly 37 weeks onwards
*if high risk, patient’s follow up schedule may III. Candidiasis
vary a. Most Common Presentation: Vulvar pruritus
5. MEDICATIONS b. Treatment:
Sig: Fluconazole 150mg/tab OD
1. Folic Acid: given on the first trimester
CHIEF COMPLAINT: VAGINAL BLEEDING
*Daily intake of 400 micrograms throughout
the periconceptional period I. AUB (either oligomenorrhea or
*Can give 4mg month before the conception hypermenorrhea)
and in the first trimester if with previous child !!! VERY VERY IMPORTANT IN YOUR LIFE: ‘’AUB
with NTD ON THE BACKGROUND OF REGULAR MENSES:
2. Ferrous Sulfate: starting second trimester ALWAYS RULE OUT PREGNANCY FIRST’’
because it can cause gastric irritation *Determine first if the AUB is ovulatory or
anovulatory
PART 2: GYNECOLOGY 1. POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME (PCOS)
CHIEF COMPLAINT: VAGINAL DISCHARGE a. Diagnosis: use the Rotterdam Criteria, know
also the Ferriman-Gallwey Hirsutism Scoring
I. Bacterial Vaginosis b. Treatment/Management
a. Amsel’s Criteria: need to fulfill 3 out of the 4 -Lifestyle Modification (CORNERSTONE OF
criteria TREATMENT)
Milky homogenous discharge -OCP
-Metformin (only an adjunct treatment)
Clue cells
Vaginal pH > 4.5
Amine odor with 10% KOH (Whiff Test) A. Thickened Endometrium:
Pathophysiology: Estrogen is present in the
b. Treatment: patient that’s why there is a thickened
Sig: Metronidazole 500mg/tab, 1 tab BID for 7 endometrium, and what she lacks is
days Progesterone.
Management: PROGESTERONE CHALLENGE
II. Trichomoniasis
TEST
a. Speculum Examination: yellowish/greenish Sig: Medroxyprogesterone acetate 10mg/tab, 1
frothy discharge, strawberry cervix tab OD for 5 days
Oral Revalida Review 2019
How long can you wait for her to 4. Myoma is the cause of the bleeding
bleed? 5. Sarcomatous degeneration
We can wait for 2 weeks for the
3. ADENOYMYOSIS
bleeding to occur
How will I regulate the cycles? Most common risk factors: multiparity,
Give MPA 10mg/tab, 1 tab OD on Days previous CS, prior uterine surgeries
16-25 of the cycle for 6 months PE: Symmetrically enlarged uterus
Explanation: Day 16-25 coincides with
the secretory phase where
Management:
Progesterone is expected to act and you
a. Medical Management: put the patient on
will try to synchronize the normal
pseudo-pregnancy or pseudo-menopause state
physiologic process by giving
*give OCP WITHOUT THE 7 DAY ‘’NO PILL
Progesterone in the form of MPA
INTERVAL’’: do not make her bleed
Will I advise her to undergo TVS/TRS
b. Surgical Mangement: TAH/ TAHBSO (non-
after 6 months of treatment?
desirous of pregnancy) vs. Myomectomy (still
NO.
desirous of pregnancy)
Explanation: The cysts in the ovaries
are not expected to regress and what is
more important is that the patient CHIEF COMPLAINT: HYPOGASTRIC PAINS
already has regular menstrual cycles.
Differentials:
B. Thin Endometrium (not estrogen primed):
1. Endometriosis
Management: COMBINATION OCP 2. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
a. SE: (+) discharge
Cyproterone Acetate + Ethinyl Estradiol (Althea)
b. IE: (+) cervical motion tenderness: move the
Sig: Take 1 tablet for 21 days straight, no drug
cervix from side to side or up and down
intake for 7 days in order to make her bleed
c. Treatment:
*good for hyperandrogenic presentations (i.e.
*Outpatient:
acne) due to the Cyproterone acetate
Ceftriaxone 250mg IM, single dose +
Doxycycline 100mg PO BID for 14 days
2. MYOMA
± Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 tab BID for 7
PE: Nodularly enlarged uterus days
Management:
a. Medical management *In-patient:
b. Surgical: TAH/ TAHBSO (non-desirous of
Clindamycin 900mg/IV q8 + Gentamycin
pregnancy) vs. Myomectomy (still desirous of
2mg/kg as loading dose and 1.5mg/kg q8 as
pregnancy)
maintenance dose: better penetrance in
abscesses
*NOTE: Indications to take out a myoma
1. Myoma that is causing pressure symptoms
d. Prognosis: can scar the fallopian tubes and
2. Uterus enlarge to 14 weeks AOG/ 3months
can result to infertility, and ectopic pregnancies
3. Solitary myoma that is 8 cm in size
You might also like
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Pedia Osce: 10.5 KG 45.16 CM / 17.8 in 75 CM SixDocument10 pagesReviewer For Pedia Osce: 10.5 KG 45.16 CM / 17.8 in 75 CM SixJamora ManilynNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma: West Visayas State University Medical Center - Department of PediatricsDocument9 pagesBronchial Asthma: West Visayas State University Medical Center - Department of PediatricsPGI Miayo, StephenNo ratings yet
- New Intern Guide Quick NotesDocument8 pagesNew Intern Guide Quick NotesTrisNo ratings yet
- Pedia CardDocument4 pagesPedia CardPatricia Kate RegalaNo ratings yet
- 107 Rle Virtual Duty - Opd: Internal MedicineDocument6 pages107 Rle Virtual Duty - Opd: Internal MedicineGiel Margareth LindoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Guide to Obstetrics and Gynecology History and Physical ExamsDocument3 pagesComprehensive Guide to Obstetrics and Gynecology History and Physical ExamsAgus WijayaNo ratings yet
- Top Nursing Skills, Procedures and Normal ValuesDocument25 pagesTop Nursing Skills, Procedures and Normal ValuesericNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet (Draft)Document3 pagesCheat Sheet (Draft)bonziebuddyNo ratings yet
- OB Med Order KodigsDocument1 pageOB Med Order KodigsfloramaeyecyecNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post PregnancyDocument23 pagesPre and Post PregnancyJitendra ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Abstract TEMPLATEDocument3 pagesClinical Abstract TEMPLATEDiannesa April GolosindaNo ratings yet
- OB-Reviewer With AlgorithmDocument29 pagesOB-Reviewer With Algorithmriczen mae vilaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Codigo 2013Document24 pagesPedia Codigo 2013Denise CastroNo ratings yet
- 01-05-21 - 01-12-21 - Fluid & ElectrolytesDocument8 pages01-05-21 - 01-12-21 - Fluid & ElectrolytesJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- O and G Notes Notebank NumberedDocument173 pagesO and G Notes Notebank NumberedPerscitus Ali القحطانيNo ratings yet
- OB 1.01 DystociaDocument9 pagesOB 1.01 DystociaRaquel Reyes100% (1)
- OB NotesDocument4 pagesOB NotesMaris Sarline OpenianoNo ratings yet
- Dystocia: A Case PresentationDocument63 pagesDystocia: A Case PresentationRoxanneGailBigcasGoleroNo ratings yet
- Neonatal History and Physical ExamDocument2 pagesNeonatal History and Physical ExamMuhammad Farhan KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Neonatology I: Pediatrics 1.1Document15 pagesNeonatology I: Pediatrics 1.1Kurt ZepedaNo ratings yet
- O&G Presentation GuidelineDocument2 pagesO&G Presentation Guidelineleo90_wyattNo ratings yet
- Pedia TicklersDocument24 pagesPedia Ticklersjoshua espirituNo ratings yet
- Ward Census OB Ward Aug 26 DUTYDocument26 pagesWard Census OB Ward Aug 26 DUTYRobz Apacionado100% (1)
- Revalida Reviewer AsmphDocument237 pagesRevalida Reviewer AsmphShey ShocNo ratings yet
- Dem Tickler NotesDocument1 pageDem Tickler NotesSeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancyDocument55 pagesMultiple PregnancyNathaniel YeriNo ratings yet
- PEDIA EndorsementDocument4 pagesPEDIA EndorsementFlorie Lei BulosNo ratings yet
- Pregnant Woman Admitted for Contractions at 37 WeeksDocument18 pagesPregnant Woman Admitted for Contractions at 37 Weeksdila_ayubNo ratings yet
- 2 0CommDiseaseIMPTVisionDocument3 pages2 0CommDiseaseIMPTVisionAndrea Patricia DaquialNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY PEDIA - SaavedraDocument15 pagesCASE STUDY PEDIA - SaavedraChryst Louise SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia UpToDateDocument60 pagesPreeclampsia UpToDateMauricio Marin MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Fabella NotesDocument96 pagesFabella NotesAndrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Approach to Dyslipidemia Based on 2015 CPGDocument26 pagesApproach to Dyslipidemia Based on 2015 CPGRenzy SalumbreNo ratings yet
- Physician Order Sheet Format GuideDocument9 pagesPhysician Order Sheet Format GuideRoland Philip GoNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument6 pagesHypertensionTj Kevin P-DoctorNo ratings yet
- TICKLER-PRINT-2 Pedia PDFDocument7 pagesTICKLER-PRINT-2 Pedia PDFCarlos H. AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Case 1 History & PEDocument3 pagesCase 1 History & PEcbac1990No ratings yet
- Form No. Iifb-26: Republic of The Philippines Department of Health Department of Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument1 pageForm No. Iifb-26: Republic of The Philippines Department of Health Department of Obstetrics and GynecologyAileen EmyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 3 - PediaDocument22 pagesReviewer 3 - PediaSasha ArNo ratings yet
- JI Chart OrdersDocument4 pagesJI Chart OrdersMel BillonesNo ratings yet
- Minor Gynecological ProceduresDocument2 pagesMinor Gynecological Proceduresmkct111No ratings yet
- Post - Natal Case ProformaDocument4 pagesPost - Natal Case Proformakavya sriNo ratings yet
- HIV SeminarDocument5 pagesHIV SeminarJoseph Velarde100% (2)
- Type B (Hib) Vaccine: Haemophilus InfluenzaeDocument2 pagesType B (Hib) Vaccine: Haemophilus InfluenzaeEnce MalatambanNo ratings yet
- Abnormal OBDocument34 pagesAbnormal OBLawrence NemirNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument36 pagesPlacenta Previaotartil_nimanNo ratings yet
- OSCE Reviewer 2013Document4 pagesOSCE Reviewer 2013rere choiNo ratings yet
- Osce Cranial Nerves PDFDocument42 pagesOsce Cranial Nerves PDFriczen vilaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics 2 LaboratoryDocument40 pagesPediatrics 2 LaboratoryAmaetenNo ratings yet
- OB History Endorsement FormatDocument6 pagesOB History Endorsement FormatVin CustodioNo ratings yet
- GynexDocument73 pagesGynexDominque RabastoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Pediatric Society in Cooperation With The Society of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, PhilippinesDocument32 pagesPhilippine Pediatric Society in Cooperation With The Society of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, PhilippinesShari TernolaNo ratings yet
- Group II Makati Medical Center m8 1Document107 pagesGroup II Makati Medical Center m8 1CASSANDRAJUL VARINNo ratings yet
- Tourniquet Test: Small Amount of Air Will Not Harm The TissuesDocument4 pagesTourniquet Test: Small Amount of Air Will Not Harm The TissuesjoymaeannNo ratings yet
- Obgyn PT HistoryDocument4 pagesObgyn PT HistoryDr. SheikhNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: NeurologyDocument19 pagesCase Presentation: NeurologySydrex SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Child's Abdominal Pain Admitting ConferenceDocument24 pagesChild's Abdominal Pain Admitting ConferenceRaul MangrobangNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in PregnancyDocument34 pagesHypertension in PregnancyMusekhirNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentanonymousNo ratings yet
- SioooDocument4 pagesSioooanonymousNo ratings yet
- 31Document1 page31anonymousNo ratings yet
- ZOOLOGY FINALS - AmphibiansDocument3 pagesZOOLOGY FINALS - AmphibiansanonymousNo ratings yet
- 33Document1 page33anonymousNo ratings yet
- 34Document1 page34anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- 32Document1 page32anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- 222Document1 page222anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Meeting Di AvandeDocument1 pageMeeting Di AvandeanonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- 21Document1 page21anonymousNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- 13Document1 page13anonymousNo ratings yet
- 23Document1 page23anonymousNo ratings yet
- 24Document1 page24anonymousNo ratings yet
- 16Document1 page16anonymousNo ratings yet
- 22Document1 page22anonymousNo ratings yet
- 14Document1 page14anonymousNo ratings yet
- 15Document1 page15anonymousNo ratings yet
- American Embryo Transfer Association: Certification Program GuidelinesDocument8 pagesAmerican Embryo Transfer Association: Certification Program GuidelinesFelipe MendozaNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle QuizDocument3 pagesMenstrual Cycle QuizCyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7.3: Gender and SexualityDocument13 pagesLesson 7.3: Gender and SexualityMikaella SaduralNo ratings yet
- 12 de Veyra 1 1Document5 pages12 de Veyra 1 1Kyla Lorena Malate AbelloNo ratings yet
- INFERTILITYDocument31 pagesINFERTILITYShivam. KumarNo ratings yet
- Marquez - Case Study 120Document4 pagesMarquez - Case Study 120Caren Marquez100% (1)
- Consent WaiverDocument2 pagesConsent Waiverlendiodexter92No ratings yet
- Cesarean Delivery and Peripartum HysterectomyDocument26 pagesCesarean Delivery and Peripartum HysterectomyPavan chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Ruptur UteriDocument5 pagesJurnal Internasional Ruptur UteriNovita MayasariNo ratings yet
- Legislative Oppression - Restricting Gestational Surrogacy ToDocument45 pagesLegislative Oppression - Restricting Gestational Surrogacy ToDrake Lawrence FuentabellaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric History Template 21Document3 pagesObstetric History Template 21Raniya AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Maternal ConceptsDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Maternal ConceptsEunice TrinidadNo ratings yet
- ECPs and IUD NotesDocument8 pagesECPs and IUD NotesYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNo ratings yet
- NSG 123 Module 2Document128 pagesNSG 123 Module 2rigasanaorayNo ratings yet
- Management of Reproductive Health and DysmenorrheaDocument33 pagesManagement of Reproductive Health and DysmenorrheaIntan Permatasari Putri SNo ratings yet
- Sex - 4 Books in 1 (Tantric Sex, Kama Sutra, Dirty Talk & Sex Positions) (PDFDrive)Document228 pagesSex - 4 Books in 1 (Tantric Sex, Kama Sutra, Dirty Talk & Sex Positions) (PDFDrive)AdrianaCozmaNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Unintended Pregnancies Among Pregnant Women in Kenya Evidence From Demographic and Health Survey 2014Document8 pagesDeterminants of Unintended Pregnancies Among Pregnant Women in Kenya Evidence From Demographic and Health Survey 2014International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Teenage Pregnancy - WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesTeenage Pregnancy - WPS OfficeJezyl CaseroNo ratings yet
- Obstetric History TakingDocument5 pagesObstetric History TakingAshish Mishra [33]No ratings yet
- Form 11Document1 pageForm 11Nurul Huda KhanNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument18 pagesFamily PlanningPanchal JenishNo ratings yet
- Monthly Ovulation Calendar V1.1Document2 pagesMonthly Ovulation Calendar V1.1EyeoSkyNo ratings yet
- Forms Prenatal 2Document14 pagesForms Prenatal 2Lumondot Benito MhonNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Cytology Assessment of Feto-Placental FunctionDocument3 pagesHormonal Cytology Assessment of Feto-Placental FunctionElina G100% (1)
- Infertility NotesDocument41 pagesInfertility NotesPrasadNo ratings yet
- 5 Hiv Aids in PregnancyDocument26 pages5 Hiv Aids in PregnancyBethelAberaHaydamoNo ratings yet
- Male Sexual DysfunctionDocument39 pagesMale Sexual Dysfunctionsimran kaurNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement For A Persuasive Speech On AbortionDocument8 pagesThesis Statement For A Persuasive Speech On Abortionbriannajohnsonwilmington100% (2)
- Par To Graph ExercisesDocument14 pagesPar To Graph ExercisesNational Child Health Resource Centre (NCHRC)No ratings yet
- Sexlies Stereotypes2008Document76 pagesSexlies Stereotypes2008Lenore Marcus DragmireNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)