Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trade of COVID 19 Vaccines
Trade of COVID 19 Vaccines
Uploaded by
Abhishek YadavOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trade of COVID 19 Vaccines
Trade of COVID 19 Vaccines
Uploaded by
Abhishek YadavCopyright:
Available Formats
Trade of COVID 19 Vaccines
Economic
Political PESTLE ANALYSIS Developing economies depend on high-income countries
While tariffs on vaccines are unlikely to pose a major for vaccines
challenge, they remain a barrier in selected markets
and for important vaccine-related inputs Richer countries have good vaccination rates, poor
ones are unable to procure and transport
Higher tariffs remain on vaccine-related inputs, vaccines, increasing their risk of incubating a more
increasing the final price deadlier version of the virus.
Technological
Sociological
Lack of cold storage transportation caused delayed
Age groups of 45-60 and 60+ have a higher vaccination in poor countries
vaccination penetration as compared to 18-30
and 30-45 age groups Distribution of vaccines required the use of specialized
warehousing, different modes of transport, and last-mile
% of 18-30 age group vaccinated is very low in delivery
poor countries
The production of COVID-19 vaccines is geographically
concentrated, but the demand is global
Legal
Preclinical trials, Phase wise tests, Safety &
Environmental
Efficacy Review and final launch of Vaccines was There was a sudden reduction of Green House
sped up even through legal restrictions, typically it Gases( GHGs) emission as industries ,
takes 4-10 years to develop a vaccine transportation and campaigns have shut down, air
pollution had also decreased
Drug controller groups of various countries eased
up the process and fast tracked vaccine related tests On the other hand Medical waste generation was
increased globally, which is a threat to public health
Several countries are campaigning for a patent and the environment
waiver on COVID Vaccines
Sources: OECD.org | Worldometer.info | ourworldindata.org | networkforphl.org | timesofindia.indiatimes.com
SWOT Analysis for Trade of Vaccines in Angola Country
Weakness Threats
Economic Dependency on China due Oil price war in 2020 resulted in
to previous loan and weak financials dropping prices of oil and export
revenue for Angola got hit drastically,
S STRENGTHS
Vaccine returns and wastage
Lack of proper health infrastructure
exacerbating its already severe
economic woes.
WEAKNESS
distribution across the country Vaccine demand competition from other
African countries
Angola T
W
Opportunities Strengths
With just 5% of 3.18 crore population Angola’s capital Paz Flor has really
THREATS vaccinated, there is significant scope picked up well in the vaccination drive
for vaccination firms to cater to the across the country, the smooth pre-
OPPORTUNITIES remaining population at lower rates and registration process has already
O employing economies of scale in the
process
received accolades.
Angola has invested heavily in cold
Leverage the existing 21 major chain capacity so all vaccines can be
vaccination hubs across the country to used
pump up the vaccination rate
Angola is making use of the Oxford-AstraZeneca, Pfizer-BionTech and Sinopharm COVID-19 vaccines under WHO’s COVAX scheme.
In Angola, from 3 January 2020 to 5:41pm CEST, 2 July 2021, there have been 38,965 confirmed cases of COVID-19 with 903 deaths, reported
to WHO. As of 27 June 2021, a total of 1,488,292 vaccine doses have been administered.
Sources: SCMP.com | covid19.who.int | afro.who.int | edition.cnn.com
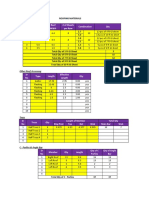
EXCEL SIMULATION ASSUMPTIONS AND STEPS
Initially started with pure trial and error.
Started noticing difference in costs for the same quantity of doses for different countries.
Understood the dependence of costs on the shipping time between from and to pairs.
Tried allocating maximum doses to routes with the lowest shipping time meanwhile maintaining enough supplies from supplier nations.
Did smart trial and error post that and arrived at the solution. Major challenge was allocating for US. Had to find smaller gaps in shipping route.
Finally arrived at a shipping cost of $766,500.
Thank You
You might also like
- ZF Intarder 3 Buses Repair ManualDocument6 pagesZF Intarder 3 Buses Repair Manualjoyce100% (60)
- Formwork and ScaffoldingDocument43 pagesFormwork and ScaffoldingAarti Vij50% (2)
- Numerical Reasoning FormulasDocument7 pagesNumerical Reasoning FormulasRachid HC100% (1)
- Medical English - Reading 6 - From Vaccine Nationalism To Vaccine Equity - Finding A Path ForwardDocument3 pagesMedical English - Reading 6 - From Vaccine Nationalism To Vaccine Equity - Finding A Path ForwardfuilungwongNo ratings yet
- Public Health in PracticeDocument3 pagesPublic Health in Practiceapi-547285914No ratings yet
- Who Gat 008 Global Vaccine Market Report March 12Document15 pagesWho Gat 008 Global Vaccine Market Report March 12ilyaseabsiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Clinical Nursing - 2021 - Al - E2 - 80 - 90amer - COVID - E2 - 80 - 9019 Vaccination Intention in The First Year of The Pandemic ADocument25 pagesJournal of Clinical Nursing - 2021 - Al - E2 - 80 - 90amer - COVID - E2 - 80 - 9019 Vaccination Intention in The First Year of The Pandemic AIsac MartinsNo ratings yet
- Jpha 14 5 2290Document5 pagesJpha 14 5 2290WOYOPWA SHEMNo ratings yet
- Effect of Covid and CorruptionDocument10 pagesEffect of Covid and CorruptionOctavio ChonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 BlashDocument5 pagesPresentation 1 BlashSai TejaswyNo ratings yet
- ECON Case AnalysisDocument4 pagesECON Case AnalysisAvivi GailNo ratings yet
- Is Omicron Signaling A Shift To Endemic Covid?Document27 pagesIs Omicron Signaling A Shift To Endemic Covid?Kurotul AiniahNo ratings yet
- The New England Journal of Medicine - COVID-19Document3 pagesThe New England Journal of Medicine - COVID-19Estarlin Sosa JimenezNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0264410X17300452 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0264410X17300452 MainBambangIrawan48No ratings yet
- Nejmp 2030600Document3 pagesNejmp 2030600Gonzalo Moyano BalbisNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Race Is Over Ready or NotDocument6 pagesVaccine Race Is Over Ready or NotInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Impact On Global Food IndustryDocument8 pagesCOVID-19 Impact On Global Food IndustryRavirajNo ratings yet
- Willingness-To-Pay For A COVID-19 Vaccine and Its Associated Determinants in IndonesiaDocument8 pagesWillingness-To-Pay For A COVID-19 Vaccine and Its Associated Determinants in IndonesianovireandysasmitaNo ratings yet
- Kingston Gleaner Nov 18 2022 P 38Document1 pageKingston Gleaner Nov 18 2022 P 38whoopsoopsNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 ViralDocument3 pagesCovid 19 ViralManpinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Vaccine in AfricaDocument2 pagesVaccine in Africakhadijahussain107No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1074761321002612 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S1074761321002612 Mainellslister15No ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy in South Africa: How Can We Maximize Uptake of COVID-19 Vaccines?Document14 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy in South Africa: How Can We Maximize Uptake of COVID-19 Vaccines?A009Karin Kurniati NurfatmahNo ratings yet
- Public Acceptance of COVID-19Document12 pagesPublic Acceptance of COVID-19Mr. NobodyNo ratings yet
- Socal - Pandemia y Cadena de AbastecimientoDocument5 pagesSocal - Pandemia y Cadena de AbastecimientoPonchi PonchiNo ratings yet
- Covid Africa Article, 04dec20Document1 pageCovid Africa Article, 04dec20Natalie WaqarNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Giving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and RDocument31 pagesGiving Developing Countries The Best Shot: An Overview of Vaccine Access and ROxfamNo ratings yet
- Ariffin Et Al FrontbackDocument4 pagesAriffin Et Al FrontbackHamza HamzaNo ratings yet
- New For Pole Line Hardware Superior Corrosion Resistant OptionsDocument1 pageNew For Pole Line Hardware Superior Corrosion Resistant OptionsWency JavateNo ratings yet
- Roofing Materials EstimateDocument1 pageRoofing Materials Estimatejhomel garciaNo ratings yet
- Zealong Tea IntroductionDocument10 pagesZealong Tea IntroductionPalin NeoNo ratings yet
- Manual Event Corporate TownhallDocument14 pagesManual Event Corporate TownhallDiva Bella Permata - D3 KeperawatanNo ratings yet
- Phillips Street LightDocument3 pagesPhillips Street LightMarak SaibalNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Education: B. Ed (1.5 YEAR)Document287 pagesResearch Methods in Education: B. Ed (1.5 YEAR)HiraNo ratings yet
- Unit-4-Methods of TrainingDocument40 pagesUnit-4-Methods of TrainingManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Julius DissertationDocument54 pagesJulius DissertationTuryamureeba JuliusNo ratings yet
- Revenge AND Death Spell Casters REVIEWS HTTPDocument10 pagesRevenge AND Death Spell Casters REVIEWS HTTPPsychics NyameNo ratings yet
- 2015 SALN FormDocument2 pages2015 SALN FormCHERRYMIE DIONSONNo ratings yet
- Circuto de Chip 5846Document159 pagesCircuto de Chip 5846Angela Fernandez MonteroNo ratings yet
- Investor's Handbook RDS (PLC) FOI 2007-2011Document92 pagesInvestor's Handbook RDS (PLC) FOI 2007-2011Peggy W SatterfieldNo ratings yet
- Soal Pas Big 8 2020-2021Document8 pagesSoal Pas Big 8 2020-2021Maratus SolikhahNo ratings yet
- Black Male Outsider - Teaching As A Pro-Feminist Man (2008)Document268 pagesBlack Male Outsider - Teaching As A Pro-Feminist Man (2008)Sana Al-AshiNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics 2 Q4M2Document30 pagesGen Physics 2 Q4M2Virly MelladoNo ratings yet
- The Purchase Funnel: Definition & IntroductionDocument8 pagesThe Purchase Funnel: Definition & IntroductionDivya AhujaNo ratings yet
- Biokimia Resume Jurnal Kelompok 1Document9 pagesBiokimia Resume Jurnal Kelompok 1Indana ZulfaNo ratings yet
- Sonic Supreme 700 DL 2022-05-13Document14 pagesSonic Supreme 700 DL 2022-05-13andr.bauntiNo ratings yet
- 5K5SSWHDocument8 pages5K5SSWHGustavo GagliardoNo ratings yet
- Project Report/seminar On Lime Soil StabilizationDocument28 pagesProject Report/seminar On Lime Soil StabilizationShubhankar Roy100% (6)
- Week 2 Practicum ReflectionDocument2 pagesWeek 2 Practicum Reflectionapi-287584590No ratings yet
- SSCM1023 Chap 1 PolarDocument22 pagesSSCM1023 Chap 1 Polarbarre PenroseNo ratings yet
- Gender and Sexuality in Popular FictionDocument19 pagesGender and Sexuality in Popular FictionJacksonNo ratings yet
- CadburyDocument24 pagesCadburyRuchita Desai100% (1)
- Research Paper On Hair StylistDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Hair Stylistovkpwsgkf100% (1)
- EAPP Writing A Reaction Review Critique PaperDocument50 pagesEAPP Writing A Reaction Review Critique PaperGraycie Zednem50% (2)