Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Process Hazard Analysis
Uploaded by
محمد المريسيOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Process Hazard Analysis
Uploaded by
محمد المريسيCopyright:
Available Formats
Process hazard analysis: It is a systematic approach used to identify hazard, accident, or
scenarios from a process.
PHA usages and Benefits: The analysis pinpoints weaknesses in the design and operation and
provides information to help improve safety, which will reduce all types of risks and provide
management with a solid technical basis upon which to plan for long term, profitable business.
Objectives for conducting PHA
1. Identify the hazards inherent; identify the credible failures likely to lead to accident
scenarios; evaluate the consequences and likelihood of the various scenarios.
2. Propose changes where warranted to equipment design, process conditions, and
operating procedures to mitigate the risk to a tolerable level; and document the PHA
study in a sufficiently complete, accurate, and concise manner
Factors for selecting PHA techniques
Motivation for the study; Type of results needed; Type of information available to
perform the study; Characteristics of the analysis problem; Perceived risk associated with
the subject processor activity; Resource availability and analyst/management preference;
Amount of experience available with the technology involved; and Organization and/or
industry accident/incident experience.
PHA Techniques
1. Safety Reviews (formal & Informal)
2. Checklist Analysis: list of possible problems and areas to be checked.
3. Relative Ranking Analysis – The Dow Fire and Explosion Index
4. Preliminary Hazard Analysis: identify possible hazards from a very initial stage,
preferably at the design stage of the plant or the facility.
5. What-If Analysis: identify hazardous situations or specific accident scenarios that
could produce an undesired hazardous event.
6. Hazard and Operability Study (HAZOP): a formal procedure to identify hazards
in a chemical process facility.
7. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis: evaluates how equipment can fail and the
effect these failures can have on an installation.
8. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): the exact sequence of primary and intermediate event
failures likely to lead to a top event failure.
9. Event Tree Analysis (ETA): examine the possible consequences of an initial
undesired event.
10. Human Reliability Analysis (HRA): Success Likelihood Index Methodology to
evaluate the probability of a human error occurring throughout the completion of
a specific task.
You might also like
- Process Hazard AnalysisDocument2 pagesProcess Hazard AnalysisSarath CNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Hazard Identification & Risk Assesament Techq.Document144 pagesUnit 2 - Hazard Identification & Risk Assesament Techq.Madhan M100% (3)
- Selection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques PDFDocument16 pagesSelection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques PDFdediodedNo ratings yet
- Industrial Process Hazard Analysis: What Is It and How Do I Do It?Document5 pagesIndustrial Process Hazard Analysis: What Is It and How Do I Do It?Heri IsmantoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Plant Hazard Evaluation GuideDocument48 pagesChemical Plant Hazard Evaluation Guideanpuselvi125100% (1)
- Comparison of Pha Methods PDFDocument10 pagesComparison of Pha Methods PDFQayyum KhanNo ratings yet
- Rio Pipeline Conference Presentation v5Document20 pagesRio Pipeline Conference Presentation v5Sara ZaedNo ratings yet
- SHM - Practical 12 - Risk Assessment MethodsDocument8 pagesSHM - Practical 12 - Risk Assessment MethodsBhaliya AadityaNo ratings yet
- 5 - HazopDocument23 pages5 - HazopMuhammad Raditya Adjie PratamaNo ratings yet
- Principles Hazop Fta Eta FmeaDocument2 pagesPrinciples Hazop Fta Eta FmeaDidier Hung Leung SangNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification Techniques in IndustryDocument4 pagesHazard Identification Techniques in IndustrylennyNo ratings yet
- Xxii Paper 10Document9 pagesXxii Paper 10Ariyandi Yuda PraharaNo ratings yet
- DEM 609 Module-3 Risk Diagnostic and AnalysisDocument24 pagesDEM 609 Module-3 Risk Diagnostic and AnalysisJoseph Berlin JuanzonNo ratings yet
- CH-4 Preliminary Hazard Analysis.Document9 pagesCH-4 Preliminary Hazard Analysis.Ayah AL SMADINo ratings yet
- Risk Cost Assess.00Document19 pagesRisk Cost Assess.00johnny_cashedNo ratings yet
- Risk Assesment MethodDocument4 pagesRisk Assesment MethodRIANA3411No ratings yet
- Risk Assesment MethodDocument4 pagesRisk Assesment MethodRIANA3411No ratings yet
- HSE_lecture Note 5 (1)Document61 pagesHSE_lecture Note 5 (1)Ngọc AnnhhNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 SafetyDocument26 pagesUnit 01 SafetySundar RajanNo ratings yet
- Hazard IdentificationDocument43 pagesHazard IdentificationMANISH BHADAURIANo ratings yet
- Quality Risk Management in Pharmaceutical Dispensing Center: M. Chitmetha, S. Prombanpong, and T. SomboonwiwatDocument8 pagesQuality Risk Management in Pharmaceutical Dispensing Center: M. Chitmetha, S. Prombanpong, and T. SomboonwiwatmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Hazard Operability Study (HAZOP) in A Fertiliser Plant: K. Muthukumar, M. Suman MohanDocument7 pagesHazard Operability Study (HAZOP) in A Fertiliser Plant: K. Muthukumar, M. Suman MohanŘëhmàñ ÀĺîNo ratings yet
- PHA ProcedureDocument15 pagesPHA ProcedureMohammed Zubair100% (1)
- Hazop-Hazid, Sil StudyDocument15 pagesHazop-Hazid, Sil Studydesign electricalNo ratings yet
- Week 9: Lecture Notes / SAFE DESIGN: Safety Is A Management DecisionDocument5 pagesWeek 9: Lecture Notes / SAFE DESIGN: Safety Is A Management DecisionJustinAddodNo ratings yet
- Process Safety Management: A Legal and Technical Overview: Session No. 526Document15 pagesProcess Safety Management: A Legal and Technical Overview: Session No. 526Waqas Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Three Knights Presents Risk-Based InspectionDocument20 pagesThree Knights Presents Risk-Based InspectionAMLO45No ratings yet
- Sms Tools& Analysis MethodDocument27 pagesSms Tools& Analysis Methodsaif ur rehman shahid hussain (aviator)No ratings yet
- T12A Papierz Arkadiusz TORASDocument6 pagesT12A Papierz Arkadiusz TORASArek PapierzNo ratings yet
- Hazard Operability Study ProcedureDocument14 pagesHazard Operability Study ProcedureJulius ChavezNo ratings yet
- Process Hazard AnalysisDocument103 pagesProcess Hazard AnalysisSabrinaQurrotaayun50% (2)
- Risk analysis of a chemical industry using ORA procedureDocument17 pagesRisk analysis of a chemical industry using ORA procedureUsama NiaziNo ratings yet
- TRIZ Method by Genrich AltshullerDocument5 pagesTRIZ Method by Genrich AltshullerAnonymous JyrLl3RNo ratings yet
- Mani Unit IIDocument16 pagesMani Unit IIMani VedhaNo ratings yet
- For Sample Only: ContentDocument20 pagesFor Sample Only: ContentAmirulAkmalNo ratings yet
- Process Safety ManagementDocument23 pagesProcess Safety ManagementMuhammad AbbasNo ratings yet
- Final Test of System Safety - Julian Hanggara AdigunaDocument6 pagesFinal Test of System Safety - Julian Hanggara AdigunaThe Minh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Faculty Hazard AnalysisDocument41 pagesChemical Engineering Faculty Hazard AnalysisCaratsSVTNo ratings yet
- HAZOPDocument7 pagesHAZOPfairusNo ratings yet
- XBRA 3103 OSH Risk Management Assignment Jan 2020 V1Document16 pagesXBRA 3103 OSH Risk Management Assignment Jan 2020 V1Amran Sharif100% (4)
- Process Hazard AnalysisDocument18 pagesProcess Hazard AnalysisJeyakandan MarudiahNo ratings yet
- 501 - 6.2.1.31 Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA) ProcedureDocument11 pages501 - 6.2.1.31 Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA) ProcedureJIGNESH SUTARIYANo ratings yet
- HAZOPDocument9 pagesHAZOPGeorge JohnNo ratings yet
- W22 - Chapter 11 Hazard IdentificationDocument66 pagesW22 - Chapter 11 Hazard Identificationiamayesha725No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment MethodsDocument24 pagesRisk Assessment MethodsXie ShjNo ratings yet
- FMEA - A PHA Tool for Process Safety Risk AssessmentDocument46 pagesFMEA - A PHA Tool for Process Safety Risk Assessmentswapan kumar hazraNo ratings yet
- A Report On HAZOP AnalysisDocument15 pagesA Report On HAZOP AnalysisachyutNo ratings yet
- Hazard IdentificationDocument17 pagesHazard IdentificationSibanda MqondisiNo ratings yet
- Modelado y Seguridad (Casos) Raoni2018Document11 pagesModelado y Seguridad (Casos) Raoni2018Ivan CisnerosNo ratings yet
- HAZOP Saudi Aramco HAZOP GuidelinesDocument92 pagesHAZOP Saudi Aramco HAZOP Guidelinesjakejohns100% (15)
- Gas and Oil Reliability Engineering: Modeling and AnalysisFrom EverandGas and Oil Reliability Engineering: Modeling and AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Reliability, Maintainability and Risk: Practical Methods for EngineersFrom EverandReliability, Maintainability and Risk: Practical Methods for EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Aircraft System Safety: Assessments for Initial Airworthiness CertificationFrom EverandAircraft System Safety: Assessments for Initial Airworthiness CertificationNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Debugging Playbook: System Testing, Error Localization, And Vulnerability RemediationFrom EverandDebugging Playbook: System Testing, Error Localization, And Vulnerability RemediationNo ratings yet
- Security Controls Evaluation, Testing, and Assessment HandbookFrom EverandSecurity Controls Evaluation, Testing, and Assessment HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Rethinking Bhopal: A Definitive Guide to Investigating, Preventing, and Learning from Industrial DisastersFrom EverandRethinking Bhopal: A Definitive Guide to Investigating, Preventing, and Learning from Industrial DisastersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Guidelines for Hazard Evaluation ProceduresFrom EverandGuidelines for Hazard Evaluation ProceduresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Seeking the Truth from Mobile Evidence: Basic Fundamentals, Intermediate and Advanced Overview of Current Mobile Forensic InvestigationsFrom EverandSeeking the Truth from Mobile Evidence: Basic Fundamentals, Intermediate and Advanced Overview of Current Mobile Forensic InvestigationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 4.D Process Safety Management Emergency Response TrainingDocument3 pages4.D Process Safety Management Emergency Response Trainingمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Chemical MSDSDocument7 pagesWater Treatment Chemical MSDSمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Levelized Cost of Energy LCOE - A Misleading Measure of Value For A Carbon-Free WorldDocument1 pageLevelized Cost of Energy LCOE - A Misleading Measure of Value For A Carbon-Free Worldمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Homework 2: Error Checking Hints: For Many Problems We Will Provide Information About The Solution ThatDocument2 pagesHomework 2: Error Checking Hints: For Many Problems We Will Provide Information About The Solution Thatمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Week 11 ReportDocument3 pagesWeek 11 Reportمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- BOARD OF PUBLIC UTILITIES-Proceedings by Authority: Board Members: Present AbsentDocument9 pagesBOARD OF PUBLIC UTILITIES-Proceedings by Authority: Board Members: Present Absentمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Recommendation Letter1Document2 pagesRecommendation Letter1محمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- CE427 Cooling Tower LabDocument4 pagesCE427 Cooling Tower Labمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Extended Outline Format GuideDocument1 pageExtended Outline Format Guideمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- HazardDocument2 pagesHazardمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Script For AnswerDocument4 pagesScript For Answerمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- 2) List Down The Hazards Cause by Video 1 and 3Document1 page2) List Down The Hazards Cause by Video 1 and 3محمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Responsibility of The Workers, Operator and ManagerDocument1 pageResponsibility of The Workers, Operator and Managerمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- 2) List Down The Hazards Cause by Video 1 and 3Document1 page2) List Down The Hazards Cause by Video 1 and 3محمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Grab Repair: Repair On Needs at Anytime and AnyplaceDocument8 pagesGrab Repair: Repair On Needs at Anytime and Anyplaceمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Plant Design Project LogbookDocument4 pagesPlant Design Project Logbookمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- A Layers of Protection AnalysisDocument1 pageA Layers of Protection Analysisمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Mathworks Installation Help PDFDocument42 pagesMathworks Installation Help PDFJoJoMoNo ratings yet
- 4 Lopa IntroductionDocument24 pages4 Lopa IntroductionHanna MeyerNo ratings yet
- Mathworks Installation Help EsDocument44 pagesMathworks Installation Help EsGabriela Ocampo EscobarNo ratings yet
- University of Groningen MagazineDocument14 pagesUniversity of Groningen MagazineKhanh Phuong PhamNo ratings yet
- CAT 6040 Hydraulic Excavator Undercarriage Service TrainingDocument18 pagesCAT 6040 Hydraulic Excavator Undercarriage Service TrainingWillian Ticlia Ruiz100% (1)
- Welfare Schemes in TelanganaDocument46 pagesWelfare Schemes in TelanganaNare ChallagondlaNo ratings yet
- Nigelaycardo 1Document8 pagesNigelaycardo 1ANGELICA AYCARDO FLORESNo ratings yet
- Midterm MMMDocument2 pagesMidterm MMMasdfghjkl zxcvbnmNo ratings yet
- Why encouraging entrepreneurship to boost economies is flawedDocument9 pagesWhy encouraging entrepreneurship to boost economies is flawedLaureanoNo ratings yet
- Working at Height PolicyDocument7 pagesWorking at Height PolicyAniekan AkpaidiokNo ratings yet
- PPR - LISTS - Registered Medicine Price List - 20221127 BahrainDocument318 pagesPPR - LISTS - Registered Medicine Price List - 20221127 BahrainvdvedNo ratings yet
- Sip Annex 3 Gap Analysis Template EditedDocument5 pagesSip Annex 3 Gap Analysis Template EditedRiza GusteNo ratings yet
- FB6100 DSCDocument132 pagesFB6100 DSCTahir FadhilNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Perkins 4012 46TAG1A 46TAG2ADocument18 pagesCatalogue Perkins 4012 46TAG1A 46TAG2AAbdoul-aziz Ben Ousmanou100% (1)
- Medical Certificate: (Coaches, Assistant Coaches, Chaperone)Document1 pageMedical Certificate: (Coaches, Assistant Coaches, Chaperone)Keith Marinas Serquina100% (1)
- IB Student's Soil Systems GuideDocument7 pagesIB Student's Soil Systems GuideYohanes Sumantri RatnodiyantoNo ratings yet
- Adult Assessment: Head To Toe Assessment Is The Baseline and Ongoing Data That Is Needed OnDocument2 pagesAdult Assessment: Head To Toe Assessment Is The Baseline and Ongoing Data That Is Needed OnAldrin NavarroNo ratings yet
- Install Panel WallDocument10 pagesInstall Panel WallLuis PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Veena Singh-176-189 - Findings, Implications and ConclusionsDocument14 pagesVeena Singh-176-189 - Findings, Implications and ConclusionsValerine SNo ratings yet
- Onan RV GenSet Service ManualDocument136 pagesOnan RV GenSet Service ManualAlbert A Ghazaleh100% (2)
- Chapter 18Document10 pagesChapter 18nehallakdawalaNo ratings yet
- Devsecops Course Content: Module-1 Devops BasicsDocument3 pagesDevsecops Course Content: Module-1 Devops Basicshelo nameNo ratings yet
- Global Leader: in Glass IonomerDocument2 pagesGlobal Leader: in Glass IonomerAnggini ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Premium detergent market insights and Nirma case studyDocument32 pagesPremium detergent market insights and Nirma case studyBhavya ShahNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Rheumatology: Applications and ChallengesDocument39 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Rheumatology: Applications and ChallengesMaryame BoutkhilNo ratings yet
- Neurological Assessment CaseDocument13 pagesNeurological Assessment Casedrrajmptn0% (1)
- Ergo in Workplace PDFDocument7 pagesErgo in Workplace PDFsightbdNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement 1Document4 pagesThesis Statement 1Ieka SyafiqahNo ratings yet
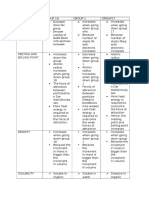
- Physical Properties of Groups 1, 17 and 18 ElementsDocument5 pagesPhysical Properties of Groups 1, 17 and 18 ElementslenovosubaNo ratings yet
- Dgca Module 06 Part 02Document15 pagesDgca Module 06 Part 02Deepak Choudhary DCNo ratings yet
- Assay SolutionsDocument1 pageAssay SolutionsAlex RamirezNo ratings yet
- CaraKumpul - Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kls 12Document7 pagesCaraKumpul - Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kls 12akusayanklenaNo ratings yet
- What Is Communication: What Is Communication MEANING OF COMMUNICATION: It Is Very Difficult To Define The TermDocument12 pagesWhat Is Communication: What Is Communication MEANING OF COMMUNICATION: It Is Very Difficult To Define The Termmanik ghoshNo ratings yet