Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MC3 Lec 1 Overview of Medical Microbiology
Uploaded by
CrishaGarra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesMC3 Lec 1 Overview of Medical Microbiology
Uploaded by
CrishaGarraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
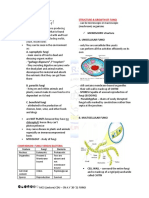
OVERVIEW OF MEDICAL INDIGENOUS MICROBIOTA
- resident microbes in a particular organ /
MICROBIOLOGY organ system
Why are indigenous microbiota
TERMS beneficial to man?
• MICROBIOLOGY – study of (1) inhibit growth of pathogens in those
microbes; most of these microbes areas where they live by occupying space
essentially need the use of various (2) deplete the food supply
types of microscopes in order to be (3) secrete materials that may prevent or
seen and studied reduce the growth of pathogens
• MICROBES – very small living and
nonliving entities OPPORTUNISTIC PATHOGENS
o 2 TYPES:
➢ Pathogens that usually don’t cause
(1) ACELLULAR MICROBES – “infectious any problem but have the potential
particles” ; include viruses and prions to if they gain access to a part
(2) CELLULAR MICROBES – include all where they do not belong
bacteria, archaea, protozoa, algae, fungi
➢ Example: Escherichia coli (E. coli)
don’t cause harm as long as it stays
in the GIT but is dangerous if they
gain access to the urinary bladder,
blood, skin causing infection in the
aforementioned organs
➢ Some opportunistic pathogens strike
when the host is stressed,
weakened, or immunosuppressed
• PATHOGENS – disease-causing
microbes ➢ These are microbe waiting for the
OPPORTUNITY to cause disease.
• NON-PATHOGENS- microbes that do
not cause disease MICROBES CAUSE 2 CATEGORIES OF
DISEASES:
IMPORTANCE OF STUDYING MEDICAL (1) INFECTIOUS DISEASE
MICROBIOLOGY - when a pathogen colonizes the body and
subsequently causes disease
• acknowledge which of the microbes
should we look out for (pathogenic) (2) MICROBIAL INTOXICATION
and which ones we should take care – when a person ingests a toxin that has
for (non-pathogenic) been pre-formed by a microbe.
• understand the diverse role of
microbes in the human body
MC3 (Lecture) CDU – CN A.Y ’20-’21 OVERVIEW OF MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY
BOTH of them cause disease but the
difference is where the toxin is formed.
One, is inside the body, one is already
preformed or already created outside of the
body and taken in its toxic form.
MC3 (Lecture) CDU – CN A.Y ’20-’21 OVERVIEW OF MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Solution Manual For Digital Control System Analysis and Design 4th Edition by Phillips ISBN 0132938316 9780132938310Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Digital Control System Analysis and Design 4th Edition by Phillips ISBN 0132938316 9780132938310jenniferwatersgbrcixdmzt96% (24)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7Micah T. Bardaje100% (9)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Bacteriology - Semifinals - Neisseria and MoraxellaDocument10 pagesBacteriology - Semifinals - Neisseria and MoraxellaUshuaia Ira Marie L. GallaronNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of FungiDocument14 pagesEconomic Importance of FungiShubham Lande100% (1)
- Greek Gods and GodessesDocument17 pagesGreek Gods and GodessesCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- MC3 Lec 5 BACTERIA (Highlighted)Document14 pagesMC3 Lec 5 BACTERIA (Highlighted)CrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- MC3 Lec 6 FUNGI NOTES 1Document7 pagesMC3 Lec 6 FUNGI NOTES 1CrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- MC3 Lec 2 Microbial Cell StructureDocument4 pagesMC3 Lec 2 Microbial Cell StructureCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- MC3 Lec 1 Overview of Medical MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesMC3 Lec 1 Overview of Medical MicrobiologyCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Procedure Guide For Bag Technique Part 1Document1 pageProcedure Guide For Bag Technique Part 1CrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Ethical Theory 4 - UtilitarianismDocument18 pagesEthical Theory 4 - UtilitarianismCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Procedure Guide For Bag Technique Part 3Document2 pagesProcedure Guide For Bag Technique Part 3CrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Procedure Guide For Bag Technique Part 2Document1 pageProcedure Guide For Bag Technique Part 2CrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- DeontologyDocument13 pagesDeontologyCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Ethical Theory - Ethical EgoismDocument6 pagesEthical Theory - Ethical EgoismCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Acts of ManDocument1 pageActs of ManCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Ethical Theory 1 - SubjectivismDocument8 pagesEthical Theory 1 - SubjectivismCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Performance Checklist - ROMDocument3 pagesPerformance Checklist - ROMCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Unit-Vii Heat and Cold Applications Presented By: Mrs. PrashmaDocument49 pagesUnit-Vii Heat and Cold Applications Presented By: Mrs. PrashmaCrishaGarra100% (1)
- NCERT Class 12 BiologyDocument311 pagesNCERT Class 12 Biologynaveen reddy100% (1)
- Detoxifiere Mercur Etc-GhidDocument175 pagesDetoxifiere Mercur Etc-GhidRadulescu EugenNo ratings yet
- Hodgkin Lymphoma 1Document17 pagesHodgkin Lymphoma 1taufik perdanaNo ratings yet
- Sharma Et Al-2020-Frontiers in ImmunologyDocument17 pagesSharma Et Al-2020-Frontiers in ImmunologySadio KeitaNo ratings yet
- The Human Genome ProjectDocument20 pagesThe Human Genome ProjectSvetlana SemykinaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition and Antifungal Activity of The Myrtus Communis and Pistacia Lentiscus EssentDocument26 pagesChemical Composition and Antifungal Activity of The Myrtus Communis and Pistacia Lentiscus Essentbio20100% (1)
- 2018 A Concise Dictionary of PaleontologyDocument320 pages2018 A Concise Dictionary of PaleontologyPredrag Radović100% (2)
- Vem12 - GoatsDocument104 pagesVem12 - Goatsjayr ludoviceNo ratings yet
- SOP 12: Validation of Bioanalytical Methods: Background and ObjectivesDocument4 pagesSOP 12: Validation of Bioanalytical Methods: Background and ObjectivesMaheshNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE - Arroceros Urban BiodiversityDocument18 pagesARTICLE - Arroceros Urban BiodiversityEmelynNo ratings yet
- The Origin of The UniverseDocument7 pagesThe Origin of The UniverseEve Lyn RemedioNo ratings yet
- 1physics-An Introduction SSC PresentationDocument28 pages1physics-An Introduction SSC PresentationPrincess ZoyaNo ratings yet
- Msds Asam MefenamatDocument6 pagesMsds Asam MefenamatKristal Resa Diena RNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument4 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsJonas Galeos0% (1)
- AS DebateDocument3 pagesAS DebateVincent OngNo ratings yet
- R Reeggaarrddiinngg Tthhee Eexxaam Miinnaattiioonn: GDD ? H@Qka A9Fk KMJ? GFK H9Cakl9FDocument3 pagesR Reeggaarrddiinngg Tthhee Eexxaam Miinnaattiioonn: GDD ? H@Qka A9Fk KMJ? GFK H9Cakl9FAamir HamaadNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group System. LegitDocument11 pagesABO Blood Group System. LegitShestrelmay Launico UmingaNo ratings yet
- Desalination Approach of Seawater and Brackish Water by Coconut Shell Activated Carbon As A Natural Filter MethodDocument7 pagesDesalination Approach of Seawater and Brackish Water by Coconut Shell Activated Carbon As A Natural Filter MethodEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems For KidsDocument12 pagesHuman Body Systems For Kidsnk20No ratings yet
- CMY1501 - Theme 4 Examination ActivityDocument5 pagesCMY1501 - Theme 4 Examination ActivityNelani GreeffNo ratings yet
- Virtual Microscope by BIONETWORK: Name: - DateDocument6 pagesVirtual Microscope by BIONETWORK: Name: - DateMuhammad NaraNo ratings yet
- Land Change Modeler ArcGIS Software BrochureDocument6 pagesLand Change Modeler ArcGIS Software BrochureFabio Leonel Casco GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Marine Debris in Mangroves and On The Seabed: Largely-Neglected Litter ProblemsDocument2 pagesMarine Debris in Mangroves and On The Seabed: Largely-Neglected Litter ProblemsRidho HasanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Breech PresentationDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Breech Presentationeskempertus0% (2)
- Everyday Science (My Notes) - CSS ForumsDocument18 pagesEveryday Science (My Notes) - CSS Forumsawais ali shahNo ratings yet
- Histology Self Quiz BoneDocument3 pagesHistology Self Quiz BoneJoonHong AnNo ratings yet