Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rang Ham Mat Benh Vien Rang Ham Mat TP HCM
Uploaded by
top theOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rang Ham Mat Benh Vien Rang Ham Mat TP HCM
Uploaded by
top theCopyright:
Available Formats
https://sanduoc.
net/phac-do-dieu-tri-benh-
rang-ham-mat-benh-vien-rang-ham-mat-tp-hcm/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7114004/
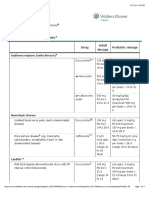
Irreversible pulpitis, necrotic pulps, and localized acute apical abscesses
no need antibiotic in no systematic signs
Soft tissue swelling of endodontic origin (apical abscess/alveolar abscess)
pyrexia in last 24h antibiolic
Acute facial swelling of dental origin/facial cellulitis
IF abscess Signs of systemic involvement and septicemia (e.g. fever, malaise, asymmetry, facial swelling,
lymphadenopathy, trismus, tachycardia, dysphagia, respiratory distress)
The antibiotic of choice is
1. amoxicillin (2–3 days, max 5 days)
Children > 3 months and < 40 kg: 20–40 mg/kg/day in divided doses 8 hourly
children > 40 kg: 250–500 mg 8 hourly
2. or phenoxymethyl penicillin (2–3 days, max 5 days):
children <12 years: 25–50 mg/kg/day in divided doses 6 hourly and
children ≥12 years: 250–500 mg 6 hourly.
Recommended antibiotic regimen for penicillin-allergic patient
metronidazole (3 days): children 30/mg/kg/day in divided doses 6 hourly
azithromycin: children > 6 months up to 16 years: 5–12 mg/kg daily for 3 days,
clarithromycin (7 days):7.5 mg/kg 12 hourly.
Dental trauma
Systemic antibiotics have been recommended as adjunctive therapy for avulsed permanent incisors with an open
or closed apex.
Tetracycline (doxycycline twice daily for 7 days). Trẻ em trên 8 tuổi uống 25 - 50 mg/kg thể trọng/ngày chia 2 - 4 lần.
Penicillin V or amoxicillin can be given as an alternative in patients under 12 years of age
Pediatric periodontal diseases
Dental plaque-induced gingivitis, eruption gingivitis, pubertal gingivitis, gingivitis related to mouth breathing,
and primary herpetic gingivostomatitis are managed by appropriate local therapeutic interventions including
professional oral hygiene and reinforcement of brushing twice daily for at least 2 min and no antibiotics should
be prescribed.
Patients diagnosed with aggressive periodontal disease (now periodontitis) may require
antibiotic of choice for aggressive periodontitis
amoxicillin (50 mg/kg/day)
metronidazole 30 mg/kg/day 8 hourly for 7 days.
Recommended antibiotic regimen for penicillin-allergic patient is
azithromycin (3 days): 10 mg/kg daily or metronidazole.
****
cephalosporins should not be used in an individual with a history of anaphylaxis, angioedema, or urticaria with penicillin or
ampicillin
Another concern that dentists have expressed involves patients who require prophylaxis but are already taking antibiotics
for another condition. In these cases, the AHA guidelines and 2021 AHA scientific statement for infective endocarditis 7,
9
recommend that the dentist select an antibiotic from a different class than the one the patient is already taking. For
example, if the patient is taking amoxicillin, the dentist should select azithromycin or clarithromycin for prophylaxis.
You might also like
- Unit 8 Review Tests: Listen To The Conversation. Then Choose The Answer That Correctly Completes Each SentenceDocument4 pagesUnit 8 Review Tests: Listen To The Conversation. Then Choose The Answer That Correctly Completes Each SentenceChristian Mina64% (11)
- Questions 1 - 100Document15 pagesQuestions 1 - 100Vicky Cezar Villanueva50% (2)
- Drug Adult Dose Child Dose Precautions and ContraindicationsDocument9 pagesDrug Adult Dose Child Dose Precautions and ContraindicationsanshulNo ratings yet
- Phil HealthDocument3 pagesPhil HealthNicole Elma CaparasNo ratings yet
- المضادات الحيويه د.أيمن ابراهيمDocument6 pagesالمضادات الحيويه د.أيمن ابراهيمDr Asaad Al-MosawiNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Daftar ObatDocument6 pagesKumpulan Daftar ObatZega AgustianNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic GuidDocument11 pagesAntibiotic Guidlaur_rbNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryFrom EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryNo ratings yet
- Class Indications: CephalexinDocument2 pagesClass Indications: CephalexinAgatha Pralita KusumawardhiniNo ratings yet
- Dosis Lazim AntibiotikDocument21 pagesDosis Lazim AntibiotiknovaNo ratings yet
- Guide Paed Bone JNTDocument11 pagesGuide Paed Bone JNTDorica GiurcaNo ratings yet
- Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection. 1Document20 pagesAcute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection. 1Joana Carolina QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics and Its Use in Pediatric Dentistry: A ReviewDocument5 pagesAntibiotics and Its Use in Pediatric Dentistry: A ReviewMayangdevi SPNo ratings yet
- G AntibioticTherapyDocument3 pagesG AntibioticTherapyJacoboGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics 1Document41 pagesAntibiotics 1AlaaNo ratings yet
- Co Amoxiclav (Broad Spectrum Penicillin)Document3 pagesCo Amoxiclav (Broad Spectrum Penicillin)Danielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument27 pagesAcute Otitis MediassssceNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanisms of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Amoxicillin Brand NameDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanisms of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Amoxicillin Brand NameRye AnchNo ratings yet
- Newmicrosoftworddocument10 170825021755Document15 pagesNewmicrosoftworddocument10 170825021755hassonamonaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticGuidelines PrimaryDocument12 pagesAntibioticGuidelines PrimaryHandriyato SukmaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Adjuncts To Perio Dontal TreatmentDocument56 pagesAntibiotic Adjuncts To Perio Dontal Treatmentyasmin99No ratings yet
- التهاب الجيوب الانفية والاذن الوسطىDocument2 pagesالتهاب الجيوب الانفية والاذن الوسطىDavid HosamNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics and Antibacterial DrugsDocument69 pagesAntibiotics and Antibacterial DrugsJames PerianayagamNo ratings yet
- Prescribing Antibiotics and Analgesics in ChildrenDocument4 pagesPrescribing Antibiotics and Analgesics in ChildrenPreetam PatnalaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Pharmacology 2Document3 pagesAssignment On Pharmacology 2Fazle Rabbi 173-29-1103No ratings yet
- Bpac Antibiotics Booklet PDFDocument20 pagesBpac Antibiotics Booklet PDFVenny Tri Pahlevi IINo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument56 pagesAntibioticstintinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guideline For Sinusitis Treatment (Rhinosinusitis)Document4 pagesClinical Practice Guideline For Sinusitis Treatment (Rhinosinusitis)Nungki ArdilaNo ratings yet
- CDPH Guidelines Dental Antibiotic UseDocument5 pagesCDPH Guidelines Dental Antibiotic UseAMVTNo ratings yet
- Sinustits FileDocument4 pagesSinustits FilefakrulnersmudaNo ratings yet
- CefaclorDocument3 pagesCefaclorAyah PaasaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Used in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery1Document38 pagesAntibiotics Used in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery1mcshah19100% (1)
- Antibiotics: Use and Misuse in Pediatric Dentistry - A ReviewDocument23 pagesAntibiotics: Use and Misuse in Pediatric Dentistry - A ReviewKarishma SirimullaNo ratings yet
- Ranicef Tablets Cefdinir Tablets 300MG FidsonDocument13 pagesRanicef Tablets Cefdinir Tablets 300MG FidsonWright JohnNo ratings yet
- Chemical Periodontal TherapyDocument23 pagesChemical Periodontal Therapyneji_murniNo ratings yet
- Dental Abscess Primary and Permanent Teeth CDT 2019Document7 pagesDental Abscess Primary and Permanent Teeth CDT 2019jaka tingkirNo ratings yet
- Drugs in OrthodonticsDocument67 pagesDrugs in OrthodonticsMaitreye PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in Periodontics PerioDocument51 pagesAntibiotics in Periodontics PerioSiddhartha BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cefprozil - AHFS 2011Document15 pagesCefprozil - AHFS 2011DetriNo ratings yet
- Oral Management of Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy and ChemotherapyDocument26 pagesOral Management of Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy and Chemotherapymiss0meNo ratings yet
- Ionizing Radiation Its Effects On Oral TissuesDocument34 pagesIonizing Radiation Its Effects On Oral TissuesrehanNo ratings yet
- Patients On Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy: Oral Manifestation of ChemotherapyDocument5 pagesPatients On Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy: Oral Manifestation of Chemotherapyمحمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Formulari Ubat KKM 3/2012Document238 pagesFormulari Ubat KKM 3/2012afiq83100% (3)
- Antibiotics: Choices For Common InfectionsDocument30 pagesAntibiotics: Choices For Common InfectionsAlfeus GradyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Infections: Section A: AntibioticsDocument43 pagesChapter 9: Infections: Section A: AntibioticsAndina NsNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Lyme Disease : Official Reprint From Uptodate ©2014 UptodateDocument3 pagesTreatment of Lyme Disease : Official Reprint From Uptodate ©2014 UptodaterohNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Pediatric Odontology. An UpdateDocument6 pagesAntibiotic Prophylaxis in Pediatric Odontology. An UpdateJavier Farias VeraNo ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTICSDocument51 pagesANTIBIOTICSamrharidi446No ratings yet
- Zinnat TabletsDocument5 pagesZinnat TabletsAndrei Marian BorcescuNo ratings yet
- CEFOXITINDocument30 pagesCEFOXITINJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Terapi AnakDocument10 pagesTerapi AnakIka KrastanayaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument31 pagesAntibioticsAkash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mino Cyc LineDocument3 pagesMino Cyc LineAaliyah OralloNo ratings yet
- Master RQsDocument81 pagesMaster RQsBahaa Ibrahim Helmi100% (2)
- Amoxicillin 125 MG 250 MG 5 ML Oral SuspensionDocument16 pagesAmoxicillin 125 MG 250 MG 5 ML Oral SuspensionAshrafNo ratings yet
- AmoxcillinDocument7 pagesAmoxcillinMohamed FarahatNo ratings yet
- Management of Deep Carious LesionsFrom EverandManagement of Deep Carious LesionsFalk SchwendickeNo ratings yet
- Peri-Implant Complications: A Clinical Guide to Diagnosis and TreatmentFrom EverandPeri-Implant Complications: A Clinical Guide to Diagnosis and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria how to recognize the disease, how to keep from catching it, how to treat those who do catch itFrom EverandDiphtheria how to recognize the disease, how to keep from catching it, how to treat those who do catch itNo ratings yet
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!From EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Station #4 - Clinical Scenario - ListDocument1 pageStation #4 - Clinical Scenario - Listtop theNo ratings yet
- Station #4 - Clinical Scenario - ListDocument1 pageStation #4 - Clinical Scenario - Listtop theNo ratings yet
- Station #4 - Clinical Scenario - ListDocument1 pageStation #4 - Clinical Scenario - Listtop theNo ratings yet
- The Lecture: "Tumours of The Mammary Gland."Document21 pagesThe Lecture: "Tumours of The Mammary Gland."top theNo ratings yet
- 1. !!!prac. СPRDocument55 pages1. !!!prac. СPRtop theNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Third Molar Impaction in Patient With Mandibular Anterior Teeth CrowdingDocument5 pagesPrevalence of Third Molar Impaction in Patient With Mandibular Anterior Teeth CrowdingArina Al-KhaqNo ratings yet
- Torus Palatinus - Google SearchDocument1 pageTorus Palatinus - Google Searchmkilfoyle11No ratings yet
- Localized Dental Abrasion Caused by An Unusually Vicious Habit: Cases Report and Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesLocalized Dental Abrasion Caused by An Unusually Vicious Habit: Cases Report and Literature ReviewTheodora ComanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy BonesDocument11 pagesAnatomy BonesDunkin DonutNo ratings yet
- 1722-Texto Del Artículo-3066-1-10-20200426Document7 pages1722-Texto Del Artículo-3066-1-10-20200426Mishell Semanate BautistaNo ratings yet
- Detolla 2000Document5 pagesDetolla 2000guptaamitalwNo ratings yet
- Occlusal Splint: A Vital Adjunct in Full Mouth Rehabilitation For Cases of Severely Worn DentitionDocument5 pagesOcclusal Splint: A Vital Adjunct in Full Mouth Rehabilitation For Cases of Severely Worn DentitionErisa BllakajNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 4 - Kasus SimpleDocument12 pagesJurnal 4 - Kasus SimpleKurnia SelaNo ratings yet
- Dental Morphology and CrowdingDocument6 pagesDental Morphology and CrowdingDiego SolaqueNo ratings yet
- Applications of Ozone Therapy in DentistryDocument6 pagesApplications of Ozone Therapy in DentistryYanimel SosaNo ratings yet
- Writing Dentistry Sample Test 1Document5 pagesWriting Dentistry Sample Test 1Eduardo Antonio Comaru GouveiaNo ratings yet
- Jcpe 12368Document7 pagesJcpe 12368Monika WerdiningsihNo ratings yet
- Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth Without Ferrule Using A Novel H-Shaped Short PostDocument13 pagesFracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth Without Ferrule Using A Novel H-Shaped Short PostTiago CostaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy by DR Naser AlBarbariDocument24 pagesAnatomy by DR Naser AlBarbariTanmay JhulkaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Occlusion On 11 May 2022Document25 pagesSeminar On Occlusion On 11 May 2022Dr Saurav kumar DuttaNo ratings yet
- BDS 2ND Year New SchemeDocument3 pagesBDS 2ND Year New SchemeSumeet SodhiNo ratings yet
- ACP, ch2, 2.6.1 and 2.6.2, Khalid AlshareefDocument3 pagesACP, ch2, 2.6.1 and 2.6.2, Khalid AlshareefKhalid Bin FaisalNo ratings yet
- Ellis 2014Document32 pagesEllis 2014Sthefany Alesa Gálvez BazánNo ratings yet
- Dental Vet Brochure Picture 1Document18 pagesDental Vet Brochure Picture 1Daniela PachecoNo ratings yet
- X RayDocument8 pagesX RayAla JuvalaNo ratings yet
- Pronunciati On Practice 2: English PronunciationDocument19 pagesPronunciati On Practice 2: English PronunciationMario OvejeroNo ratings yet
- Orthodontics Questions and Answers PDFDocument6 pagesOrthodontics Questions and Answers PDFM7md OdehNo ratings yet
- Personal Information: Curriculum Vitae Information FormDocument3 pagesPersonal Information: Curriculum Vitae Information FormLatifa AlsalehNo ratings yet
- Deflexion Cuspidea en Premolares Con Bulk Fill PDFDocument9 pagesDeflexion Cuspidea en Premolares Con Bulk Fill PDFJoshua LiraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Burn 4Document2 pagesChemical Burn 4Yeni PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Endostar E3. Only Three Steps.: Endo StarDocument8 pagesEndostar E3. Only Three Steps.: Endo Stariulian tigauNo ratings yet
- The Steps For Construction of Complete Denture: Dr. Nagi ShaatDocument15 pagesThe Steps For Construction of Complete Denture: Dr. Nagi ShaatAssssssNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Root Cementum: Part 26. Effects of Micro-Osteoperforations On Orthodontic Root Resorption: A Microcomputed Tomography StudyDocument10 pagesPhysical Properties of Root Cementum: Part 26. Effects of Micro-Osteoperforations On Orthodontic Root Resorption: A Microcomputed Tomography StudyMonojit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkullDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The SkullYeraldin EspañaNo ratings yet