100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views1 pageCPD Concept Map
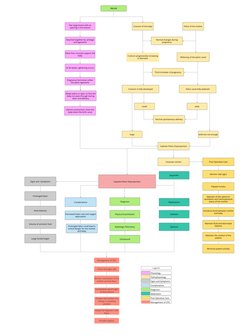
The document discusses the pelvis and changes that occur during pregnancy. It notes that the two large pelvic bones have an opening that widens during pregnancy due to softening ligaments and cartilage. This allows the baby's head to pass through the birth canal during labor and delivery. The third trimester brings further widening to fully accommodate the baby. In some cases called cephalo-pelvic disproportion, the pelvis may not widen enough, requiring a cesarean section delivery.
Uploaded by
Shandle Dynne BaenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views1 pageCPD Concept Map
The document discusses the pelvis and changes that occur during pregnancy. It notes that the two large pelvic bones have an opening that widens during pregnancy due to softening ligaments and cartilage. This allows the baby's head to pass through the birth canal during labor and delivery. The third trimester brings further widening to fully accommodate the baby. In some cases called cephalo-pelvic disproportion, the pelvis may not widen enough, requiring a cesarean section delivery.
Uploaded by
Shandle Dynne BaenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd