Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Expts 3 To 4 Review
Uploaded by
Kyra Bianca R. Famacion0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views4 pagesThis document describes qualitative analysis methods for organic compounds. It discusses tests to identify carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and functional groups like alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and hydrocarbons. Combustion analysis and reactions with reagents like limewater, Fehling's solution, and sodium bicarbonate are used to deduce elemental and functional group composition.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lab Expts 3 to 4 Review
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes qualitative analysis methods for organic compounds. It discusses tests to identify carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and functional groups like alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and hydrocarbons. Combustion analysis and reactions with reagents like limewater, Fehling's solution, and sodium bicarbonate are used to deduce elemental and functional group composition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views4 pagesLab Expts 3 To 4 Review
Uploaded by
Kyra Bianca R. FamacionThis document describes qualitative analysis methods for organic compounds. It discusses tests to identify carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and functional groups like alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and hydrocarbons. Combustion analysis and reactions with reagents like limewater, Fehling's solution, and sodium bicarbonate are used to deduce elemental and functional group composition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Qualitative Analysis of Elements in Organic Compounds
A. Carbon and Hydrogen
Combustion:
C 12 H 22 O 11 + 48CuO →12 C O 2 ↑+11 H 2 O+ 24 C u2 O
Sugar black powder moisture dark red/brown
(white crystals) formed solid
H 2 O (moisture) formed N
At the other end of delivery tube:
C O2 ↑+ Ca ( OH )2 →CaC O3 ↓+ H 2 O
Lime water white
precipitate
CaC O3 ↓ ¿white precipitate) formed C
B. Test for Oxygen
Ferrox paper: absorbed with SC N and Fe3 +¿¿ions
−¿ ¿
Fe3 +¿¿ forms blood red complex with SC N
−¿ ¿
2+¿ (aq )¿
−¿( aq)→ Fe( SCN ) ¿
Fe3 +¿ (aq )+SC N ¿
blood red complex
Oxygen in the compound forms a deep red to purple complex with Fe ( SCN )2+ ¿¿
2+ ¿¿
( SCN )2 +¿ Fe−−O −−Fe ( SCN ) ¿
C. Sodium Fusion
Na metal and an organic compound melt together (fusion) during heating
They undergo a redox reaction in which Na is oxidised and hetero elements
are reduced
R= alkyl group RX , R3 N , R 2Na
S→ NaX , NaCN , Na2 S
heat
Ions of X, N, and S are dissolved and tested
D. Test for N, S, X
Lassaigne’s test (presence of N):
2 NaCN + FeS O 4 → Fe(CN )2 + Na2 S O 4
Fe(CN )2+ 4 NaCN → N a4 Fe(CN )6
Na4 Fe(CN )6+ 4 Fe Cl3 → F e 4 [ Fe ( CN )6 ]3
Prussian blue ppt
(bluish green)
Test for Sulfur (S):
N a2 S + Pb ( CH 3 COO )2 → PbS ↓+ 2 Na CH 3 COO
Black ppt
Test for Halogens (X) (Silver Nitrate Test):
+ ¿ ( aq ) ¿
Ag+¿ ( aq)+ NaX → AgX ↓ +N a ¿
Cl white ppt
Br, I yellow ppt
- Yellow ppt indicates presence of Br or I but may not imply the absence
ofCl
- White ppt of AgCl may be obscured by the intense yellow color of AgBr or
AgI
- For better differentiation among halogens:
1. Acidify fusion filtrate with 3N H2SO4, boil, cool
2. Add carbon tetrachloride CCl4
3. Add few drops of NaClO (laundry bleach), shake
a. If the CCl4 layer remains colorless Cl
b. If the CCl4 layer is brown Br
c. If the CCl4 layer is violet I
Qualitative Analysis of Organic Functional Groups
A. Test for Hydrocarbons (Unsaturated)
Baeyer’s Test for Multiple Bonds KMnO4 Sol.
- Uses dilute alkaline KMnO4 to Oxidize the C-C double or triple bond
- >1 drop of reagent to give purple color unsaturation or easily
oxidized
functional group is present
- Positive Test: brown suspension of MnO2
- Cyclohexane ( - ) Cyclohexene/Linoleic Acid ( - ) Bromobenzene ( + )
Ignition Test for High Degrees of Unsaturation
- Unsaturated bonds form luminous flame and sooty deposits
15
C6 H6+ → 6 C O 2 +3 H 2 O(+C ( s) )
2O 2
- Positive Test: sooty yellow flame (aromatic, unsaturated)
- Negative Test: luminous flame/not sooty/less yellow (aliphatic, saturated)
- Benzophenone ( - ) Cyclohexane ( + )
B. Alcohols by Jones Oxidation
Jones Reagent
- Consists of chromium trioxide CrO3 and sulphuric acid dissolved in a
mixture of acetone and water. As an alternative, potassium dichromate
can be used in place of chromium trioxide
- Positive Test: Green color within 15 sec of addition with reagent
- Negative Test: Remain orange
- 1-butanol > 2-butanol >>> t-butylaic
C. Aldehydes and Ketones
- Formaldehyde has a sharp, somewhat unpleasant odor
- Aromatic Aldehydes have very pleasant “flavour”
- Benzaldehyde has the characteristic odor of almonds
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine/DNPH Test (General Test for Carbonyl
Compounds)
- General test for aldehydes and ketones
- Positive Test: yellow, orange, yellow-orange, reddish-orange precipitate
- Formaldehyde ( + ) Benzaldehyde ( + ) Acetone ( + )
Tollen’s Test (General Test for Aldehydes)
- General test for aldehydes
- Oxidation reaction in which aldehydes reacts with ammoniacal silver nitrate to
yield a ppt of silver metal, which appears as a mirror
- Positive Test: Silver metal like a mirror
- Formaldehyde ( + ) Benzaldehyde ( + ) Acetone ( - )
O H¿
A g2 O+ 4 N H 3+ H 2 O →2 Ag ( N H 3 )+¿+2
2
Fehling’s Test (General Test for Aliphatic Aldehydes)
- General test for aliphatic aldehydes
- Oxidation reaction
- Fehling’s A sol. → CuSO 4
- Fehling’s B sol. → NaOH + potasium tartate (Rochelle Sal t)
- Positive Test: Red C u2 O precipitates
- Formaldehyde ( + ) Benzaldehyde ( - ) Acetone ( - )
D. Carboxylic Acids
Sodium Bicarbonate Test for Carboxylic Acids
- Evolution of carbon dioxide
- Positive Test: Bubbles presence of CO2
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practical Chemistry-Theroy & Excercise Module-6-4Document58 pagesPractical Chemistry-Theroy & Excercise Module-6-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Principles Related To Practical ChemistryDocument61 pagesPrinciples Related To Practical ChemistrySai Sasivardhan GampaNo ratings yet
- Target 3 Level 2 Chapter 10Document16 pagesTarget 3 Level 2 Chapter 10Rohan ArekatlaNo ratings yet
- D-Block ElementDocument6 pagesD-Block Elementd anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Pratical Organic Chemistry (13th)Document4 pagesPratical Organic Chemistry (13th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Pratical Organic Chemistry (12th)Document4 pagesPratical Organic Chemistry (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
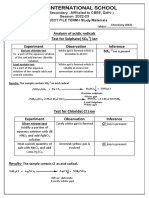
- Zoom International School: Analysis of Acidic Radicals Test For Sulphate (SO) Ion Experiment Observation Inference SODocument6 pagesZoom International School: Analysis of Acidic Radicals Test For Sulphate (SO) Ion Experiment Observation Inference SOSiddhant SinghNo ratings yet
- Practical Organic Chemistry: (A) Functional Group AnalysisDocument4 pagesPractical Organic Chemistry: (A) Functional Group AnalysisManjunath NaikNo ratings yet
- 142 Exp 11 Cal Poly Group IDocument4 pages142 Exp 11 Cal Poly Group IAnonymous cgKtuWzNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis PDFDocument61 pagesQualitative Analysis PDFAniruddha KawadeNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Instructions: Cu Ni CR Fe FeDocument4 pagesPreliminary Instructions: Cu Ni CR Fe FeEmmanuel Ryan100% (1)
- Salt AnalysisDocument9 pagesSalt AnalysisAnanyaNo ratings yet
- Practical Chemistry - OcDocument14 pagesPractical Chemistry - Ocdakshanatab255No ratings yet
- Catholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Document13 pagesCatholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Document7 pagesEdexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Ibrahim BtNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 6Document2 pagesLab Report 6bjddjkNo ratings yet
- AS Level Qualitative AnalysisDocument8 pagesAS Level Qualitative AnalysismahahajNo ratings yet
- E05 Identification of Inorganic CompoundsDocument22 pagesE05 Identification of Inorganic CompoundsNicolás Rodríguez RubianoNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesSalt Analysis Cheat Sheetgsg171869No ratings yet
- Ligands in Coordination Compound-1Document9 pagesLigands in Coordination Compound-1Sukanya PaulNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetDocument5 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetYug VanviNo ratings yet
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic CompoundsDocument20 pagesPurification and Characterisation of Organic CompoundspsshivaNo ratings yet
- 4th Form Qualitative Analysis Sheet Summary SheetDocument2 pages4th Form Qualitative Analysis Sheet Summary SheetFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Acidic, Basic RadicalDocument13 pagesAcidic, Basic RadicalWael Elwekel100% (2)
- Principles Related To Practical Chemistry Part - 2Document17 pagesPrinciples Related To Practical Chemistry Part - 2Insane insaanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document2 pagesExperiment 2sathiashekarNo ratings yet
- 18 - Qualitative Analysis (Cation) - 1Document4 pages18 - Qualitative Analysis (Cation) - 1Aditya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetDocument4 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetSumit Dhall74% (50)
- Chemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetDocument4 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetyashvpNo ratings yet
- C12 AnalysisDocument21 pagesC12 AnalysiskhôiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt Analysis Cheatsheet v1Document5 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis Cheatsheet v1lalit8888No ratings yet
- Post-Lab 4 Qualitative Analysis-SolutionsDocument7 pagesPost-Lab 4 Qualitative Analysis-SolutionsUzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Organic Functional Group Tests - Practicals Chemistry Class 12Document4 pagesOrganic Functional Group Tests - Practicals Chemistry Class 12Rudraksh mittalNo ratings yet
- Class-IX Subject-Chemistry Half-Yearly Syllabus Handout-4 Chapter-18 Chemical TestsDocument6 pagesClass-IX Subject-Chemistry Half-Yearly Syllabus Handout-4 Chapter-18 Chemical TestsZunaira AliNo ratings yet
- Identification of Acid Radicals (Anions) : Prepared by R.K. Malik'S Newton Classes, RanchiDocument7 pagesIdentification of Acid Radicals (Anions) : Prepared by R.K. Malik'S Newton Classes, RanchiAadarsh YadavNo ratings yet
- Exp6 chm361 PDFDocument11 pagesExp6 chm361 PDFShafiqahFazyaziqahNo ratings yet
- Practicle Org ChemistryDocument8 pagesPracticle Org ChemistryjjknarutotokyoNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument47 pagesUntitled DocumentJeffrey HoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis 3Document17 pagesQualitative Analysis 3Joseph UdoudoNo ratings yet
- BARIUM CHLORIDE Ex. 11Document6 pagesBARIUM CHLORIDE Ex. 11wizard hamdsNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972From EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973From EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973No ratings yet
- Fourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974From EverandFourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974V. GutmannNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryFrom EverandOrganometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryF. G. A. StoneNo ratings yet
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookFrom EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Selected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionFrom EverandSelected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionNo ratings yet
- Initial Data Base: Number of Family MembersDocument10 pagesInitial Data Base: Number of Family MembersKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion TLGDocument2 pagesFamacion TLGKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 2Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 2Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion TLGDocument2 pagesFamacion TLGKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Health Stat Activity 104-2-1Document3 pagesHealth Stat Activity 104-2-1Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading FamacionDocument1 pageJournal Reading FamacionKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- 4 Jurnal Ethics in Community NursingDocument10 pages4 Jurnal Ethics in Community NursingSalwa SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Famacion IMCI AssignmentDocument2 pagesFamacion IMCI AssignmentKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN Survey ToolDocument14 pagesFamacion - CHN Survey ToolKyra Bianca R. Famacion100% (1)
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 2Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 2Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion IMCI AssignmentDocument2 pagesFamacion IMCI AssignmentKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN Survey ToolDocument14 pagesFamacion - CHN Survey ToolKyra Bianca R. Famacion100% (1)
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Final WeekDocument3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Final WeekKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion IMCI AssignmentDocument2 pagesFamacion IMCI AssignmentKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Final WeekDocument3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Final WeekKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Protozoa StructuresDocument2 pagesProtozoa StructuresKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Task 1 The Construction of The Monastery of The Transfiguration in Malaybalay City, Bukidnon. Designed by Leandro LocsinDocument2 pagesTask 1 The Construction of The Monastery of The Transfiguration in Malaybalay City, Bukidnon. Designed by Leandro LocsinKyra Bianca R. Famacion0% (2)
- Famacion - Art Appropriationinal Final Output Part 1Document2 pagesFamacion - Art Appropriationinal Final Output Part 1Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- FinalsDocument1 pageFinalsKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Cestodes, Trematodes, Nematodes Life CyclesDocument10 pagesCestodes, Trematodes, Nematodes Life CyclesKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Plasmodian Life CycleDocument6 pagesPlasmodian Life CycleKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- English 7 Graded GtkyDocument1 pageEnglish 7 Graded GtkyKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Historical or Cultural MappingDocument1 pageHistorical or Cultural MappingKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - The White BirdDocument1 pageFamacion - The White BirdKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Talk Show With Invited ArtistDocument1 pageTask 3 Talk Show With Invited ArtistKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Task 1 and Task 3Document2 pagesTask 1 and Task 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- ENG7 - Group - Historical Cultural MappingDocument27 pagesENG7 - Group - Historical Cultural MappingKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - Task 2 Cultural Mapping For Movable HeritageDocument2 pagesFamacion - Task 2 Cultural Mapping For Movable HeritageKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Description of MaterialsDocument4 pagesDescription of MaterialsArjun Kj100% (1)
- Installation and Removal of High MastDocument3 pagesInstallation and Removal of High MastMohd Hafiz Muhamed100% (1)
- Antenna ConceptsDocument28 pagesAntenna Conceptssameerajamal100% (1)
- M and J Slab Gate ValveDocument12 pagesM and J Slab Gate Valvetxlucky80No ratings yet
- MasterTop 1200 EngDocument3 pagesMasterTop 1200 EngMohiuddin MuhinNo ratings yet
- MEC-A4-125B EnglishDocument2 pagesMEC-A4-125B Englishdragos manoleNo ratings yet
- Simple Span Beam MathcadDocument9 pagesSimple Span Beam Mathcadsebastian9033No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Quiz 1Document3 pagesChapter 6 Quiz 1mdawg467No ratings yet
- Part Number Part Description Condition Quantity UOM Tag InfoDocument375 pagesPart Number Part Description Condition Quantity UOM Tag Info李聪No ratings yet
- Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Foundation On Clays Meyerhof PDFDocument3 pagesUltimate Bearing Capacity of Foundation On Clays Meyerhof PDFNadherNo ratings yet
- 01) Machine Design I PDFDocument24 pages01) Machine Design I PDFDebasis soorNo ratings yet
- JBPM TutorialDocument56 pagesJBPM Tutorialc_prateeshNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document25 pagesLab 1Self McNo ratings yet
- Azeotropic DistillationDocument6 pagesAzeotropic DistillationDea YusufNo ratings yet
- Material Price ListDocument6 pagesMaterial Price ListPMED NORTH NCRBGNo ratings yet
- Colores: (Phila: in Praesentia)Document32 pagesColores: (Phila: in Praesentia)Gustavo NunesNo ratings yet
- Analisis de La Susmpension Con AdamsDocument18 pagesAnalisis de La Susmpension Con AdamscorsasportNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual-C140-18 PDFDocument271 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual-C140-18 PDFYusroni Nainggolan0% (1)
- HTTP Freecircuitdiagram - Com 2009-05-18 Wailing-Alarm-sirenDocument4 pagesHTTP Freecircuitdiagram - Com 2009-05-18 Wailing-Alarm-sirenmahmud ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Module 3-4Document75 pagesGroup 2 - Module 3-4Neil Matthew Jarabelo DandanNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine ManualDocument48 pagesGas Turbine ManualShivam Kumar100% (3)
- Automotive Ethernet Black BookDocument44 pagesAutomotive Ethernet Black BookGrulletto Grullone100% (1)
- ReadMe NetDocument2 pagesReadMe NetMariano MartinezNo ratings yet
- Sendai Mediatheque - Data, Photos & Plans - WikiArquitectura PDFDocument7 pagesSendai Mediatheque - Data, Photos & Plans - WikiArquitectura PDFhariNo ratings yet
- W210 Schematics 2of2Document30 pagesW210 Schematics 2of2mahmoud magdy100% (1)
- TV Sharp 19K-M100 DiagramaDocument36 pagesTV Sharp 19K-M100 DiagramaJomasando10100% (1)
- Owners Manual w11520291 RevbDocument48 pagesOwners Manual w11520291 RevbjuliodaviladupontNo ratings yet
- Despiece SUSP. DEL 930EDocument2 pagesDespiece SUSP. DEL 930EAndersson Campos VásquezNo ratings yet
- Alfa VapDocument2 pagesAlfa Vapkresimir.mikoc9765No ratings yet