Professional Documents
Culture Documents
08-INSTALLATION - (B) Check Valves
Uploaded by
Modassir Zaheen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pages08-INSTALLATION - (B) Check Valves
Uploaded by
Modassir ZaheenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE
AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Cast Iron, Malleable Iron and
Bronze Swing Check and Lift Check Valves
● Swing Check valves operate in horizontal pipelines, or in vertical pipelines provid-
ed the flow is in an upward direction. Lift check valves operate in horizontal
pipelines only.
● Swing and Lift Check valves are not suitable for end of line service and have not
been designed as fire safe valves.
● Service temperature and pressure indicated on the identification plate or body
marking should not be exceeded.
● Valves must be installed into a well-designed system and it is recommended that
the system be inspected in accordance with the appropriate member state legisla-
tion. In the UK – The Pressure Equipment Directive 97/23/EC and The Pressure
Systems Safety Regulations 2000.
INSTALLATION
Preparation Crane Fluid Systems - Technical Sales
• Ensure valve is suitable for service con- Department.
ditions e.g. pressure, temperature, service • The valves have been designed for load-
media. ings, appropriate to its intended use and
• Remove dust caps/flange protectors, other reasonably foreseeable operating
where fitted. conditions. Loadings caused by traffic,
• The Installation shall be designed to pro- wind and earthquake have not been taken
vide adequate means of draining and vent- into account.
ing to avoid harmful effects such as water • It is the responsibility of the installer to
hammer, vacuum collapse, corrosion and ensure that the valves do not exceed the
uncontrolled chemical reactions and to per- allowable limits of pressure. However the
mit cleaning, inspection and maintenance equipment is designed to withstand a
in the correct manner. momentary pressure surge of up to 10%
• The product has not been designed to above the maximum working pressure.
include corrosion, erosion or abrasion • The piping system shall be so designed
allowances. Any queries regarding service to reduce the risk of fatigue due to vibration
applications should be addressed to the of pipes.
Ces instructions sont aussi disponibles en français.
Diese Anweisungen sind auch verfügbar deutsch.
Queste istruzioni sono anche disponibili nell'italiano.
Valve Location should not be used for temperatures
Valves should be located to ensure ease above 200° C.
and safety of operation and access allowed – Always use the correct size and num-
for subsequent maintenance. ber of bolts.
– Find out the correct assembly torque
Piping Supports for the specific gasket and conditions
The products have not been designed to applicable, and use a torque wrench to
withstand excessive forces and moments. achieve this. Use the correct tightening
The system shall be so designed to pre- sequence.
vent excessive forces and moments. The – Do not match a flat-faced flange to a
piping supports must be carefully aligned raised face flange.
and at the correct distance between cen-
tres for the size and type of pipe. The fol- Threaded Joints
lowing publications provide details of cor- • The valves are supplied with taper
rect spans and installation details: threads and, with the use of a thread
BS3974, Specification for Pipe Supports sealant will give a pressure tight seal.
(Available from BSI) • To avoid distortion of the valve, when fit-
DOI Directorate of M & E Engineering ting and tightening the pipe, the valve must
Services, M & E No. 3 (Available from be gripped using the flats provided at the
HMSO) same end as the pipe is being fitted.
• Care should be taken to avoid ‘pipe end-
Flange Joints ing’. This is a condition that occurs when
Bronze and cast iron flanges may be dam- the pipe is screwed in too far resulting in
aged by over tightening the bolts. The fol- distortion of the valve seat.
lowing procedures will reduce this risk: • The male thread on the pipe must have
– Make sure the pipe flanges are correct- fully formed, undamaged threads.
ly aligned.
– Full-face gaskets reduce the stresses in
flat face flanges and should be used
with bronze flanges.
– Low strength carbon steel bolting has
traditionally been used to restrict the
load imposed on grey iron flanges, but
– Bolted cap valves – re-tighten nuts in
OPERATION vicinity of leak. If leakage still occurs,
isolate pipeline, dismantle body/cap
All check valves permit flow in one direction
joint and renew cap gasket. Be careful
only and close automatically if flow revers-
not to over tighten bolting. If information
es. They are entirely automatic in action,
is required relating to torque values
depending upon pressure and velocity of
then contact the Crane Fluid Systems
flow within the line. The discs and associ-
Technical Department.
ated moving parts may be in a constant
• On swing check valves the hinge pin plug
state of movement if the velocity pressure
should be inspected for wear. It should be
is not sufficient to hold the disc in a wide
noted that these valves are designed so
open and stable position. Premature wear
that the hinge pin is a loose fit in the body
and noisy operation or vibration can be
and the disc a loose fit in the hinge.
avoided by selecting the size of check
valve on the basis of flow conditions.
ROUTINE
MAINTENANCE
• All check valves and non-return are
designed to permit inspection without
removing the valve body from the pipeline.
The portion of the pipeline in which the
valve is installed must be isolated before
any dismantling and inspection is carried
out.
• Check for leaks at the body/cap joint. To
remedy:
– Screwed in caps. – re-tighten joint. If
leakage still occurs, isolate pipeline,
dismantle body/cap joint, clean seating
faces and remake joint. (Note: for gas-
keted joints use replacement gaskets).
(water hammer), they should be added to
GENERAL the working pressure to obtain the total
CONSIDERATIONS pressure acting on the valve. The total
must not exceed the pressure rating of the
• Maximum operating pressure reduces as
valve. A pressure surge, or shock, is usual-
service temperature increases. Pressure
ly caused by the rapid closure of a check
and temperature limitations are shown by
valve or quarter turn valve resulting in a
the valve body marking or on the identifica-
sudden reduction in flow rate.
tion plate.
• The surfaces of valves in service may be
• Valves are not designed to operate under
subject to extreme temperatures; care
high shock loadings. Where pressure
should be taken when handling.
increases occur due to shock loading
PED Category By Valve Size (DN) Product Applications
Fig No. Material SEP 1 2 3 Group Group Group Group
(Not CE 1 Gas 2 Gas 1 Liquid 2 Liquid
Marked)
C1253 Bronze 8-50 65-80 ✓ ✓ ✓
D104 Bronze 15-50 ✓ ✓ ✓
D116 Bronze 10-32 40-50 65-80 ✓ ✓ ✓
D138/D140 Bronze 10-40 50-80 ✓ ✓ ✓
D142 Bronze 15-32 40-50 65-80 ✓ ✓ ✓
F201 Malleable Iron 15-25 32-50 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
F491 Cast iron 50-65 80-125 150-200 ✓ ✓ ✓
F492 Cast iron 50-80 100-250 ✓ ✓ ✓
F493 Cast iron 50-65 80-125 150-300 ✓ ✓ ✓
FM469 Cast iron 50 65-125 150-300 ✓ ✓ ✓
FM490 Cast iron 50-150 200 ✓ ✓ ✓
FM492 Cast iron 50 65-125 150-300 ✓ ✓ ✓
The above products are not suitable for use with unstable fluids
Part No. 0A 03675X
Nacton Road • Ipswich • Suffolk • IP3 9QH • United Kingdom
Technical Helpline Tel: +44 (0)1473 277400 Fax: +44 (0)1473 277411
Email: enquiries@cranefs.com Website: http://www.cranefs.com
A Crane Co company.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Installation, Maintenance and Operating Instructions Cast Iron, Malleable Iron, Brass and Bronze Gate ValvesDocument4 pagesInstallation, Maintenance and Operating Instructions Cast Iron, Malleable Iron, Brass and Bronze Gate ValvesModassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Bladder TanksDocument8 pagesBladder TanksModassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- D138 - Swing Check ValveDocument1 pageD138 - Swing Check ValveModassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Drain Cocks Drain Cocks: Bronze Draining Tap PN16Document1 pageDrain Cocks Drain Cocks: Bronze Draining Tap PN16Modassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- DN250 - DN600 PN16 DN250 - DN300 Class 125: Features & BenefitsDocument1 pageDN250 - DN600 PN16 DN250 - DN300 Class 125: Features & BenefitsModassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 06-TECHNICAL DATA - (C) D298 - StrainersDocument1 page06-TECHNICAL DATA - (C) D298 - StrainersModassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- 08-INSTALLATION - (A) Ball ValvesDocument4 pages08-INSTALLATION - (A) Ball ValvesModassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 06-TECHNICAL DATA - (A) D171 Ball ValveDocument1 page06-TECHNICAL DATA - (A) D171 Ball ValveModassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- 08-INSTALLATION - (C) StrainersDocument4 pages08-INSTALLATION - (C) StrainersModassir ZaheenNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- PSV Sizing (Liquid)Document2 pagesPSV Sizing (Liquid)Saeid Rahimi Mofrad50% (2)
- Victaulic Fire Protection Price List PDFDocument99 pagesVictaulic Fire Protection Price List PDFpogisimpatikoNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Drainage Pumps: Catalogue Drainage and SewageDocument90 pagesDrainage Pumps: Catalogue Drainage and SewageStefanNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Check Valves PDFDocument12 pagesCheck Valves PDFdedyNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Valve Interview Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesValve Interview Questions and AnswersQasim Iqbal100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- PLL 2144Document80 pagesPLL 2144Amit TandelNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Pressure Drop Calculation Summary SheetDocument13 pagesPressure Drop Calculation Summary SheetAmol KanadeNo ratings yet
- Fuel SystemsDocument40 pagesFuel SystemsJohn RichardNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- E 021 04 PDFDocument4 pagesE 021 04 PDFGeorge CobraNo ratings yet
- Avionics Ventilation System: Equipment Air Inlet Air OutletDocument4 pagesAvionics Ventilation System: Equipment Air Inlet Air Outletjontis jasoliyaNo ratings yet
- Flowserve ValvesDocument144 pagesFlowserve ValvesRockny2011No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- P Regusol enDocument12 pagesP Regusol enmiaasieuNo ratings yet
- Hunter Pro Spray Sprinkler Owners ManualDocument20 pagesHunter Pro Spray Sprinkler Owners ManualhabeebrahNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Review1 - Ampo Poyam Valves PrivateDocument15 pagesReview1 - Ampo Poyam Valves PrivateStani KunjumonNo ratings yet
- BU 1 Report PDFDocument117 pagesBU 1 Report PDFSharmaine FalcisNo ratings yet
- Manual Novec 1230Document98 pagesManual Novec 1230Moises Matos Martins de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Heating System B.O.QDocument4 pagesHeating System B.O.QHemn Rafiq TofiqNo ratings yet
- Data Sheets 67c Series Instrument Supply Regulators Bulletin Fisher en en 6026372Document12 pagesData Sheets 67c Series Instrument Supply Regulators Bulletin Fisher en en 6026372chevytriramadhanNo ratings yet
- Manual EPD Optima IOM SPDocument36 pagesManual EPD Optima IOM SPelsonjsNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection IndexDocument1 pageFire Protection IndexBams ArifinNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Equipment Definition: Component LiteratureDocument5 pagesEquipment Definition: Component LiteratureAbbas AkbarNo ratings yet
- Racor Filters Manual PDFDocument16 pagesRacor Filters Manual PDFcarloseduromNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Gpa 2174 - 93Document15 pagesGpa 2174 - 93jairo7662No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine ValvesDocument16 pagesSteam Turbine ValvesBradley Nelson100% (5)
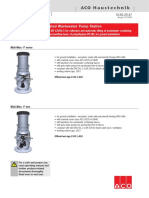
- ACO Haustechnik: Muli-Max - F Prefabricated Wastewater Pump StationDocument60 pagesACO Haustechnik: Muli-Max - F Prefabricated Wastewater Pump StationPetre DragomirNo ratings yet
- 电厂专业英语术语Document81 pages电厂专业英语术语meirangongNo ratings yet
- Lift Station Design Checklist: DNR - Wi.govDocument7 pagesLift Station Design Checklist: DNR - Wi.govabo omerNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Basic MeDocument117 pagesGroup 2 - Basic MeFrances Dale CapulongNo ratings yet
- Pumping Station ProgrammeDocument11 pagesPumping Station Programmeshinto_thekkekkaraNo ratings yet
- Sales Guide, Companion Valco Melton ERO Folding Carton Industry SolutionsDocument15 pagesSales Guide, Companion Valco Melton ERO Folding Carton Industry SolutionsZamroni KarimNo ratings yet