Professional Documents
Culture Documents
m7 (Part 1) PDF by MR - Raza
Uploaded by
Chitrali SontakkeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
m7 (Part 1) PDF by MR - Raza
Uploaded by
Chitrali SontakkeCopyright:
Available Formats
1
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
Note: - Abbreviations are used in this pdf, some of them are mentioned. Regarding any
query/suggestion, feel free to ask.
; a/c = aircraft, +ve = positive, -ve = negative, obj. = object, cat. = category, wrt = with
respect to, m. = maintenance, b/w = between, Wx – Weather, WxR = Weather Radar,
Qty = quantity, Mfd = Manufacturer, O/p = operation, st. = straight, bcz – because, hv –
have, r – are, Chk – check, ckt – circuit. Etc.
1. Hidden lines – Dash Lines – Short dashes evenly spaced. Phantom – 1 long, 2 short evenly
spaced dashes. For alternate position of parts or missing parts. Leader lines – Solid line with
one arrowhead
2. Datum – Imaginary vertical plane from which all horizontal measurements are taken. Appear
as vertical line perpendicular to a/c’s horizontal axis. No fixed rule for location. Identified in
a/c specification or TCDS (for TCDS, separate equipment list.) Arm – horizontal dist. of
part/eqp. from datum. Aft datum +ve arm & Forward to datum -ve arm.
3. Orthographic projection – 6 views (front, top, bottom, rear, right, left). One view – cylindrical,
spherical or square. Two view – space is limited and two-three view most common.
Symmetrical obj. – half views.
4. Max. takeoff wt. – useful load + empty load
5. TCAS – Only transponder equipped a/c will be detected by TCAS.
6. Assembly drawing – Description of object made of two or more parts, states object’s way, size,
and shape, relationship b/w various parts. Complex than detail drawing accompanied by it.
7. Towing – A qualified person must be in the cockpit/flight station.
8. Taxing – Carried out by rated pilot/ qualified airframe & powerplant technician.
9. Tiedown of heavy a/c – (a) Head a/p into prevailing wind. (b) Lock, cover, guard it (c) Attach
tiedown reels. Tiedown stakes for temporary tiedown only or ¼” cable or ½” manila line.
10. Vernier scale – On sleeve of micrometer.
11. Cape chisel – A narrow chisel, to chip grooves and key holes. Diamond pt. chisel – To cut V
shaped grooves in sharp corners. Roundnose - rough out small concave surface,filleted corner.
12. Flexible hacksaw blade – Only teeth hardened. Speed – 40 to 50 per min. TPI – 14 TO 32.
13. Lightening strike discharged through – static wicks/ null field discharger.
14. To carry some amount of current, Al wire should be 2 wire gauge number larger than Cu wire
eg. AN – 4 Al & An – 6 Cu.
15. Soldering – Soldering for good strength & good fluidity strength also to clear and remove
oxide. Not preferred on Steel. Flux prevents oxidatn. Soldering done at 600-850* F, (293-592C).
16. Low T brazing; silver soldering – Hard soldering – Ag & Au – 600* - 850 * C.
17. Low T brazing also known as silver soldering is a brazing process. Filler metal as Ag & Cu with
M.P. 505-850*C. Bi & Cd decreases M.P. in soldering.
18. Brazing inspection – Solder evenly distributed throughout the gap. No attempt to fill gap b/w
metals by solder or brazing rod.
19. Soft solder – Solder of alloy of Sn & Pb
20. Radiographic – X-ray & Gamma radiations. Metal fabrications and non-metallic products.
Radiograph or shadow pic is observed. Fast and reliable process. To find defects or flaws in
airframe structures or engines with little or no assembly. Extensive training req., only
qualified radiographers allowed, experienced personnel.
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
2
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
a. Xray method sequence – (a) exposure to radiation - Units in KV.,
(b) processing of film – Developer chemical soln. An acid bath, fixing bath then clear
water wash, (c) interpretation of radiograph – Most imp. phase, interpretation
conducted close to radiographic op., 3 cat. of flaws – Voids, inclusions, dimensional
irregularities. Voids & inclusions may be 2D or 3D. Geometry/Shape, Size and location
of flaw are imp. to analyze, Inclusion – Flaw which contains entrapped material of
greater or lesser density, a source of corrosion.
21. Identifying fire extinguishers – marking by decalcomanias, painting etc. at a dist. of 3 feet; at
wall panels, large enough to be identifiable at 25 feet.
22. False/hung start – when engine starts normally but rpm remains at some low value rather
than increasing to normal starting rpm. Starter receiving insufficient power dropping out soon.
23. Check nut wrench – A thin, single/double ended wrench used for turning check/jam nut. 15®
offset angle. Not intended for hard use. Used on narrow spaces.
24. Lever jaw wrench – gripping tool with adjustable jaws, could be locked, used as wrench,
clamp, plier, vise.
25. Combination wrench – 2 openings of same size. One box & other open. where space limited.
26. Pipe wrench – Designed with adjustable jaws, serrated to grip round pipe & cylindrical parts.
27. Strap wrench – For turning cylindrical parts or pipes, removing bezels & holding/revolving job.
28. Adjustable wrench – One jaw is fixed but other moved by thumbscrew or spiral screwworm.
29. Sp. Inspection instruction – AMM, & Modification – EO, Mfd issues - SB
30. Tip of screw driver turn blue due to excessive heat. Burrs or abrasion on file cause blisters.
31. Unsalvageable comp. – certified life limit reached, non-reparable defect,not meet design spec.
32. Parcolubrizing – Iron and steel parts chemical treatment, oil absorptive phosphate coating.
33. Brinelling – Shallow/spherical depression in surface by parts in contact under high load.
34. Sq. mill – to measure rectangular conductors eg. Bus bars, &
Circular mill – to measure circular conductors eg. Wires
35. Lightening damage – (a) Strike damage – Burning, circular hole, discoloration at L.E., tail unit,
fuselage nose, tip. (b) Static discharge damage – Local pitting, burning at TE, tip, antenna.
36. Dry powder extinguisher – Effective on class B & C fires. Best for Class D.
37. Methyl Bromide (CH3Br – Halon 1001, 2), Chloro Bromo Methane (CH2ClBr – Halon 1011, 3),
DibromoDifloroMethane(CBr2F2 – Halon 1202, 4), CarbonTetraChloride (CCl4 – 104, 3) & dry
powder aren’t recommend for a/c use. BromoChloroDifluoromethane (CBrClF2 – Halon 1211),
CO2-5a & Bromotrifluoromethane (CF3Br – Halon 1301, 6) used in a/c.
38. Bill of material – part no, name, material, qty & source. Hammer size – wt. of head w/o handle.
39. Soft hammer made from – Hockery, Rawhide, Rubber & Leather.
40. Telescopic gauge – ½”-6” and small gauge – up to 1/2”.
41. 5-8% of slackness is req in flexible hose installation. Flexible hose is determined by inner dia.
Before installation, tested for 1.5 times system P.
42. Zero fuel wt. – Heaviest wt. of a/c w/o any usable fuel in it.
43. Pictorial Drawing 3 types – Perspective (like photograph), Isometric (3D view, parallel &
dimensioned), Oblique (like isometric but 2 of the 3 axes are perpendicular), Exploded View
(individual parts and relative positions)
44. Diagrams are graphic representation, 4 types –
a. Installation (diagram of installation of flight guidance control comp., in a/c maint. &
rep. manual)
b. Schematic (Do not indicate location but the relative location wrt to another comp.
Both Installation and Schematic used extensively on a/c manuals. In troubleshooting.
c. Block (Simplified relationship b/w components drawn as a rectangle block).
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
3
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
d. Wiring Diagram (Electrical wiring & circuitry analysis, it is always quite complicated)
45. Most A/c M.M. contain troubleshooting section arranged by ATA spec codes in 500 pages.
46. Projections – Majority – 3rd angle orthographic projection (Side of the object nearest to it in
adjacent view), Older drawings – 1st angle (Side of the object remote from it in adjacent view).
47. Isometric projection – Pictorial view of obj., axes inclined at 30* to plane of projection.
48. Flowcharts – Sequence or flow of events
a. Troubleshooting flowchart – For detection of faulty comp., series of Y/N questions.
b. Logic flowcharts – Use symbols to indicate specific types of logic gates. To determine
digital o/ps.
49. Never approach a single rotor h/c from rear. And if storm, a/c tied down.
50. In TIG – Non-consumable filler rod used while in MIG – Consumable electrode (machine fed).
TIG also called GTAW: Gas Tungsten Arc Welding.
51. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)–Low V & High current
52. Min. bend allowance – 6 times O.D. for R.F. Cables (coaxial/triaxial) & 10 times for wire group.
53. Hacksaw cutting in one direction only i.e. fwd. Spring overheat – loose temper and efficiency.
54. Annealed sheet spring – heat treated after forming. Parts containing small radii or compound
curvatures must be formed in annealed condition later heat treated to tempered condition.
55. Rigid tubing – never apply compound to the faces to tubing or flare, metal to metal contact
is destroyed b/w fitting and flare necessary to produce seal.
56. A crooked flare is the result of tubing not cut squarely.
57. Sp. gravity measured by hydrometer. Surface-subsurface corrosion identified by eddy current.
58. De-icing boots impregnated with conductive cement. Rep. requires a great deal of labor.
59. Cotter pin – AN 380 Cd plated LCS used for safe tying. AN 381 – Corrosion res. Steel cotter pin.
60. ADF – In MF OR LF bandwidth. Never use insulation on crimping.
61. Type B rivets (5056 -F A alloy) used for Mg parts. Al should never be welded to Mg.
62. Annealing – Heating above CT and slow cooling. Normalizing – Only steel, above CT, Air cooled.
Normalizing increases the strength of steel 20% above that of annealed material.
63. WxR color – R, G, Y & Affected by lightening, hail, turbulence and rain.
64. Turnbuckles – for minor adjustment of cable length & cable tension, right & left handed
thread, internally threaded barrel, equally turned 1/6thX2. Not more than 3 threads exposed.
65. Aliphatic Naptha – Used for acrylic & rubber clearing. Also for wipe down of cleaned surface
before painting. Flashes at 80*F. Aromatic Naptha – Toxic & attacks acrylics and rubber parts.
66. Small tubing conduit, less than 18 gage – 32TPI, for 18gage – 24 TPI.
67. Ultrasonic Inspection – locate defects in all types of materials. Minute cracks checks, voids
too small for X-Ray to detect. It req. access to only one surface of material. Two methods –
Immersion & Contact testing (pulse echo, resonance, through transmission).
68. Pulse echo – flaws detected by measuring amplitude of signals reflected and the time req. for
these signals to travel b/w surfaces & discontinuity. St. beam, angle beam (acute). Pulser,
transducer, amp. used. St beam – thickness of the piece & angle beam – width.
69. In composite, ultrasonic inspection – Low freq, High freq, Pulse echo method.
70. In composite, pulse echo method used to find – delamination, cracks, porosity, water &
disbonds of bonded comp. But not disbond or defect b/w laminated skin & honeycomb core.
71. 14TPI Hacksaw – machine steel, cold rolled & thick sections. Fast cutting, 18TPI – Solid stock
(Al, Babbit, C.I, HSS, Tool steel) Smooth surface, 24 TPI – Pipe, Sn, Brass, Small structural steel,
sheet metal over 18gage, 32TPI – Cutting small tubing, conduit, sheet metal less than 18gage.
72. Drift punch/pin punch – For loosening st. pin, taper pin, rivets or small parts being disassemble
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
4
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
73. WxR – 3 types – (i) Actual on board for detecting & displaying weather activity, (ii) Lightening
detectors, (iii)Satellite & other source WxR info uploaded to the a/c from outside source. Freq.
range 5.44 GHz – 9.375 GHz. Heavy return (red), Medium return (yellow), Light return (green).
74. CbrClF2 (halon 1211) – liquified gas, UL toxicity 5, colorless, non-corrosive, evaporates rapidly,
no residue, does not freeze or cause cold burns, not harm fabrics, heavy blanketing mist upon
fire, interferes chemically with combustion, prevent reflash after fire is extinguished.
75. Surface gauge – For checking/ drawing II lines & to find center of round material.
76. Thermal deicing uses hot air.
77. Defueling is done similar to refueling, function switch is – defuel.
78. Penetrant inspection is NDT for defects open to surface, parts non-porous. Al, Mg, Brass, Cu,
CI, SS, Ti. Indicate lack of bond, surface cracks & porosity.
79. Size of flat cold chisel is determined by width of cutting edge.
80. Rake angle – angle of flute in relation to the work.
81. Keep the area around electrical work or elect. Eqp clean and uncluttered to prevent elect. fire.
82. Hydraulic GPU – Also called hydraulics mule provide hydraulic P to operate the a/c during m.
to drain, fitter, refill & check. Elect. powered, variable V of fluid at variable P.
83. Water in aviation fuels of two forms: Dissolved(vapor) & free water. It T decreases – dissolved
water becomes free water and problems of ice crystal & filter clog.
84. Favorable condition for microorganism growth in fuel is warm T, presence of FeO & mineral
salt in water.
85. When surge of high V electricity passes through good electrical conductors such as Al & steel,
damage is likely to be minimal. Critical range of steel is 1300 -1600* F.
86. Bearing – Electrical/Lightening damage – Dark brown/ grayish black fluting (comugation) or
crators in raceways & rollers. Balls discolored. Zigzag burns in ball bearing raceways. Dark
Bottom – Corrugation, Rusty bottom – vibration. Lack of damage to raceways means vibration.
87. Lightning strike a/c – Only inspection of magnetism- demagnetized area, fuselage skin burning
& pitting. Not of tyres for creep & not of skin str for wrinkles, pulled rivets or cracks.
88. Wt. & balance data – F.M. & P.O.H., Quality system – safety quality assurance.
89. Oxy-acetylene welding is not used for Mg or high Ni alloy, not recommended for SS, inert gas
or plasma arc welding.
90. In welding, flux reduces effects of oxidation, floats oxide & impurities & do no harm &
produces strong weld. Not used for welding of C-steel bcz slag is formed.
91. Intergranular corrosion – An attack along the grain boundaries of improperly/inadequate
heat-treated alloys. Can be detected by ultrasonic & eddy current. Severe cleaning req.
92. Aviation fuel of two types – (I) AVGAS: Aviation Gasoline, (II) Jet A fuel, AVGAS in reciprocating
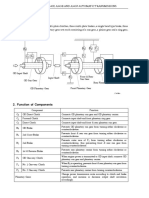
engine. 3 grades – 80/87 RED, 100/130 GREEN, 100LL BLUE, 115/145 (limited use). Color band
on piping & fuel eqp. Turbine fuel for turbojet & turboshaft of 3 types, Jet A & Jet A1 both
kerosene, Jet B blend of AVGAS & Kerosene. Jet fuel – black color, Actual color – clear/straw
color/ undyed color.
93. ADI – Info of an a/c pitch & roll attitude wrt glide slope (GS) & localizer (LOC).
94. ILS – Localizer, Marker, Glideslope, approach runway lighting.
95. Stresses applied in a/c – Bending, torsion, compression, tension, shear (cutting action force).
96. During starting all avionics eqp. turned off due to surge current and spike V.
97. Bonding term is used in light a/c only while grounding in heavy a/c.
98. St. fluted drills – Brass, soft metal and thin sheet, Flat drills – Brass, Oil hole drills – Deep hole
drilling, Twist drill – General purpose. Cutting edge of drill experiences shear stress.
99. Stop drilling is done for cracks by welding, cracks around flanged lightening holes using no. 40
drill bits. It is a temporary m.
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
5
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
100. The best angle to grind a drill for work on steel or cast iron is 59° (included angle equals
118°). A cutting angle up to 70° is best for extremely hard metals, whereas the angle may be
as small as 40° for a soft material like fiber. Cutting lip or lip clearance angle of 8° to 12°.
101. Dead center – Sharp edge at the extreme tip of the drill.
102. Cable guided by Fairleads, Pulleys and pressure seal. Cable fittings include Terminals,
Bushings, Thimbles & Shackles.
103. Fits – (i) Loose fit – large allowance, (ii) Free fit – liberal allowance, (iii) Medium fit – medium
allowance, (iv) Snug fit – zero allowance, (v) Wringing fit – zero to -ve allowance, (vi) Tight fit
– slight -ve allowance, (vii) Medium force fit – -ve allowance, (i) Heavy force fit – considerable
-ve allowance.
104. Human performance – Human capabilities and limitations which seek safe interference b/w
human & machine., Human factor – Principle which applies to aeronautical specification,
training, certification, ensure safety and efficiency.
105. During fueling – Remove the fuel tank cap after grounding the filler neck.
106. Production planning org. shall hv complexity of work and safety of a/c.
107. Tie down anchors sometime called “pad eyes” are ring like fittings installed when parking area
is poured. Seapalnes in stormy Wx – Tie down & secure to anchor.
108. Load cell attaches to the top of a jack; load cell hv concave shape & jack convex. Jackpads, jack
and ____ is used.
109. Commonly used torque wrenches – (i) Deflecting beam, (ii) Dial indicating, (iii) micrometer
& (iv) electronic setting
110. Wing rigging – (i) Symmetry, (ii) Incidence, (iii) Dihedral
111. Plastic material cleaned by detergent & soap.
112. Boroscope inspection is visual inspection in hot section of jet engine.
113. Piston engine – Checked 5-30 min after engine shutdown. Jet engine – Just after shutdown.
114. Rake angle – angle of flute in relation to work. Helix angle – Angle by helix of thread at pitch
dia with plane perpendicular to axis.
115. 2117-T4 Al alloy, 5056 Al alloy, Monel are most used materials to fabricate pull-thru rivets.
116. Pull thru rivets hv 2 head styles – (i) 100* countersunk, (ii) Protruding head like MS20470.
117. Gage block used to calibrate micrometer, caliphers & dial indicators. It can measure accurately
in millionth of inch. Sized according to thickness. Consist of 81 blocks.
118. 3 main types of pins in a/c – taper (AN385), flathead, cotter. Threaded (AN386). Flathead pin
– Clevis pin, MS20392 is installed with head up so that if cotter pin fails, this will remain.
119. AN 385 & 386; taper pins carry shear load where absence of play is essential.
120. If oil P is not shown in 30 sec in reciprocating engine then stop the engine & determine trouble.
121. Bearing corrosion is caused by moisture & chemical attack. Stored by rust preventive oil.
122. Spring material – Cr-V (SAEE6150).
123. Halogenated hydrocarbon are most effective for class B & C fires can be used on A & D type.
124. Portable hydraulic unit provide a/c hydraulic system for internal/external leakage.
125. O2 cylinder – black & right handed valve thread. Acetylene – Maroon & left handed thread.
126. Push pull rod eliminates varying tension & permits either tension or compression stress.
127. Al heat treatment at T above 900*F & quenching. Generally heat treatment – 825*-980*F.
128. A/c wt gain due to dirt & grease. Depend on the function of flight hrs, atm. conditions & type
of landing field.
129. Turboprop engine is accelerating – do not take bleed air from it. Do not energize starter while
engine is rotating. Starting procedure – (i) Compressor rotating (ii) Start switch (iii) Boost up
pump (iv) Ignition switch (v) Power lever at starting position (vi) Depress start switch (vii)
Maintain power lever at start (viii) Disconnect GPU
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
6
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
130. 2P281C-20; 2- wire associated with no. 2 engine. P – electrical power system, 281 – Basic wire
no., C – Section of wire in ckt, 20 – Gage of the wire.
131. 10KB106; 10 – Grip length, KB – Closed end key, 106 – Screw & thread size.
132. Marking placed at each end of the wire at the interval of 12-15”. Wire less than 3” need no
marking, 3-7” wire marked at midway. High T wires, shielding wires, multicolor cable &
thermocouple wire – sleeves to carry identification. Wire harness – number marked sleeves or
p sensitive tape.
133. After m. technician ckt tools returned to tool crib for storage.
134. Delamination, blister in composites checked by NDI method.
135. A gear rack is used to change rotary motion to reciprocating.
136. Ball bearing & tapered roller bearing - both radial and axial loads. Other roller – mainly radial.
Other ball – mainly axial/thrust load. Ball bearings hv grooved inner & outer raceways. Angular
Contact Bearing – Radial & Axial load in one direction. A spherical roller bearing hv one/two
rows of rollers which run in a spherical raceway in the outer ring, thus enabling the bearing to
accept a minor degree of misalignment between opposite bearings. It is capable of
withstanding heavy radial loads, and moderate axial loads from either direction. Needle roller
bearing – L >> D, pure radial load, oscillatory movement, limited space, subject to brinneling.
137. A/c alignment balancing – wing dihedral, incidence, all joint parts & fuselage.
138. Balancing patches applied to balance propeller in spinner fit.
139. Alloy 2017 hardened for driving 1hr after quenching. Alloy 2024 hardened 10-20 min after
quenching/ removal from refrigeration. If kept below 32*F after quenching, it remains soft for
days. 1100 – For riveting Al alloy sheets, 5056 – For riveting Mg sheet, 2117 – Riveting Al alloy
sheets, receive 1 heat treatment of anodizing after heat treatment to prevent intergranular
oxidation. 2024 are Al alloy rivets. 2117-T (Field rivets).
140. Pinched/frayed cable checked by TDR – Time Domain Reflector.
141. Severe turbulence indication of severity obtained from accelerometer or fatigue meter.
Reading exceeding -.5g & +2.5g on transport cat a/c – damage may be found at wings, fuselage,
tailplane, control surfaces, skin wrinkles, pulled rivets or similar.
142. Load Factor – Transport cat a/c; 2.5g to 3.8g/ -1g to -1.5g, Aerobatic – 4.5g to 6g & -1.7g to -3
143. Erosion – loss of metal from surface by mechanical action of F.O e.g. sand and dust.
144. BITE can be built into an individual LRU or a part of a computerized C.M.S. (i) Signals are sent
by BITE, (ii) To isolate the faults (iii) To verify correct op. parameters. It’s displays are selected
C.M.S’s CDU: can be printed or downloaded. ACARS sends BITE m. data to ground m. staff while
a/c is en-route. M. function of BITE is accessible only when a/c s on the ground. ACARS – A/C
Communication Addressing & Reporting System.
145. Basic size – Theoretical absolute dimension, w/o any limits. Limits – Max & Min allowable
dimension, above & below basic size. Tolerance – Permissible variation above & below basic
size. Clearance - Diff. in size b/w mating parts. Outside dimension < Internal Dimension. Gap
b/w holes & shaft. Allowance – Intentional diff., min clearance.
146. Lightening holes are cut in rib sections, fuselage frames & other str parts to decrease wt. size
determined by design specification. Using hole saw, punch, fly cutter.
147. Inspection of wornout pulleys, fairlead is very difficult, critical fatigue area is checked by
passing a rag piece to snag or broken wire, kinking of wire cable can be avoided if properly
handled or installed. When inspect control cables – inspect pulleys, fairlead & guards.
148. In welding if base metal overheated – porous & brittle weld.
149. Corrosion on static spring – reduces load capacity. Cyclic loading spring – fatigue & corrosion
leads to loss of fatigue strength. Overheating – blistering & change of color (in extreme cases
due to loss of temper) & not it is not suitable now. Checks done on spring – Length
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
7
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
measurements & load/deflection chk (rig is used for compressive, tensile or torsional loads).
Spring inspection is not done as daily inspection but on opportunity basis. It is replaced if fails.
150. Eddy currents – Intersection of magnetic field & circulatory currents results in power change.
Most widely used. Free electrons. Done on jet engine turbine shaft & vanes, wing skins, wheels,
bolt holes, spark plug bores for cracks, heat or frame damage. Diff. in hardness state in reading.
To inspect casting, stampings, machine parts, forgings & extrusions. Magnitude & phase of
counterfield is dependent upon R & µ of specimen. Similar to wheatstone bridge ckt is formed.
Can be performed w/o removing surface coating e.g. primer, paint & anodizing film. Surface &
sub surface corrosion, pits can be detected.
151. Empty wt. C.G. range is an allowable variation of travel within C.G. limit. Empty wt. – All
operating eqp that has fixed location & actually installed in a/c.
152. Roller chain consist of - outer & inner plate, bearing pins, bushes. 3 principle dimensions –
pitch, roller dia, width b/w inner plates. After installations, chain tested for freedom of twist.
153. Combination of gust + airspeed – structural damage.
154. Moisture entrapped in filler rod & damp flux causes porosity in weld. Flux containers made of
Al/glass are suitable but steel or brass not used as these cause contaminations of the flux.
155. Thermography – Uses thermal methods, differential in thermal conductivity, defect free areas
conduct heat more rapidly & efficiently. Most effective for thin laminates or for surface defects.
156. CCL4 releases harmful gases when sprayed on hot metals.
157. Ohm meter is used to check integrity & continuity of bulb filament & others.
158. Hand snip – St snip (cutting st. line, Yellow color), Aviation snip – For cutting heat treated Al
alloy & S.S. As thick as 0.051”. Two types (left to right & T to L), cut 1/32” from layout line.
Finished by hand filing.
159. Manila rope – Inspected periodically for mildew & rot. Nylon or Dacron ropes are preferable
than manila for tensile strength. Manila shrinks when wet.
160. Vernier scale of a micrometer – II graduation (10division) on sheet of m.m representation of
one ten thousandth of an inch.
161. Most common a/c cables are 7x7 & 7x19; 7 – 6 strands aound +1 at centre, extra flexible for
primary control system, pulley. Medium flexibility for trim tab control, engine control, indicator
control. Dia – 1/16” TO 3/8”.
162. Resistance welding is done with Low V & High Current.
163. BNC is most widely used cable connector in RF cables. Modulator – Modify the signal.
164. Corrosion caused by – Indentations, Burrs cracks, Dissimilar metals
165. The product of wt. & arm (moment) about fulcrum (pivot pt. & at c.g.) are equal for a lever.
166. Protection from EMI/HIRF – Bonding, Shielding & Grounding but shielding most effective.
167. Direct connections to a Mg str not used in ground return cz they may create a fire hazard. CFC
and other similar low-resistive materials must not be used in power return paths.
168. Voltage drops in the return path can cause voltage regulation problems. Likewise, repeated
localized material heating by current surges can cause material degradation.
169. Delamination - separation of plies, debonding of skin from the core & moisture & corrosion.
170. Environment resistant connectors - subjected to fluids, vibration, heat, mechanical shock,
corrosive elements, etc. Firewall class connectors - these plus to prevent the penetration of
the fire and continue to function without failure for a specified period of time. Hermetic
connectors - pressure seal for maintaining pressurized areas. EMI/RFI protection req – sp.
attention to the termination of individual and overall shields, Backshell adapters and EMI
grounding fingers used.
171. In bearing radial load is when direction of load is at right angle to shaft, axial load when II to
shaft. Radial load due to RPM change & axial result from compression & turbine thrust load.
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
8
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
172. Hardness – property of resisting permanent distortion. Hardness & Strength – closely related,
Hardness & Brittleness – V. Closely related. Malleability – worked into curve w/o crack/break.
173. Toughness – shock absorbing char., withstand tearing/shearing & stretching, w/o breaking.
174. Rivet pitch – dist. b/w the centers of neighboring rivets in same row. Smallest – 3 rivet dia.
175. Fusibility – Steel (2500*F – titterton, 2600* - EASA), Al alloy – 1100*F.
176. Elastic limit – A pt. beyond which an obj cannot be loaded w/o any permanent distortion.
177. % of MAC = CG-LEMAC/MAC X 100
178. Alodizing is done on Al alloy.
179. Prick punch – Made of hardened tool steel. Ground to a slender pt. 30-60* included angle.
180. Storage of a/c in cold Wx – Flaps fully extended, Water drained from tanks, Windows open.
181. Rivets used for riveting sheets exposed to slipstream – Brazier rivet.
182. Max elongation % limit for chains – 2%.
183. LPI – Visible dye; Red indication, Fluorescent dye; Yellow Green (defect) Blue Violet (if sound).
184. Bolt & cotter pins installed in high vibration area. Tow bar is subject to tension stress.
185. Fairleads - Made from a nonmetallic material (phenolic), metallic material (soft aluminum).
Completely encircles the cable, used to guide cables in a straight line should never deflect the
alignment more than 3 ° from a straight line.
186. Most Anodic - Mg, Al - Zn, Cd, Cr – Fe, Cr Fe, Cr Fe Ni – Solder, Sn, Pb – Ni, Brass, Bronze, K
Monel, Monel, Cu, Inconel, Titanium, Cr Fe, Cr Fe Ni - Ag, Au, Pt – Most cathodic
187. A solid conductor with metal braids outside is called coaxial cable. Hermetic connector used.
188. Severe Turbulence - Accelerometers or fatigue meters used, if reading exceeds -0·5 g and +2.5
g for transport cat. aircraft, damage is expected at main assembly points e.g. wing-to-fuselage
joints tail-to-fuselage joints engine mountings areas of the wings, fuselage, tailplane and
control surfaces. Also, skin wrinkles, pulled rivets are observed.
189. Coin dimpling – 2 methods of Hot dimpling, first coin dimpling (electrically heated dyes used),
second sheet is heated by its resistance to the passage of electric current.
190. Spin dimpling is most widely used method of Cold-dimpling.
191. Nozzle is attached to the ground wire. Another ground wire terminates in alligator chip is
connected to grounding post and this is done before the fuel tank cap is removed from filler
neck. Fuel truck has 2 ground wires; first ground on apron & other with a/c.
192. When Cu wire is replaced with Al wire, the Al wire should be 2 size larger than Cu wire to
ensue same R of replaced wire. L of Al wire is never < Cu wire & Wt of Al = 2/3 wt of Cu wire.
193. Mg – world’s lightest metal, silvery while, wt = 2/3 of Al. Mg alloys 18% less wt than Al panels.
194. Mg & alloys r most chemically active & most difficult to protect. In early stage Mg corrosion V
>> V of original metal. Paint lifts off, white spot created. Snow like mounds & white whiskers.
195. In a/c inspection is carried out acc. to Flight Hour & Calendar days (more effective).
196. SATCOM – VHF range, allow communication data & voice.
197. Bonding while fueling is done by conductive wire. Bonding – Discharge static charge.
198. Low Z path is req to provide radio freq return ckt & EMI reduction. Electrical conductivity is
considered to prevent radio interference.
199. Safety & quality policy include a statement of compliance with procedures by designated
personnel, encourage them to report error & comply with audit persons.
200. The mfg is permitted to weigh a particular model’s 10-20% & apply avg to all the a/c.
201. The R of each connection should normally not exceed .003 ohms.
202. Growlers are used to test armature coil & generator.
203. False brinelling is freeting corrosion _________________.
204. Corrosion removal – Cleaning & stripping of corroded area, removing corrosion as practicable,
neutralizing residual material in pits & crevices, restoring protective film, temp./perm. finish.
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
9
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
205. Metal particles b/w teeth of file removed by tapping edge of file & using file card/wire brush.
206. The dia of wire determines the total dia of the cable; cables preformed in helical shape- strand.
207. Gear;
a. Gear with i/p force Drive gear (its Dia – effort arm), Other is – Driven gear (Dia-
resistance arm), both turns in opp. direction.
b. Mechanical Adv in terms of force = Effort Arm divided by Resistance arm &
Mechanical Adv in terms of distance (RPM) = R arm divided by Effort Arm.
c. Large Gear drives smaller – smaller one turns faster but less force available. For force
gain – Small drives larger gear e.g Reduction gear box (less o/p rpm & more o/p force).
d. Bevel Gears – To change plan of rotation.
e. Worm Gear – High mechanical adv in terms of force, equal to no. of teeth of spur
gear. This is a force gaining machine.
f. Planetary sun gear system – P o/p shaft of engine drives sun gear which rotates
planetary gear & ultimately ring gear.
g. Gear ratio – Teeth ratio, inverse of speed ratio. If G.R = 2:9 then S.R = 9:2.
h. Reduction gearing – Drives engines at higher RPM (more power) while Propeller at
low RPM (Better efficiency). Gears made of Steel forgings for withstanding high stress.
3 types of reduction gearing – Spur planetary, Bevel planetary & Spur-Pinion.
i. Gear Terms; Backlash or lash – Clearance b/w gear teeth & pt. of mesh for lubrication
& expansion. Idler Gear – Imposed b/w driving & driven gear. To connect b/w two
shafts, to maintain direction of rotation. Bevel Idler – when 2 shafts intersect/co-axial.
Intermediate Gear – B/w driving gear & one or more driven gear. Compound gear –
One or more driving face bolted or splined, no of shats. Pinion – Smaller of the two
mating pair of gear. Either could be drive & driven. Lay-Shaft – Supports
idler/intermediate gear, fixed/supported by bearing. Rack & Pinion - Rotary
movement to linear. Step-up drive – O/p RPM increased. Step-down drive – O/p RPM
reduced, torque increased.
j. Spur gear – A wheel or cylinder with teeth cut II to axis. Used for transmitting motion
1
b/w shafts that are II. It’s tooth are of involute form . It’s P angle of gear – 14 .
2
k. Size of a gear is given in terms of pitch dia. Pitch dia ratio is same as gear ratio.
l. Gear train – Simple & Compound; Simple – 2 or more gears on separate shafts.
Compound – Series of gears with 2 of the intermediate on the same shaft, same speed.
It permits greater range of gear ratio combinations in limited space.
m. Pitch Circle – Imaginary circle through the pts at which teeth of meshing gear contact.
n. Pitch dia (D)– dia of pitch circle. Diametral Pitch (DP) – no. of TPI per dia. Circular
pitch – Dist b/w 2 corresponding pts on adjacent teeth along the pitch circle.
Addendum (S)– Tooth outside the pitch circle. Dendendum (S+F) – Below the pitch
circle = Addendum + Clearance. Outside dia (O) – Pitch dia + 2 x addendum. Clearance
(F)– Diff b/w whole depth & working depth or clearance b/w top & bottom of tooth.
Whole depth (W) – Addendum + Dedendum (includes clearance). Working depth (2S)
– Twice the addendum. Centre to Centre dist (C) – dist. center of one gear to meshing
1 1
gear = 2D1 +2D2.
o. Stub tooth – Thicker. Not smooth. High strength. Combination of two DP; thick & dia.
p. Chordal thickness – Chord length. Corrected Addendum – Dist from top to chord.
Pitch circle passes through chord extremes. These two are necessary to measure the
size of the gear using Vernier caliper.
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
10
M7 (PART 1) PDF by Mr.Raza
Dear readers, in this PDF, majority of the portion is of M7 but of M6 too. A dedicated PART 2 for M6
would be available soon. Contact given below.
Alhamdulillah
Thanks for choosing this document
Pdf by - Mr.Raza | EMAIL -MONISHAMARPATAN@GMAIL.COM /WHATSAPP - 9424485787
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Differential Gear System Mini Project - ReportDocument40 pagesDifferential Gear System Mini Project - ReportSalman Saifuddin84% (25)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- F5a51 PDFDocument86 pagesF5a51 PDFmilton piva100% (3)
- Group 242 - NP242 Transfer CaseDocument26 pagesGroup 242 - NP242 Transfer CaseretulikNo ratings yet
- 357 05 Kessler Drive Axle AssemblyDocument84 pages357 05 Kessler Drive Axle AssemblyJavier Barrios Sarricolea100% (1)
- MAAG GEAR Techinal and Commercial Considerations Related To The Cement Mill ProductionDocument43 pagesMAAG GEAR Techinal and Commercial Considerations Related To The Cement Mill ProductionLLNo ratings yet
- U660 CatalogDocument4 pagesU660 Catalogmickabd2002100% (1)
- Hyundai SparePartsDocument44 pagesHyundai SparePartsMarcel Baque100% (1)
- Module 1120 27-Jun-19Document13 pagesModule 1120 27-Jun-19Chitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Module 11a 2019 April & June SessionDocument38 pagesModule 11a 2019 April & June SessionChitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Module 11 QBDocument17 pagesModule 11 QBChitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Ratan Maurya (M-11distribution of Power Supply)Document5 pagesRatan Maurya (M-11distribution of Power Supply)Chitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Module 11A 1Document23 pagesModule 11A 1Chitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Ratan Maurya (M-11power Supply)Document4 pagesRatan Maurya (M-11power Supply)Chitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Module 7 DGCADocument78 pagesModule 7 DGCAChitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Ratan Maurya (M-11aircraft Software)Document3 pagesRatan Maurya (M-11aircraft Software)Chitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- MOD-7 Notes & DGCA QSDocument98 pagesMOD-7 Notes & DGCA QSChitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Kroes and Wild... 331 To 372Document38 pagesKroes and Wild... 331 To 372Chitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Associate Technician: Basic DetailsDocument4 pagesAssociate Technician: Basic DetailsChitrali SontakkeNo ratings yet
- 6020B Swing Drive - System OperationDocument5 pages6020B Swing Drive - System Operationzawmoe aungNo ratings yet
- Funk Drivetrain Components Selection Guide 1Document28 pagesFunk Drivetrain Components Selection Guide 1Elena UriñaNo ratings yet
- Kisssoft Changelog Version 2020 - Service Pack 4: WrongDocument14 pagesKisssoft Changelog Version 2020 - Service Pack 4: WrongpasswordNo ratings yet
- VORECONDocument8 pagesVORECONHafedh HammamiNo ratings yet
- VOITH Vorecon Variable Speed Panetary GearDocument8 pagesVOITH Vorecon Variable Speed Panetary GearFrank PuchiNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Hino Dutro 1999 DemoDocument15 pagesService Manual Hino Dutro 1999 DemoMe YouNo ratings yet
- Power Train PDFDocument33 pagesPower Train PDFMohamed AbdelmagedNo ratings yet
- Major Break DownsDocument57 pagesMajor Break Downskaswade BrianNo ratings yet
- Final - Chain Drive & TyresDocument11 pagesFinal - Chain Drive & TyresMahmoud MohsenNo ratings yet
- FORCE CatalogueDocument85 pagesFORCE CatalogueMaterialsOne100% (1)
- ME LabDocument28 pagesME LabAdriel JohnNo ratings yet
- 7 Planetary GearDocument76 pages7 Planetary GearSimalakamaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For SIMOTICS S-1FK7 Servo Geared MotorDocument2 pagesData Sheet For SIMOTICS S-1FK7 Servo Geared MotorMarcone Marques TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Lect-7 Automobile - Power Transmission Part-2 12-Dec-2021Document34 pagesLect-7 Automobile - Power Transmission Part-2 12-Dec-2021santosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Machine Design IIDocument11 pagesMachine Design IIExequiel MedinaNo ratings yet
- Gearbox Components and Parts Everything You Need To KnowDocument9 pagesGearbox Components and Parts Everything You Need To KnowSulafa yoga AimanaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Computational Fluid Dynamics For A CVT Transmission Lubrication System of Agricultural TractorDocument13 pagesMethods of Computational Fluid Dynamics For A CVT Transmission Lubrication System of Agricultural TractorAdrianNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Service Manual CT S GuideDocument6 pagesCaterpillar Service Manual CT S GuideJosé Luis Cavas OlmosNo ratings yet
- Single Speed Powershift Transmission Hyster H30-60H Repair ManualDocument39 pagesSingle Speed Powershift Transmission Hyster H30-60H Repair ManualArmando OrtaNo ratings yet
- An Analytical Method of Aircraft Gearboxes: To Predict EfficiencyDocument25 pagesAn Analytical Method of Aircraft Gearboxes: To Predict EfficiencyAnonymous lEX5U51wOANo ratings yet
- Gear / Gearbox Transmission Error (TE)Document1 pageGear / Gearbox Transmission Error (TE)Yaser MohamedNo ratings yet
- TransmissionDocument30 pagesTransmissionEZHILARASAN RNo ratings yet
- Planetary Gear Unit 1. Construction: Chassis - A340E, A340F, A343E and A343F Automatic Transmissions CH-14Document5 pagesPlanetary Gear Unit 1. Construction: Chassis - A340E, A340F, A343E and A343F Automatic Transmissions CH-14Maxi SardiNo ratings yet