Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essentials of Polysomnography: A Training Guide and Reference For Sleep Technicians
Uploaded by
Samsung User0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
433 views2 pagesOriginal Title
sleep-32-12-1649
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
433 views2 pagesEssentials of Polysomnography: A Training Guide and Reference For Sleep Technicians
Uploaded by
Samsung UserCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Book Review
Essentials of Polysomnography: A Training Guide and Reference for Sleep
Technicians
By William H. Spriggs, BS, RPGST; Jones and Bartlett, Publishers, Boston; 2008; ISBN: 9780763781064; Hardcover,
615 pages, $159.95 US.
Joseph T. Daley, MD, PhD; Samuel T. Kuna, MD
University of Pennsylvania and the Philadelphia VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA
Downloaded from https://academic.oup.com/sleep/article/32/12/1649/2454364 by guest on 28 August 2021
THE FOUNDATION OF EVERY SLEEP CENTER CUR- ful in assisting individuals in the initial phases of a career in
RENTLY RESTS ON THE POLYSOMNOGRAM. WITHOUT sleep medicine to recognize what they have learned and areas
THE SUCCESSFUL COLLECTION OF THESE DATA, THE of weakness on which to focus. Though perhaps beyond the
clinical evaluation of patients with sleep disorders would floun- scope of the book, the technical aspects of ambulatory portable
der due to the lack of objective data on which to base diagnoses monitor recordings are not addressed, despite the growing use
and guide therapeutic interventions. Essential to this founda- of portable monitor testing to evaluate patients with suspected
tion is the well-trained and knowledgeable polysomnographic obstructive sleep apnea.
technician. In addition to providing a thorough discussion of all the tech-
To this end, William H. Spriggs, BS, RPGST has attempted nical aspects of polysomnography, the author also emphasizes
to produce a comprehensive textbook, titled Essentials of Poly- the technician’s critical role as a member of the sleep center
somnography: A Training Guide and Reference for Sleep Tech- team. A chapter devoted to the “Life as a Sleep Technician”
nicians, directed at these important individuals on the frontlines explores the importance of maintaining an environment that is
of sleep medicine. This book provides a resource not only for conducive to patient care and safety and putting the patient at
polysomnographic technicians, but for all involved in the field ease during what otherwise might become a stressful experi-
of sleep medicine who desire an in-depth understanding of ence. The importance of the literal “bedside manner” can be
polysomnography. It is well organized, and the wealth of in- lost when one focuses on the complex technologic require-
formation is presented in a systematically outlined progression ments of polysomnography: therefore, it is commendable to see
that is easy to read and understand. The book contains numer- it emphasized early in the book.
ous examples of polysomnographic recordings that illustrate That being said, accurate and consistent scoring of polysom-
the topics covered in the text. nograms is an essential feature of reliable sleep studies and,
The initial chapter outlines the importance of sleep on an ultimately, appropriate patient care. The numerous polysomno-
individual and societal level and reviews the characteristics of graphic examples in the book provide a comprehensive scoring
normal sleep. Next, the author provides an overview of patho- atlas. Although their presentation employs the most recent no-
logic sleep that could also serve as an excellent introduction menclature and scoring criteria recommended by the American
to general practitioners hoping to recognize sleep disorders in Academy of Sleep Medicine, some of the examples may con-
their patients. The next sections encompass the nuts and bolts fuse readers. In particular, the important differences between
of polysomnography: patient flow, the equipment used in poly- the oronasal thermistor and the nasal pressure signals as surro-
somnographic recordings, and sensor placement. Successive gate markers of airflow, including the distinction between these
chapters are devoted to the signals acquired during the poly- 2 signals in the scoring rules of apneas, are not addressed. The
somnogram, identification and troubleshooting of artifacts, American Academy of Sleep Medicine scoring manual speci-
filter settings, and sleep staging. An excellent chapter entitled fies that an apnea requires a flat line on the oronasal thermistor
“Abnormal Events” cites the scoring rules and provides many signal.1 Many have criticized that controversial decision, stat-
examples of important findings, eg, limb movements and ap- ing that the oronasal thermistor signal only detects expiratory
nea/hypopneas. Other chapters discuss positive airway pres- airflow and cannot recognize airway obstruction on inspiration.
sure titration, electrocardiographic abnormalities, and pediatric Although the reviewers agree that respiratory events with a flat
polysomnography. Finally, there is a comprehensive self-test nasal pressure signal but persistent fluctuations in the oronasal
with annotated answers that surveys the information provided signal should be scored as obstructive apneas (see example on
throughout the book. This last portion will be particularly use- page 373), these events would be scored as hypopneas based on
criteria in the American Academy of Sleep Medicine scoring
manual.
Submitted for publication August, 2009
Also, there are large sections of the book with examples of
Accepted for publication August, 2009
Address correspondence to: Samuel T. Kuna, MD, Pulmonary, Critical
polysomnographic epochs displayed across the top half of the
Care & Sleep Section, Philadelphia VAMC (111P), 3900 Woodland Av- page, leaving the remainder of the page blank. The resulting
enue, Philadelphia PA 19104; Tel: (215) 823-4400; Fax: (215) 823-5876; low amplitude of the signals makes it difficult to appreciate
E-mail: skuna@mail.med.upenn.edu some of the findings. Full-page displays or examples printed in
SLEEP, Vol. 32, No. 12, 2009 1649 Book Review—Daley and Kuna
landscape format would have made it easier to appreciate the physiologic recordings and complement the practical training,
findings of interest. When electroencephalographic frequency experience, and supervision that lead to the high-quality record-
or amplitude or the duration of the event is critical to classifi- ings essential for providing excellent patient care.
cation, the inclusion of time and microvolt scales would have
been helpful. Perhaps in part due to the inherent subjectivity Disclosure Statement
that arises from scoring qualitative signals, there are examples Dr. Kuna has received research support and use of equipment
presented in the chapters and the self-test with which the authors from Respironics. Dr. Daley has indicated no financial conflicts
of this review disagree. Specifically, the examples of bruxism of interest.
are not what we view as the classic images, as the bursts of
electromyography are timed to inspiration and occur at a lower references
frequency than that associated with most chewing movements. 1. Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL, Quan SF. American Academy of
Sleep Medicine. The AAMS Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and As-
These shortcomings aside, this textbook achieves its stated sociated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications, 1st ed:
goal as a reference for the polysomnographic technician. It will Westchester, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine; 2007.
serve as a useful guide to the performance of these complex
Downloaded from https://academic.oup.com/sleep/article/32/12/1649/2454364 by guest on 28 August 2021
SLEEP, Vol. 32, No. 12, 2009 1650 Book Review—Daley and Kuna
You might also like
- Essentials for Practice of Medicine in the Frontline: From Tropical Africa; Pleasantly DifferentFrom EverandEssentials for Practice of Medicine in the Frontline: From Tropical Africa; Pleasantly DifferentNo ratings yet
- CPAP Titration AASM 2008Document15 pagesCPAP Titration AASM 2008Sam samiNo ratings yet
- Educational Material: Educational Skills Workshop 25, 27 Hands-On PolysomnographyDocument136 pagesEducational Material: Educational Skills Workshop 25, 27 Hands-On PolysomnographyPhạm Văn HiệpNo ratings yet
- Cancer-Leading Proteases: Structures, Functions, and InhibitionFrom EverandCancer-Leading Proteases: Structures, Functions, and InhibitionNo ratings yet
- Ravi Gupta, S. R. Pandi-Perumal, Ahmed S. BaHammam - Clinical Atlas of Polysomnography (2018, Apple Academic Press)Document547 pagesRavi Gupta, S. R. Pandi-Perumal, Ahmed S. BaHammam - Clinical Atlas of Polysomnography (2018, Apple Academic Press)psicosmosNo ratings yet
- Ambu Sleepmate Poster PDFDocument1 pageAmbu Sleepmate Poster PDFMinh Triết LêNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For Neurological Disorders (2) 2Document11 pagesPhysical Therapy For Neurological Disorders (2) 2Muskan AhujaNo ratings yet
- 298830Document34 pages298830Mohamed belhasan100% (1)
- PolysomnographyDocument23 pagesPolysomnographyGonzalo Sebastian Bravo RojasNo ratings yet
- MCQ AnswersDocument2 pagesMCQ AnswersJeyarajasekar TtrNo ratings yet
- EEG Basics PDFDocument127 pagesEEG Basics PDFAhmed Gaber100% (1)
- 15 Menieres DiseaseDocument72 pages15 Menieres DiseaseDrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- ATSDR Case Studies in Environmental Triggers of AsthmaDocument85 pagesATSDR Case Studies in Environmental Triggers of AsthmaRaihan LuthfiNo ratings yet
- Neural Mechanisms of Salivary Gland SecretionDocument247 pagesNeural Mechanisms of Salivary Gland SecretionMassimo Baudo100% (1)
- PSQIDocument2 pagesPSQIAdrian HartantoNo ratings yet
- Sleep and Disorders of Sleep in Women, An Issue of Sleep Medicine ClinicsDocument138 pagesSleep and Disorders of Sleep in Women, An Issue of Sleep Medicine ClinicsPatrickNo ratings yet
- Ap Cell Tour 1 ProteinDocument28 pagesAp Cell Tour 1 Proteinapi-235744933100% (1)
- Electrographic and Electroclinical Seizures BirdsDocument50 pagesElectrographic and Electroclinical Seizures BirdsNEUROMED NEURONo ratings yet
- Sedation Analgesia ParalysisDocument10 pagesSedation Analgesia ParalysisAvi CNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis-Pedrosa, Joan ADocument27 pagesDiagnosis-Pedrosa, Joan AJoan Alde PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Brain DeathDocument24 pagesBrain DeathKawaljit KaurNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Spinal Fluid & The MeningesDocument25 pagesCerebral Spinal Fluid & The MeningeschintyamontangNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics Study GuideDocument44 pagesGeriatrics Study GuideahkrabNo ratings yet
- Moca Vs MMSEDocument2 pagesMoca Vs MMSEYw LiuNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Assessment RationaleDocument16 pagesNeurologic Assessment RationaleflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Milk Proteins Good & BadDocument3 pagesMilk Proteins Good & BadJose PalomarNo ratings yet
- RPSGT Exam BlueprintDocument2 pagesRPSGT Exam BlueprintKarloveyNo ratings yet
- CCEB Exam Content July 2013Document24 pagesCCEB Exam Content July 2013StarLink1No ratings yet
- A Clinical Guide To Pediatric SleepDocument304 pagesA Clinical Guide To Pediatric Sleepchucrallah1968No ratings yet
- HfiDocument4 pagesHfiakalaw3No ratings yet
- CV - David Gozal M.D. (USA)Document87 pagesCV - David Gozal M.D. (USA)MSKCNo ratings yet
- Anticonvulsants 2Document1 pageAnticonvulsants 2Taif Salim100% (1)
- Sleep Technology Terms & DefinitionsDocument42 pagesSleep Technology Terms & DefinitionsJorge B CNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Management in Pediatrics PDFDocument68 pagesRespiratory Management in Pediatrics PDFPAKINUGNo ratings yet
- Sarnat 1976Document10 pagesSarnat 1976João Paulo RaposoNo ratings yet
- Lactose Intolerance Among Severely Malnourished Children With Diarrhoea Admitted To The Nutrition Unit, Mulago Hospital, UgandaDocument10 pagesLactose Intolerance Among Severely Malnourished Children With Diarrhoea Admitted To The Nutrition Unit, Mulago Hospital, UgandaSuci Joe ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Yeast Infection PDFDocument12 pagesYeast Infection PDFAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Suck-Swallow and Swallow Respiration in Preterm InfantsDocument8 pagesCoordination of Suck-Swallow and Swallow Respiration in Preterm Infantsilg1No ratings yet
- The AASM Manual For The Scoring of Sleep and Associated EventsDocument136 pagesThe AASM Manual For The Scoring of Sleep and Associated EventsSerkan KüçüktürkNo ratings yet
- Picu Drug Dosage Chart AmitDocument9 pagesPicu Drug Dosage Chart AmitIze C VijiNo ratings yet
- Wilkins 6 - Neurological Assessment - AssignmentDocument33 pagesWilkins 6 - Neurological Assessment - AssignmentArifurRahman100% (1)
- Pathways To Become RPSGTDocument53 pagesPathways To Become RPSGTJustin AlmedaNo ratings yet
- Vanessa's Curriculum VitaeDocument6 pagesVanessa's Curriculum VitaeVanessa Colleen Farrer MiltonNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ashok Deorari - Non Invasive Ventilation Way Forward For IndiaDocument11 pagesDr. Ashok Deorari - Non Invasive Ventilation Way Forward For IndiaKalyan DamisettiNo ratings yet
- Drugs During Pregnancy Methodological Aspects 2016Document120 pagesDrugs During Pregnancy Methodological Aspects 2016MohamadNo ratings yet
- KATH - DCH Treatment GuidelinesDocument173 pagesKATH - DCH Treatment GuidelinesCarterine ListNo ratings yet
- Shared Medical Appointments For DiabetesDocument10 pagesShared Medical Appointments For Diabetesapi-259806108100% (1)
- Non-Invasive Ventilation NIV: Yazeed Abed El Khaleq Respiratory St4 BNHHDocument24 pagesNon-Invasive Ventilation NIV: Yazeed Abed El Khaleq Respiratory St4 BNHHYazeedNo ratings yet
- Eye Movement Disorder PDFDocument115 pagesEye Movement Disorder PDFGilberto FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Sleep Medicine 2022 FullDocument1,530 pagesSleep Medicine 2022 Fullyowewe7363No ratings yet
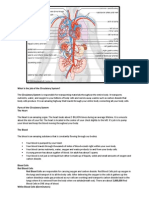
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemcatchivanNo ratings yet
- Clinicians To Pediatric Sleep Disorders 2007Document370 pagesClinicians To Pediatric Sleep Disorders 2007Mihaela MuscaluNo ratings yet
- Diagn Approach of Abdominal PainDocument53 pagesDiagn Approach of Abdominal PainNuriNo ratings yet
- The Origins of The History and Physical ExaminationDocument21 pagesThe Origins of The History and Physical ExaminationNEuRoLoGisT CoFFeeCuPNo ratings yet
- Methods of Postural Assessment Used For Sports Persons: Abst TDocument4 pagesMethods of Postural Assessment Used For Sports Persons: Abst TUmesh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument6 pagesDiagnosis of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusMuhammad Akhram ResmanaNo ratings yet
- It sJustAQuizDocument24 pagesIt sJustAQuizPrerna SehgalNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Ect March 2020Document120 pagesAnaesthesia For Ect March 2020Sangkaran KumarNo ratings yet
- Guideline Update: March 2017Document24 pagesGuideline Update: March 2017Samsung UserNo ratings yet
- 1179 FullDocument17 pages1179 FullSamsung UserNo ratings yet
- Polysomnography (Sleep Medicine) : Program Description OptionsDocument2 pagesPolysomnography (Sleep Medicine) : Program Description OptionsSamsung UserNo ratings yet
- Practice Parameters For Using Polysomnography To Evaluate Insomnia: An UpdateDocument7 pagesPractice Parameters For Using Polysomnography To Evaluate Insomnia: An UpdateSamsung UserNo ratings yet
- Provider Compliance Tips For PolysomnographyDocument3 pagesProvider Compliance Tips For PolysomnographySamsung UserNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Management of Clinical Mastitis in Goat: A Case StudyDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Management of Clinical Mastitis in Goat: A Case StudyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Pedia ADCONDocument24 pagesPedia ADCONRaul MangrobangNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 9 PE and Halth 2nd Quarter Examination FinalDocument2 pagesMAPEH 9 PE and Halth 2nd Quarter Examination Finalcecile80% (10)
- Autopsy: Bocoboc, Castillo, Miguel, Nalupta, RoldanDocument28 pagesAutopsy: Bocoboc, Castillo, Miguel, Nalupta, RoldanAya CstlNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For LEUKEMIASDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan For LEUKEMIASMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- RRL Mental IllnessDocument1 pageRRL Mental IllnessGaguka NamanNo ratings yet
- Polio VaccineDocument10 pagesPolio VaccineLiiaa SiiNouunaa JupheeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Lawrence LuceñoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- Pertussis - Not Just For Kids: Clinical PracticeDocument8 pagesPertussis - Not Just For Kids: Clinical PracticeMihaela-Alexandra PopNo ratings yet
- Managing Multiple Comorbidities - UpToDateDocument15 pagesManaging Multiple Comorbidities - UpToDateGaby GarcésNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DiseaseDocument27 pagesRespiratory Diseaseعبدالسلام الأسمرNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci (Streptococcus)Document26 pagesMicrobiology: Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci (Streptococcus)Shuler0071No ratings yet
- Team Approach With Diabetes Patients: HistoryDocument5 pagesTeam Approach With Diabetes Patients: HistoryEdgar SchultzNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic DisordersDocument85 pagesSchizophrenia and Other Psychotic DisordersEsraRamosNo ratings yet
- Henderson's 14 ComponentsDocument6 pagesHenderson's 14 ComponentsJim RashidNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Fixator Extern Circular IlizarovDocument10 pages4.1 Fixator Extern Circular IlizarovTudorica AdrianNo ratings yet
- DM 2021-0114 Guidelines On The MGMT and Admin of The Initial 600,000 Donated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine (Vero Cell) Inactivated Coronavac (Sinovac) DosesDocument17 pagesDM 2021-0114 Guidelines On The MGMT and Admin of The Initial 600,000 Donated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine (Vero Cell) Inactivated Coronavac (Sinovac) DosesRalph Julius MendozaNo ratings yet
- ShouldiceDocument16 pagesShouldiceAbdullah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Icmr Specimen Referral Form For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) : Nic - (Https://Covid19Cc - Nic.In) Page 1/18 27-04-2021 13:49:04Document18 pagesIcmr Specimen Referral Form For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) : Nic - (Https://Covid19Cc - Nic.In) Page 1/18 27-04-2021 13:49:04Sumit PatelNo ratings yet
- Philippine College of Science and Technology College of NursingDocument21 pagesPhilippine College of Science and Technology College of NursingAijem RyanNo ratings yet
- Sterile TechDocument85 pagesSterile TechBSN II - Tutor, Rel joshuaNo ratings yet
- Chamani Essay VAPEDocument2 pagesChamani Essay VAPEChamani MadawalaNo ratings yet
- Health Lesson Plan-BandagesDocument8 pagesHealth Lesson Plan-BandagesJaybee MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- Manual of Definitive Surgical Trauma CareDocument256 pagesManual of Definitive Surgical Trauma Carebovine splendor100% (3)
- CLICO Group Health and Life Coverage 1Document12 pagesCLICO Group Health and Life Coverage 1buckianNo ratings yet
- Complication of Sinus DiseaseDocument27 pagesComplication of Sinus DiseaseukhuholicNo ratings yet
- How We Can Spread AwerenessDocument47 pagesHow We Can Spread AwerenessFaurel AzmiNo ratings yet
- A Simple Approach To Shared Decision Making in Cancer ScreeningDocument6 pagesA Simple Approach To Shared Decision Making in Cancer ScreeningariskaNo ratings yet
- Konsep Wound ManajemenDocument24 pagesKonsep Wound ManajemenNiken DewiNo ratings yet
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)