Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nutrient and Gas Requirements - Autotroph Structure and Function
Uploaded by
JimmyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrient and Gas Requirements - Autotroph Structure and Function
Uploaded by
JimmyCopyright:
Available Formats
Autotroph Structure and Function
Discuss the structure of vascular and non-vascular plants
1. Distinguish between vascular and non-vascular plants.
o Answer
Vascular plants
Possess vascular tissue, which is specialised for transporting fluids (Not found
in leaves or roots)
Xylem
Phloem
Non-vascular plants
Non-vascular plants do not possess this system
2. Identify the two plant tissues.
o Answer
Xylem and phloem
3. Identify the two organs present in plants.
o Answer
Roots and leaves
4. Distinguish between xylem tissue and phloem tissue.
o Answer
Xylem
Transports water and inorganic nutrients (mineral ions) absorbed from the soil
up the plant
Phloem
Transports dissolved sugars produced by photosynthesis from the leaves
throughout the plant, and organic substances
5. Identify the three systems present in most plants.
o Answer
Vascular, root and shoot systems
Discuss the main functions of the leaves.
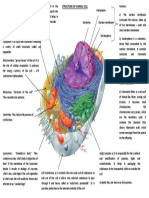
1. What is the cross-section of a leaf.
o Answer
2. Identify the main functions of a leaf.
o Answer
Absorb sunlight and carbon dioxide, and produce glucose from photosynthesis
Exchange gases with the air
3. Describe the features of most leaves that allow them to absorb the maximum amount
of sunlight for photosynthesis.
o Answer
Thin and flat structure maximises their surface area allowing the optimum
absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
Thin shape enables internal cells to receive adequate light energy
4. Outline the function of the epidermal tissue.
o Answer
Protects inner tissue and prevents evaporation of water by secreting a waxy
cuticle
5. Outline the function of palisade and spongy mesophyll cells
o Answer
Photosynthesis (but spongy not as much as palisade mesophyll cells)
6. Describe the distribution of vascular tissue in the leaf and how this assists the leaf to
carry out its functions.
o Answer
Enables the leaf to carry out its functions
Distributed throughout like veins
Ensures cells receive the required nutrients and have a system to get rid of
waste
7. Discuss how the products of photosynthesis and respiration can be reused by the
plant.
o Answer
Oxygen (from photosynthesis) can be reused by the plant as an input of
cellular respiration
Carbon dioxide (from cellular respiration) can be reused by the plant as an
input of photosynthesis
Explain how imaging technologies are useful
1. Describe how radioactive tracers can be used to trace the path of elements through
living plants.
o Answer
Radioisotopes
Carbon-14 can be used to trace the movement of glucose after it has
been produced by photosynthesis by adding it to the carbon dioxide
supply of a plant
Radiation emitted by the carbon-14 in the glucose can be traced so that
the glucose can be traced
Photographic film is used to see where it had moved (dark areas)
Radioisotopes produce gamma radiation that could cause cancers or mutations
in living organisms
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Clinical Virology, 3rd EditionDocument1,416 pagesClinical Virology, 3rd EditionRichard Balili100% (1)
- Cell CycleDocument50 pagesCell Cyclesuemie100% (2)
- Examview - 7th Grade Science Benchmark YearlyDocument7 pagesExamview - 7th Grade Science Benchmark Yearlyapi-232424041No ratings yet
- The Conscription Debate in AustraliaDocument26 pagesThe Conscription Debate in AustraliaJimmyNo ratings yet
- BP Prov TemplateDocument7 pagesBP Prov TemplateJimmyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Genetic Technologies PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 9 - Genetic Technologies PDFJimmyNo ratings yet
- 2020 ECO Topic 1 International Economic Integration Notes HannahDocument23 pages2020 ECO Topic 1 International Economic Integration Notes HannahJimmyNo ratings yet
- BP StructureDocument1 pageBP StructureJimmyNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Economic Ideas - Tom NassifDocument10 pagesEvolution of Economic Ideas - Tom NassifJimmyNo ratings yet
- Conscription PostersDocument6 pagesConscription PostersJimmyNo ratings yet
- ASX Game Student Booklet - Planning, Strategies and ReflectionsDocument8 pagesASX Game Student Booklet - Planning, Strategies and ReflectionsJimmyNo ratings yet
- Business Cycle: 2019 RjzveuclaDocument6 pagesBusiness Cycle: 2019 RjzveuclaJimmyNo ratings yet
- Reflective Assessment (Semester One) : Complete Homework and Do Well in Assessments For All SubjectsDocument2 pagesReflective Assessment (Semester One) : Complete Homework and Do Well in Assessments For All SubjectsJimmyNo ratings yet
- Business CycleDocument6 pagesBusiness CycleJimmyNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument15 pagesCircular Flow of IncomeJimmyNo ratings yet
- HSC Economics Topic 1 Worksheet 2021Document9 pagesHSC Economics Topic 1 Worksheet 2021JimmyNo ratings yet
- Nest Architecture and Distribution of The Primitive Stingless Bee, Mourella Caerulea: Evidence For The Origin of Plebeia On The Gondwana ContinentDocument17 pagesNest Architecture and Distribution of The Primitive Stingless Bee, Mourella Caerulea: Evidence For The Origin of Plebeia On The Gondwana ContinentdphvuNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab Manual PSTDocument13 pagesBiology Lab Manual PSTMuhammad HusniNo ratings yet
- Is It Plagiarized?: Highlight Any Words That Are Both in The Original and The SampleDocument4 pagesIs It Plagiarized?: Highlight Any Words That Are Both in The Original and The SampleJorge RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Whole Nucleic Acid AmplificationDocument1 pageWhole Nucleic Acid Amplificationibrukner1107No ratings yet
- Sumara Gaspar - Right Beak For The Job LabDocument10 pagesSumara Gaspar - Right Beak For The Job Labapi-572157085No ratings yet
- Paper 2 Unit 1 & 2 Genetically-Modified-Foods-Benefits-and-Risks PDFDocument12 pagesPaper 2 Unit 1 & 2 Genetically-Modified-Foods-Benefits-and-Risks PDFSandeep GupteNo ratings yet
- Campylobacter Jejuni: Dr. Abdulaziz BamaroufDocument29 pagesCampylobacter Jejuni: Dr. Abdulaziz BamaroufaobamaroufNo ratings yet
- 01 Spontaneous Generation TheoryDocument4 pages01 Spontaneous Generation TheoryKlarence AnsayNo ratings yet
- In The ZooDocument2 pagesIn The ZoodiramasaNo ratings yet
- Bio 9.4Document69 pagesBio 9.4yawahabNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Cell TheoryDocument31 pagesHistorical Development of Cell TheoryRamona BaculinaoNo ratings yet
- Arbustedas Termófilas Mediterráneas (Asparago-Rhamnion)Document7 pagesArbustedas Termófilas Mediterráneas (Asparago-Rhamnion)DavidNo ratings yet
- Note On Marsh Crocodile, Presentation On Marsh Crocodile or Marsh Crocodile LifeDocument18 pagesNote On Marsh Crocodile, Presentation On Marsh Crocodile or Marsh Crocodile LifeKirfan 123No ratings yet
- Section 3.2: #4 Living and Nonliving OrganismDocument6 pagesSection 3.2: #4 Living and Nonliving OrganismNGOYA COURTNEYNo ratings yet
- Jurnal RustamDocument15 pagesJurnal RustamRustamNo ratings yet
- Loxanthocereus Hoxeyi El Cereus en Miniatura Del Sur Del PeruDocument7 pagesLoxanthocereus Hoxeyi El Cereus en Miniatura Del Sur Del PeruJhonson Klever Vizcarra RomeroNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 4 ANSWERS Biodiversity HotspotsDocument4 pagesASSIGNMENT 4 ANSWERS Biodiversity HotspotskalebNo ratings yet
- Yara Mila WinnerDocument1 pageYara Mila WinnerLouie VerginoNo ratings yet
- Burkhardt 2001 - A Man and His MenagerieDocument9 pagesBurkhardt 2001 - A Man and His MenagerieSandra QuadrosNo ratings yet
- Plant Taxonomy Paper: PteridophytaDocument28 pagesPlant Taxonomy Paper: PteridophytaSiti Hanifah NasutionNo ratings yet
- 6 ThscicenceDocument4 pages6 Thscicencelearn4chatgptNo ratings yet
- AGRI 6 MODULE 3 Version 3bDocument20 pagesAGRI 6 MODULE 3 Version 3bGlenda Sofia VeaNo ratings yet
- Culturomics of The Plant Prokaryotic Microbiome and The - 2019 - Journal of AdvaDocument13 pagesCulturomics of The Plant Prokaryotic Microbiome and The - 2019 - Journal of AdvaSarras InfoNo ratings yet
- Growing Golden Berry - Cape Gooseberry - Physalis PeruvianaDocument3 pagesGrowing Golden Berry - Cape Gooseberry - Physalis PeruvianaRandi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Mind MapDocument1 pageAnimal Cell Mind Mapsarrah asgarNo ratings yet
- Jacklin Seed Guide 2023-2024 - JPG - 2023 - v5 - 2Document18 pagesJacklin Seed Guide 2023-2024 - JPG - 2023 - v5 - 2tnaillNo ratings yet
- Plant Metabolic EngineeringDocument32 pagesPlant Metabolic Engineeringvamshibommi3477100% (1)