Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Functions of Carbohydrates
Functions of Carbohydrates
Uploaded by
erikerikOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Functions of Carbohydrates
Functions of Carbohydrates
Uploaded by
erikerikCopyright:
Available Formats
FUNCTIONS
1. Energy source.
2. Component of nucleic acids (ribose, deoxyribose)
3. Modification of proteins through glycosylation
Glycemic control is important in diabetes because hyperglycemia leads to development
and progression of microvascular (nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy) and
macrovascular (atherosclerosis 2-4x) complications
Polysaccharides and disaccharides are nonabsorbable polymers which must be
converted first into monosaccharides before being absorbed in the small intestines.
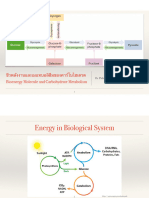
Intermediate products of glucose metabolism: pyruvic acid, lactic acid and
acetylcoenzyme A
End products of glucose metabolism: carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
ENZYMES RESPONSIBLE IN CHO CATABOLISM
1. Pancreatic and salivary amylases
Converts nonabsorbable polysaccharides into disaccharides and dextrins
2. Maltase, sucrase, lactase
Converts maltose, sucrose, and lactose into monosaccharides.
Happens in the microvilli of small intestines
Inherited deficiencies of lactase predispose an individual to lactose intolerance
You might also like
- CarbohyratesDocument47 pagesCarbohyratesEdward SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- 2.LIPIDS DigestionDocument21 pages2.LIPIDS DigestionAlaa Hisham100% (1)
- Role of Carbohydrate in Health and DiseasesDocument41 pagesRole of Carbohydrate in Health and Diseasesuttarasingh100% (2)
- Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument26 pagesMetabolism of CarbohydratesMM Qizill67% (3)
- Metabolisme KarbohidratDocument56 pagesMetabolisme KarbohidratAnonymous QCMhA4wNgBNo ratings yet
- Seminar Glucose MetabolismDocument14 pagesSeminar Glucose MetabolismPoonam PandyaNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of Lipid 12Document36 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Lipid 12Pranjul MishraNo ratings yet
- By: Maria Cristina Pamintuan, RMT, MPHDocument74 pagesBy: Maria Cristina Pamintuan, RMT, MPHSanly Duran BambaNo ratings yet
- Pink Illustrative Cute Brainstorm PresentationDocument62 pagesPink Illustrative Cute Brainstorm PresentationAlexia Mary Solei BacolodNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIDocument30 pagesLesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIAlex SmirnovNo ratings yet
- 101 Metabolism On Human BodyDocument40 pages101 Metabolism On Human BodyNur HolikNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes 2Document903 pagesBiochemistry Notes 2madhu PriyaNo ratings yet
- 3 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2022Document52 pages3 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2022MarieFranz ChuaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Biochem - Carbohydrates & LipidsDocument72 pages1 - Biochem - Carbohydrates & LipidssandeeprachuriNo ratings yet
- Kuliah II - Digestive KH, Lemak, Phosphat Asma NukleatDocument30 pagesKuliah II - Digestive KH, Lemak, Phosphat Asma NukleatHastomo Nur HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Is The Set of Life-Sustaining Chemical Reactions in OrganismDocument3 pagesIs The Set of Life-Sustaining Chemical Reactions in OrganismAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Desi Kristina 027Document25 pagesCarbohydrate Desi Kristina 027Desi kristina yantiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Lec CC1 - NotesDocument116 pagesCarbohydrates Lec CC1 - NotesDaryl Nepomuceno JulaoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument19 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismAbhithNo ratings yet
- Biochemlab CarbslipidsDocument61 pagesBiochemlab Carbslipidschpa.dalisay.auNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument19 pagesCarbohydratesNaina YadavvNo ratings yet
- KH Metab 2016Document58 pagesKH Metab 2016TaniavandarinaNo ratings yet
- ChoDocument44 pagesChosunielgowdaNo ratings yet
- MODULE - FINALS - Biochem - 1Document5 pagesMODULE - FINALS - Biochem - 1Cyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- 9 ชีวพลังงานและเมแทบอลิซึมของคาร์โบไฮเดรตDocument41 pages9 ชีวพลังงานและเมแทบอลิซึมของคาร์โบไฮเดรต22vk6svnb4No ratings yet
- Sharkey 2015Document11 pagesSharkey 2015Mauricio MedinaNo ratings yet
- This Is A SampleDocument10 pagesThis Is A SampleNashi TagazaNo ratings yet
- LGIS CarbohyrateDocument30 pagesLGIS Carbohyratehasaanmushtaq98765No ratings yet
- Lactic AcidodisDocument27 pagesLactic Acidodisdragab71No ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Part 1 of 2 Ryka MooreDocument20 pagesGlycolysis Part 1 of 2 Ryka Mooreglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Sự Tiêu Hóa Và Hấp Thụ CarbonhydrateDocument51 pagesSự Tiêu Hóa Và Hấp Thụ CarbonhydrateSỹ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: April 2014Document41 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: April 2014Koricho MengistuNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Midterm Carbohydrates: ClassificationsDocument21 pagesBiochemistry Midterm Carbohydrates: ClassificationsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument43 pagesCarbohydratesEvangelene Esquillo Sana100% (1)
- Week 15: Absorption Chemistry I. Absorption of Carbohydrates (Monosaccharides)Document3 pagesWeek 15: Absorption Chemistry I. Absorption of Carbohydrates (Monosaccharides)Lore Anne Mhae SantosNo ratings yet
- Stages of CatabolismDocument2 pagesStages of Catabolismsnehashreemohanty39No ratings yet
- Biochem B Finals Conference TopicsDocument18 pagesBiochem B Finals Conference TopicsCamille MalilayNo ratings yet
- Digestion of Corbohydrate Semester 7thDocument52 pagesDigestion of Corbohydrate Semester 7thFadi SalahNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 B.chemistryDocument7 pagesLec 3 B.chemistryHelal HamadNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of The GIT S1-10Document3 pagesBiochemistry of The GIT S1-10Kim RamosNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2Valenzuela Allene GraceNo ratings yet
- ....Document32 pages....ASmaa ELshãzlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Study GuideDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Study GuideJanEia Quisada DotillosNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument62 pagesMetabolismJerry Arandilla Jr.No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate, Protein and Lipid Metabolism-B.NDocument77 pagesCarbohydrate, Protein and Lipid Metabolism-B.NBusy worldNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument60 pagesLECTURE 2 - Carbohydrate Metabolismmuhammedgmdidra95No ratings yet
- Chemistry of CarbohydratesDocument57 pagesChemistry of Carbohydratesdrpnnreddy100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Carbohydrates MetabolismDocument54 pagesPathophysiology of Carbohydrates MetabolismMaui TingNo ratings yet
- Course Outlines: Lipid FamilyDocument31 pagesCourse Outlines: Lipid Familyahmedkazaz100% (1)
- METABOLISM of CARBOHYDRATESDocument62 pagesMETABOLISM of CARBOHYDRATESmohaysin pirinoNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism Dental and PhysiotherapyDocument43 pagesLipid Metabolism Dental and PhysiotherapyNada Atef KoraitemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document112 pagesChapter 2Oltagon Nicole DupingayNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Digestive and Absorption Process of Dietary-Sunarti-Biochemistry (2015)Document36 pagesBiochemical Digestive and Absorption Process of Dietary-Sunarti-Biochemistry (2015)nayanikatesalonikaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis 1Document33 pagesGlycolysis 1AhmedA.SharafNo ratings yet
- SCADDDocument4 pagesSCADDRajiv Kabad0% (1)
- Chapter Viii - Carbohydrates MechanismDocument34 pagesChapter Viii - Carbohydrates MechanismAngelo AngelesNo ratings yet
- Digestion Absorption 12 2019Document14 pagesDigestion Absorption 12 2019Karyan ShinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ' Section Ii: Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument6 pagesBiochemistry ' Section Ii: Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative PhosphorylationAvanca LouisNo ratings yet