Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tahuantinsuyo: Absorption of Light
Tahuantinsuyo: Absorption of Light
Uploaded by
taniaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tahuantinsuyo: Absorption of Light
Tahuantinsuyo: Absorption of Light
Uploaded by
taniaCopyright:
Available Formats
TAHUANTINSUYO
ABSORPTION OF LIGHT
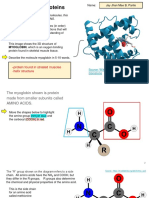
Photosynthesis begins with the absorption of light
by
the green pigment on plants called chlorophyll.
These pigments are attached to the proteins found
in the thykaloids of chloroplasts. After the light
energy is absorbed, it will then be utilized to remove
electrons in common donors like water, thereby
forming oxygen. Afterwards, the electrons will be
moved to quinine (Q), a primary electron receptor
similar to CoQ in the electron transfer chain.
ELECTRON TRANSFER
Electrons go through a chain of electron transfer molecules
in the thylakoid membrane, moving further from the primary
electron acceptor until it reaches the final electron
acceptor, which is usually NADP+. In the transfer process
of electrons, a proton gradient develops as a result of
protons being pumped out of the membrane.
GENERATION OF ATP
Through the F0F1 complex, protons move from the thykaloid
lumen to the stroma. This process generates ATP from ADP and
Pi, similar to the generation of ATP in the electron transport
chain.
CARBON FIXATION
The NADP and ATP generated in steps 2 and 3 serve as the
energy source for carbon fixation. In this step, electrons initiate
the reduction of carbon into six-carbon sugar molecules. As
these processes are independent from light, they are aptly
called dark reactions, as opposed t o the previous steps which
rely on light energy and are referr ed to as light reactions.
GROWTH
The entire process of photosynthesis ultimately results in the
production of sugar, the primary foo d source of the plant. This
product allows the plant to grow inby- terms of physical
including the expansistructure, on of its roots.
You might also like
- Proteins Guided LearningDocument17 pagesProteins Guided LearningMel MasculinoNo ratings yet
- BIOL 239 Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesBIOL 239 Lecture NoteskcqywNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab Report - DNA Extraction From Cheek CellsDocument2 pagesSample Lab Report - DNA Extraction From Cheek CellsJV Gamo100% (2)
- Photo Synthesis 101Document1 pagePhoto Synthesis 101JD CRUZNo ratings yet
- Photosyntesis: Carbon Dioxide Water Glucose OxygenDocument5 pagesPhotosyntesis: Carbon Dioxide Water Glucose OxygenEllebanna Fernandez CurbillaNo ratings yet
- Midterm NotesDocument2 pagesMidterm Noteshernys NietoNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesisjasmineNo ratings yet
- Lec. 19 PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesLec. 19 PhotosynthesisChinar BuddyNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - PhotsynthesisDocument5 pagesModule 6 - PhotsynthesisLawrence Picardal100% (1)
- Q2 Bio 1Document12 pagesQ2 Bio 1Nathalie SerafinNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument71 pagesPhotosynthesismarianne.gugulan07No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesisGustilo, Serj Andreas F.No ratings yet
- Notes On Light Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesNotes On Light Reaction of Photosynthesisxdobby260No ratings yet
- Prpm110 Lec: Photosynthesis Is The Process by Which Organisms That Contain TheDocument2 pagesPrpm110 Lec: Photosynthesis Is The Process by Which Organisms That Contain TheCASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Consists of Light-Dependent and Light-Independent ReactionsDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Consists of Light-Dependent and Light-Independent Reactionsaby251188No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisMarc Vincent CastilloNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS - Imran - Bs BotanyDocument26 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS - Imran - Bs Botanyhanza ahmadNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document32 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Allihannah PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 PPT 2 - Dark and Light ReactionDocument29 pagesQuarter 2 PPT 2 - Dark and Light ReactionKarl Patrick PachecoNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Chloroplast Structure and FunctionDocument3 pages10.1 Chloroplast Structure and FunctionTrish L.No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesisDarNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Handouts)Document5 pagesPhotosynthesis (Handouts)Jelea MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes-Part-3Document8 pagesBio Notes-Part-3kreigblitz9801No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Lecture NotesBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- 28 PhotosynthesisDocument20 pages28 PhotosynthesisAngelNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Oxidative Photophosphorylation and PhotophosphorylationDocument5 pagesDifference Between Oxidative Photophosphorylation and Photophosphorylationokaleboemmanuel53No ratings yet
- SSGBIO1 - CM Week 7Document61 pagesSSGBIO1 - CM Week 7christine ManuelNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Is The Process That Converts Solar Energy IntoDocument10 pagesPhotosynthesis Is The Process That Converts Solar Energy IntoizabelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document11 pagesChapter 13ririrachma fitriahNo ratings yet
- Flow of Energy and Matter in Ecosystems: Prepared By: Mr. Joselito Christian Paulus M. VillanuevaDocument9 pagesFlow of Energy and Matter in Ecosystems: Prepared By: Mr. Joselito Christian Paulus M. VillanuevaPaulus VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE9, Second Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesSCIENCE9, Second Quarter ReviewerkinzyItchNo ratings yet
- Section 2-1: PhotosynthesisDocument14 pagesSection 2-1: PhotosynthesisNupelda TomurcukNo ratings yet
- CSIR Unit 6@lifescience - BiotechDocument164 pagesCSIR Unit 6@lifescience - BiotechJigyasu bNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Photosynthetic Reaction CentreDocument7 pagesBacterial Photosynthetic Reaction CentreSuresh Babu TNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Notes Csir NetDocument163 pagesUnit 6 Notes Csir NetAlma VNo ratings yet
- Summary of Topic 5a Biology EdexcelDocument9 pagesSummary of Topic 5a Biology EdexcelNorth AbordoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 101 Module 5Document5 pagesGen Bio 101 Module 5Kyne GasesNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: I. Food Production II. Photosynthesis: BackgroundDocument54 pagesPhotosynthesis: I. Food Production II. Photosynthesis: BackgroundMo TeakdongNo ratings yet
- The Role of Pigments & The Reactions of Photosynthesis - Adrian VelascoDocument17 pagesThe Role of Pigments & The Reactions of Photosynthesis - Adrian VelascoatienzakarylleinandanNo ratings yet
- Learning Competency:: Marjoriechiong001@deped - Gov.phDocument9 pagesLearning Competency:: Marjoriechiong001@deped - Gov.phAnnejhel Mae PoralanNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 9 BIO 1130 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesTOPIC 9 BIO 1130 PhotosynthesisMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 2 8 PhotosynthesisDocument27 pages2 8 Photosynthesisıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- Energy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesEnergy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationlovepugsNo ratings yet
- Light ReactionDocument17 pagesLight Reactionmshtalam.edNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Notes Biology A Level PRDocument30 pagesToaz - Info Notes Biology A Level PRThoon Nadi NaiNo ratings yet
- Genbio Quatter 2Document5 pagesGenbio Quatter 2Shakira UyNo ratings yet
- AGR122 CHAPTER 4.3-PHOTOSYNTHESIS BaruDocument38 pagesAGR122 CHAPTER 4.3-PHOTOSYNTHESIS BaruAisyah NabilaNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Photosynthesiswkwhui100% (6)
- Relate Chloroplast Structure To Its Function:: Photosynthesis Summary NotesDocument7 pagesRelate Chloroplast Structure To Its Function:: Photosynthesis Summary NotesJonathan Wee Cheng YangNo ratings yet
- Light DependentDocument46 pagesLight DependentMadame Ursula100% (1)
- Describe The Factors of Electron Flow Through LightDocument12 pagesDescribe The Factors of Electron Flow Through LightSha ShaNo ratings yet
- Lecture II - Atp Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 2Document18 pagesLecture II - Atp Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 2Andre NesbethNo ratings yet
- BIO 068 Photosynthesis 2Document22 pagesBIO 068 Photosynthesis 2William CarreraNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis ReviewerLJ RacadioNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis COMPLETEDocument44 pagesPhotosynthesis COMPLETEsantoshnairsNo ratings yet
- Bio HWDocument9 pagesBio HWedgar batotoNo ratings yet
- Light Reaction ReflectionDocument2 pagesLight Reaction ReflectionMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- BIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesBIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisCath Detoperez100% (1)
- Photosynthesis StudentDocument42 pagesPhotosynthesis StudentszyzypNo ratings yet
- Apolonio, Carangian, Sanchez & Tiglao Bio 150 Lec 2: SLIDE 00: Photosynthesis Slide 2Document9 pagesApolonio, Carangian, Sanchez & Tiglao Bio 150 Lec 2: SLIDE 00: Photosynthesis Slide 2Shirley ApolonioNo ratings yet
- General Biology I Activity SheetDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology I Activity SheetAldous Pax ArcangelNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Summary By: Abdul Majid HasaniDocument12 pagesPhotosynthesis Summary By: Abdul Majid HasaniSani Stickman AxcNo ratings yet
- Sbi 4U1 Exam Evaluation Outline: Section Marks Time (Min) Student Score Knowledge Thinking/InvestigationDocument2 pagesSbi 4U1 Exam Evaluation Outline: Section Marks Time (Min) Student Score Knowledge Thinking/InvestigationEmanNo ratings yet
- GMO-friend or FoeDocument4 pagesGMO-friend or FoerahulNo ratings yet
- Easypep-A New Simplified and Optimized Workflow For Ms Sample PreparationDocument1 pageEasypep-A New Simplified and Optimized Workflow For Ms Sample PreparationkarthikNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument34 pagesCell MembranesayfilonNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics How The Body Converts Food To EnergyDocument38 pagesBioenergetics How The Body Converts Food To EnergyShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Chapter 6Document32 pagesCell Bio Chapter 6GuteNo ratings yet
- Gen TBCDocument27 pagesGen TBCHarry Wardhana HamdiNo ratings yet
- TIME TABLE Final 20-21Document23 pagesTIME TABLE Final 20-21Giggly TicklesNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Engineering of Pichia PastorisDocument14 pagesMetabolic Engineering of Pichia PastorisLore CarreñoNo ratings yet
- Ab65475 Quick Cell Proliferation Assay Kit II Protocol v2 (Website)Document12 pagesAb65475 Quick Cell Proliferation Assay Kit II Protocol v2 (Website)Venkatesh GaviniNo ratings yet
- MIBO Virus ExamDocument5 pagesMIBO Virus ExamAnonymous zHoYgoxraNo ratings yet
- Complete Cell DivisionDocument96 pagesComplete Cell DivisionAbegail Reyes100% (1)
- Vaccine HistoryDocument35 pagesVaccine HistoryEhed AymazNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Pharmacology: Gayathri Krishna, Vinod Soman Pillai, Mohanan Valiya VeettilDocument11 pagesEuropean Journal of Pharmacology: Gayathri Krishna, Vinod Soman Pillai, Mohanan Valiya VeettilautomationenggNo ratings yet
- GAT-B 2022 List of Qualified CandidatesDocument86 pagesGAT-B 2022 List of Qualified CandidatesKamesh RishiNo ratings yet
- Human Genetic Variation: DR - Shaukat IqbalDocument35 pagesHuman Genetic Variation: DR - Shaukat IqbalMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To mRNA Production and TFF.Document20 pagesIntroduction To mRNA Production and TFF.Ahmed RaslanNo ratings yet
- 2008 Book RetrotranspositionDiversityAndDocument131 pages2008 Book RetrotranspositionDiversityAndJosimar JúniorNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell CultureDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell CulturetharsinibalayogeshNo ratings yet
- Biology Passing Material KAYAKA PU COLLEGE KALABURAGIDocument23 pagesBiology Passing Material KAYAKA PU COLLEGE KALABURAGIRAJAGOPAL93% (15)
- IQ4I Research & Consultancy Published A New Report On "Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Global Market - Forecast To 2027"Document7 pagesIQ4I Research & Consultancy Published A New Report On "Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Global Market - Forecast To 2027"VinayNo ratings yet
- Caractere VirologiaueDocument29 pagesCaractere Virologiauehind el hamriNo ratings yet
- E 316Document128 pagesE 316KaoneNo ratings yet
- NEB IlluminaDocument13 pagesNEB IlluminaLei Zi DuNo ratings yet
- BT - 601Document4 pagesBT - 601PrincePiyushNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules WorksheetDocument2 pagesMacromolecules Worksheetddhhdhdhd100% (1)
- Biology 12 Principles of Life Hillis 184 CH 11 Regulation of Gene Expression 9093Document8 pagesBiology 12 Principles of Life Hillis 184 CH 11 Regulation of Gene Expression 9093Kevin ApodacaNo ratings yet