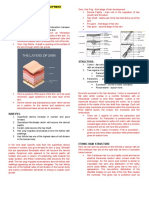
Hair structure
• elongated part, which grows from the dermis and
hair shaft protrudes above the surface of the skin
• elongated tubular structure in the skin, which is lined
hair follicle with cells
• Hair grows from a hair follicle
• One or more sebaceous glands open into the hair
sebaceous glands follicle
• sebaceous glands secrete sebum
• A fatty substance that is produced by the sebaceous
glands and passes via a short duct from the gland into
sebum the hair follicle
• depending on the amount of sebum secreted the hair
type is determined (oily - normal - dry )
arrector pilli • attached to the hair follicle; when this muscle contracts,
it causes the hair to stand up
muscle • شعر رأسه بيوقف
• the bottom of the follicle is wider and thicker.
papilla = dermal • The region below the lower end of the
or follicular • follicle is called the papilla. It is also called the dermal
or follicular papilla;
papilla • it contains blood vessels that nourish the hair follicle.
• At the bottom of the hair follicle are the unique cells
that produce the hair, itself.
hair replicating • These cells have enormous replicating abilities.
2|P age cells • They divide, and more and more cells appear, the older
ones are "pushed" upward in vertical rows and
gradually degenerate www.millenniumegypt.com
� أي منتجات بيقولوا أنها بتزود
تغذية و نمو الشعر دي بتكون
للدعاية فقط لكن نمو الشعر و
تغذيته في الواقع بيعتمد علي
1- Adequate blood supply
to the hair follicles
2- Persons good nutrition
Structure of the hair (longitudinal section).
Since the hair replicating cells degenerate and die as they move up the follicle, the
upper part of the hair is made up of dead cells, ,which remain attached to each other by
an intercellular cement-like susbstance.
In other words, the hair that protrudes above the skin (****hair shaft ) is actually dead
keratinous material.
The only living parts of the hair are the cells at the bottom of the hair at the base of the
hair follicle( ****hair replicating cells ), which constantly divide and determine the hair
quality.
as long as the cells at the bottom of the hair follicle (which form the base of the hair)
are healthy and normal, the hair can continue growing. If, for any reason, those cells
are destroyed, there will no longer be any hair growing from that follicle.
hair Color
the sameway that the melanocytes (melanin-producing cells) in the skin give it its color, the
melanocytes in the hair follicle give the hair its specific color.
Different types of melanin, which differ from one person to another according to each one's genetic
characteristics, determine the hair's final color.
Different concentrations and different chemical compositions of melanin produce blond, brown, or
black hair.
3|P age
www.millenniumegypt.com
� transverse section of the hair shaft
The hair shaft is made up of three layers: cortex medulla
1-the medulla, 2- the cortex, and 3- the Medulla
cuticle
Medulla • This is a thin layer in the center of the hair shaft
Cortex • This is the largest layer of the hair shaft; it is made up of hair
cells that are constantly moving upward, and as they do so,
they degenerate and die.
• This lies outside the cortex, and is a sort of thin outer
wrapping.
• made up of cells that partially overlap (see the
illustration).
• The cuticle is impermeable and protect the hair from the
penetration of foreign materials.
• If the cuticular layer is intact, and the cells overlap each
Cuticle other in an orderly fashion (as they are meant to), the hair
looks soft and shiny, since light rays are reflected from it
evenly.
• On the other hand, if the cuticle is damaged (for example,
by incorrect treatment of hair, such as by excessive
brushing, waving, straightening, or dyeing), the cuticular
layer loses its uniformity, the hair loses its sheen, and the
ends of the hair become frayed and split .
هيه المسئولة عن تحديد شكل الشعر هل هو صحي و المع و ناعمcuticle •
و ال هايش و متقصف األطراف
Life cycle of the hair
Every hair follicle has a regular life cycle of growth, rest, and falling out.
The cycle of any single hair is not dependent on the others—there is no, synchronization. Therefore,
it is normal and natural for up to 100 scalp hairs to be shed daily and approximately 100 other hairs will
appear in their place.
و دا رحمة من ربنا إن مش كل الشعر في مرحلة نمو واحدة و ال كله بيقع مرة واحدة
4|P age
www.millenniumegypt.com
� Stages in the life cycle of the hair
the resumption
the the
active of nthe
anagen catagen transition telogen resting active
growing
phase phase growth
phase
1- Anagen:the active growing phase
In the anagen phase the hair cells at the base of the hair follicle are divided repeatedly ,
and hair grow steadily. The length of this phase determine the maximum length that the
hair will reach , it varies from person to person.) (مرحلة نمو الشعر
2- Catagen: the transition phase
This relatively brief phase , lasting (2to4weeks) , it is a transition phase during which the
hair is stops growing.) ( مرحلة انتقالية ما قبل توقف نمو الشعر
3- Telogen: The Resting Phase
During this period, the mechanism responsible for the replication of the cells at the base of
the hair, and the subsequent hair growth, are inactive for several months. By the end of
telogen, the hair is only loosely attached to the follicle, and can be easily pulled out
simply by brushing or washing the hair, It is hairs in this phase that come away readily
from the scalp when pulled.( )مرحلة توقف نمو الشعر
4- Resumption of active growth
after the resting phase, a new hair appears from the same follicle during the next
anagen (growth) phase. As this new hair grows, it pushes the old one, vhich is shed
from the follicle. ) (مرحلة اعادة نمو الشعر بحيث كل شعرة وقعت ينمو مكانها شعرة جديدة
normally, at any given time, approximately 80% to 90% of the hairs on the head is in anagen phase
(growth ). And 10% to 15% are in a telogen phase ( resting ). Less than 1% in catagen phase .
5|P age
www.millenniumegypt.com
� Hair growth rate
Scalp hair grows at a rate of up to 0.4 mm a day. Its average length is 70 cm, but it can grow up
to 100 cm. Body hair grows at a slower rate than scalp hair, at 0.2 mm/day, these hairs
ultimately reach a length of 1 to 3 cm.
Cutting the hair has no effect on the hair growth rate .
If the hair replicating cells are healthy it is expected the hair will have agood growth rate.
Hair Care Products
Hair care
products
anti -dandruff
shampoo conditioner
preparations
1) Shampoo:
Washing hair
The scalp and hair are normally lubricated by sebum, which is secreted from the sebaceous glands.
This oily secretion protects the hair and skin against water loss and gives the hair its sheen.
On the other hand, there is some disadvantage to the oily layer on the scalp dust, soot, and other
Environmental pollutants tend to stick to it, as do particles of keratin from the skin.
The same principle that applies to cleansing the skin also applies to shampooing hair; in order to
remove the dust, soot, and other grime, as well as the cells of the keratin layer that have peeled off,
the oily layer on the scalp and hair must be removed, since these particles are embedded in it.
In addition, the same principle that applies to the action of soaps and surfactants for cleansing
the skin also applies to shampoos for cleaning the scalp and hair.
by rinsing with water. The surfactants, the active ingredients in shampoos, surround and trap
tiny droplets of fat (that contain the grime), and these are removed from the scalp and hair
Shampoos are designed to replace ordinary soap. The basic compounds within shampoos are
surfactants. Different surfactants have different properties, and vary in their abilities to clean,
create lather, and impart luster or softness to hair.
*****Shampoos usually do not contain just one surfactant, but a combination of several,
designed for use on different types of hair.
For example, some surfactants have good cleaning properties. However, other surfactants, are good
at creating foam.
6|P age
www.millenniumegypt.com
� A shampoo should be adapted to the individual in terms of the following aspects:
1. Hair type:
Is the hair dry or oily?
Has the hair been bleached, dyed, or permed?
2. Specific scalp problems:
Does the user have dandruff?
3. Safety requirements:
Does the preparation irritate the eyes or scalp? (for babies and persons with sensitive scalp)
4. Personal preferences of the user:
The shampoo's consistency and texture (a shampoo may be in the form of a liquid or a cream).
the presence of a particular fragrance,
the ease and convenience of application of the shampoo,
the ease with which it spreads through the hair,
the amount of foam it produces and its quality and texture,
how easy is it to rinse off,
the degree to which it makes the hair soft, supple, and shiny, and how easy is it to comb and
manage the hair after using the shampoo
Very important notes:
The main component of shampoo is the surfactant
Shampoo should be tailored to the particular type of hair (normal, oily ,dry )
Shampoo should contain a mixture of surfactant each has a different specific function ( for cleansing,
foaming, ..)
The type of hair is determined according to the amount if sebum secreted from the sebaceous glands
There are three types of hair:
1- Oily hair
Contain high amount of sebum
Need to be washed (2-3times per week )
requires a shampoo that is more effective in removing oil
2- Normal hair
Contain normal amount of sebum
Need to be washed (2times per week )
3- Dry hair
Contain low amount of sebum
Need to be washed (once per week )
requires a shampoo with a less vigorous, gentler cleaning effect, and an added moisturizer
what are the advantages of shampoo over the ordinary soup ??
1- ordinary has a high pH which may damage the skin and hair while the shampoo don’t
have high pH.
2- ordinary soap ( Na salt of fatty acid ) with tape water ( Mg and Ca ions ) lead to ion exchang
and formation of (Mg and Ca salts of fatty acids ) which are insoluble and form a layer on the
7|P age
www.millenniumegypt.com
� Components of shampoo :
A mixture of several surfactants (main component )
•Different surfactants have different properties, and vary in their abilities to clean, create lather,
and impart luster or softness to hair.
Moisturizers (for dry hair )
•In many cases, moisturizing agents have to be added to the shampoo because cleansing with a
surfactant results in the removal of the natural oil. Without oil, the hair becomes dull and loses
its softness, which makes it hard to comb and manage. The hair becomes more fragile and tends
to split at the ends
Conditioners (shampoo + balsam )
•The purpose of conditioners is to make the hair soft, shiny, and easier to comb and manage.
•In general, many dermatologists advise using a conditioner after washing the hair with
shampoo, rather than using a shampoo that contains a conditioner. This is because two different
functions are involved here: cleansing and conditioning. A shampoo that contains conditioner
has to fulfill several functions, the chief being cleansing the hair. Such a shampoo cannot
achieve the efficiency of a pure conditioner used independently after washing and cleaning the
hair. Furtheimore, remnants of shampoo that remain on the hair after using a conditioner-
containing shampoo must obviously contain cleansing agents, and should be avoided.
عليه و بالتالي يستحسنconditioner • الشامبو بيعد فترة صغيرة اوي على الشعر فالشعر مش بيلحق يستفيد من وضع ال
. أفصل بينهم أستخدم الشامبو األول و بعدين ال البلسم لوحدة يتحط تقريبا عشر دقايق على الشعر
Foaming Agents
•Foaming agents act by producing bubbles in the water, creating lather. In fact, there is no need
for an extensive lather to clean effectively: the effectiveness of a shampoo is mainly determined
by how the hair looks and how the user feels after washing the hair, and not by how much
lather it produces.لو الشامبو مافيهوش رغوة الشخص بيعتقد أنه بايز و بيفقد ثقته في المنتج
Water Softeners (Chelating or Sequestering Agents) as (EDTA)
•Water softeners bind ("chelate') calcium and magnesium ions present in water, and thereby
prevent their attachment to fatty acids, which would create salts that are not easily soluble.
Without the addition of water softeners, the hair, This coating stays on the hair as a thin layer and
makes the hair lose its luster.
•EDTA remove ions that present in the tap water
Thickeners:
•These make the shampoo thicker. Thickeners have nothing to do with the cleansing properties of
the shampoo. However, they make the shampoo look more attractive. Apart from that, people
tend to think that the thicker a shampoo, the more effective it is, and the richer in active
ingredients. The consistency of a shampoo is not necessarily related to its effectiveness.
Nevertheless, there is some advantage to a shampoo that is thicker in consistency, in that a
thicker shampoo is less likely to dribble down and get into the user's eyes
Dyes and Fragrances:
• The reason for using dyes or fragrances is to make the product look and smell good
Preservatives
Special Ingredients in Shampoo
•Special substances in shampoo may include various vitamins (e.g., vitamins B and E), plant
extracts, egg, honey, jojoba, aloe vera, and others. The use of these ingredients may have
significant effects on sales
•Applying such substances to the external hair can affect its appearance (but not its growth!).
The hair will look shinier and "silkier," and will be easier to comb and manage
8 | P a g e • المكونات دي بتكون موجودة في بعض أنواع الشامبو لكن جميع المكونات السابقة تقريبا بتكون موجودة في معظم أنواع
الشامبو
www.millenniumegypt.com
�Gentle shampoos
Gentle shampoos are shampoos for people with delicate skin or, more particularly, for babies.
They also are designed not to cause stinging of the eyes, which results from certain ingredients in
shampoos getting into the eyes.
The special nature of these preparations is based on the following:
They are not supposed to contain ingredients that may cause irritation, particularly
perfumes and certain preservatives.
Many contain a relatively higher concentration of amphoteric surfactants These
surfactants are relatively gentle, and do not tend to cause skin or eye irritation
2- Hair Conditioners
The cuticle is the outer layer of the hair shaft. Its integrity and health determine the appearance of
scalp hair. The properties of hair, such as its softness, luster, and pliability, are detellnined mainly by
what happens on its surface. Hair conditioners treat the external surface of the hair.
A normal, healthy cuticle looks like the arrangement of roof tiles.
If the cuticle be damaged, the surface of the hair shaft becomes irregular and disorganized, and
the hair becomes rougher and coarser. The hair becomes more brittle, and the ends tend to fray
and split
cuticle damage الشعر بيكون هايش و متقصف األطراف لما بيحصل.
Hair can be damaged by:
1- washing the hair too frequently ( as we remove sebum natural protective layer that soften
the hair )
2- too frequent combing and brushing
3- overuse of a hair dryer, perming, dyeing with permanent dyes, bleaching and
4- exposure to certain environmental conditions, such as the sun's radiation, wind, and
swimming pool water.
Hair damage result in :
1- All of the above activities damage the cuticle of the hair shaft. As a result, the hair becomes
rough, loses its luster, becomes stiff and fragile, and is harder to comb and arrange.
2- If the external surface of the hair is damaged, the hair shaft develops negative electrostatic
charges along its length. As a result of the electrical charge, the hairs repel each other, which
make it very difficult to comb or manage the hair. (so the conditioner should contain a
positively charged ion )
9|P age
www.millenniumegypt.com
� Principles behind the action of a hair conditioner:
The principles behind the actions of all types of hair conditioner are identical. The main functions of a
hair conditioner are:
1- To create a coating that covers the outer, rough layer of the hair this coating gives the
hair its smooth, uniform look.
2- To neutralize the electric charges on the surface of the hair. By doing this, the hair does
not look so unruly, and becomes much easier to comb and style; it also makes the hair
look thicker and less wispy, and prevents knots.
The active ingredients in conditioners affect only the surface of the hair. They do not
penetrate the interior of the hair (not affect the hair growth ), and certainly do not affect the
hair follicle. Their effect is only temporary and is lost within a few days.
Types of hair conditioners:
1- cationic surfactants
• In general, the surface of the damaged hair carries negative electric charges. Since cationic
surfactants carry a positive electric charge, they are attracted to these negative charges
and become attached to the surface of the hair. Thus, the outer surface of the hair acquires
a uniform coating. At the same time, the electric charges are neutralized.
• Since cationic surfactants contain long fatty chains, they produce a fatty layer on the
surface of the hair that gives it a soft, smooth feeling, and a shiny appearance. Cationic
surfactants are useful for hair that has been damaged as a result of dyeing, bleaching, or
perming. The more the outer surface of the hair is damaged, the more negative electric
charges its surface carries and the stronger the bond with the conditioner.
• The cationic surfactant is therefore attached most strongly to those areas of hair that are
the most severely damaged, so the end result is that the surface of the hair develops a
smooth, uniform look.
2- Cationic polymers
• The cationic polymers that are used in hair conditioners contain substances such as:
silicones, polyamides, polyamines, and substances based on cellulose.
• They become attached to the surface of the hair as long units of polymer chains.
• Cationic polymers fill in the defects in the hair shaft, thus allowing light to be reflected
more completely from the hair, since the hair surface is now smooth.
• These products are also cations (i.e., they carry a positive electric charge), so they also
reduce the negative static electric charge on the surface of the hair.
3- Protein conditioners
• The protein in these conditioners is extracted from animal tissues (proteins such as keratin,
collagen, casein, and others) or from other sources, such as certain plant proteins. In their
raw form, these proteins are made up of large molecules. In preparing conditioners for the
hair, the proteins are chemically broken down into smaller components. In that fowl
(peptides or amino acids), they can attach themselves to the hair and fill in the cracks and
gaps. This strengthens the hair shaft and repairs the split ends. It must he remembered that
the hair shaft is not living tissue, so that it cannot bind the protein conditioners permanently.
When the hair is washed, these substances are washed out of the hair shaft.
10 | P a g e
www.millenniumegypt.com
� Frequency of use of a hair conditioner :
The frequency with which a hair conditioner is used varies in accordance with the
user's personal preference.
People with healthy hair do not necessarily need a conditioner.
If the hair has been damaged as a result of bleaching, perming, or exposure to dry
weather, then a conditioner is helpful.
If the hair tends to be unruly, difficult to manage and dull, then a conditioner
should be used.
Dis adv. Of conditioner : conditioners should not be used too much, since an
excessive amount settles on the hair, the hair tends to lose its shine.
residue of كذا مرة بتتكون طبقات منconditioner المشكلة هيه اني لما أستخدم كمية كبيرة من ال
على سطح الشعر و بتفقده لمعانه الطبيعيconditioner
إن شاء هللا هتالقوا
فيhair بقية
المحاضرة العاشرة
الجزء األول
11 | P a g e
www.millenniumegypt.com