Professional Documents
Culture Documents
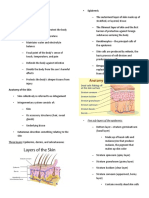
The Integumentary System: (Anatomy of The Skin, Hair, and Nails)
Uploaded by
Venus Amoroso Baguioso0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views3 pagesOriginal Title
integumentary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views3 pagesThe Integumentary System: (Anatomy of The Skin, Hair, and Nails)
Uploaded by
Venus Amoroso BaguiosoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
The Integumentary System The only stratum of the epidermis with
cells that actively grow and divide to
(ANATOMY OF THE SKIN, HAIR, AND NAILS) produce new epidermis.
It dips into the dermis of the skin to
A. SKIN form the hair follicle
Stratum spinosum and the stratum
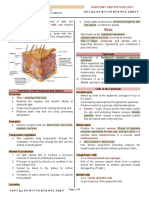
Body’s largest organ
granulosum – are superficial to the
15 % of the body’s totals weight
stratum basale.
It consists of two layers:
o Epidermis
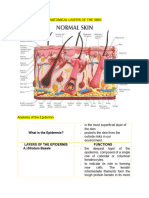
2. Stratum lucidum
o Dermis Found only in thick skin
2 LAYERS
3. Stratum corneum
1. Epidermis Most superficial stratum
Skin most superficial layer It may have as many as 20 layers of
cells.
Composed of stratified squamous epithelial
tissue Composed of tough, waterproof dead
cells that eventually flake off
2. Dermis (exfoliate).
The human body sheds thousands of the
Deep to the epidermis
dead stratum corneum cells every day.
Composed of loose/areolar connective
tissue over dense irregular connective tissue.
Cutaneous glands, the hair follicles, and
Cells of the Epidermis
most of the skin’s nerve endings can be
found in the dermis. 1. Keratinocytes
— Begin in the stratum basale and make up
Hypodermis or subcutaneous layer
the majority of the epidermal cells
Deep to the dermis — Purpose: to grow and divide
This layer attaches the skin to the rest of the — As they dicide, they push the older cells
body toward the surface.
Composed of adipose connective tissue — It produce and fill themselves with
Serve as insulating layer, a cushioning layer, keratin (a hard waterproof protein) as
and an energy source. they move toward the surface
This layer is generally thicker in women — Cornification - the keratinocytes have
than in men. completey filled with keratin and died as
the time they reach the stratum cornuem
— These cells form a very durable stratum
EPIDERMIS corneum at the surface
Superficial layer of the skin
Subdivided into four or five general layers called 2. Melanocytes
strata — Produce skin pigments called melanin
— These cells stay in the stratum basale, but
they have projections to more superficial
layers.
The Four Strata — Melanosomes – melanocyte extensions
that contain melanin-filled vesicle
1. Stratum basale — Denser patches of these cells account
Contains a single layer of cuboidal cells for freckles and moles
3. Tactile Cells
—Serve as receptors for fine touch only o are associated with a hair follicle
—They are associated with nerve cells in surrounding the hair root
the underlying dermis o Sebum – a very oily, lipid-rich
4. Dendritic Cells substance, is produced by the
— Immune system cells found in the sebaceous gland to moisturize the
stratum spinosum and the stratum skin
granulosum o Hormone estrogen and
— Alert the body’s immune system to the testosterone increase the amount
invasion of pathogens that could make it of sebum produced
through the stratum corneum o Comedo – white head or black
head
DERMIS
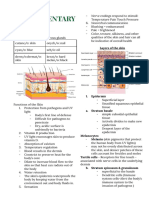
2. Sweat glands
“true skin” o *nasa book*
Blood vessels, fibers, nerve endings, hair 5. Hair follicles
follicles and cutaneous glands are found in the — the stratum basale dips down to form hair
dermis follicles in the thin skin’s dermis
1. Papillae — positioned at an angle in the dermis with a
— Superficial edge of the dermis has dermal papilla at its base.
bumps called papillae — the dermal papilla has a blood vessel,
— Direct contact with the epidermis which feeds the keratinocytes and
— Arranged in random pattern over most melanocytes contained in the hair follicles
of the body — Keratinocytes – produce the hair
— Form individual-specific patterns of — Melanocytes – produce the hair pigment
ridges on the palmar and plantar — Active keratinocytes form the hair matrix
surfaces just above the dermal papilla.
— this unique arrangement creates — Dermal Papilla – hair’s growth center
fingerprints — arrector pili muscle – this smooth muscle
2. Fibers attaches the hair follicle’s base to the
— Fibroblast – produce two types of epidermis at an angle.
protein fibers: collagen and elastin
HAIR
Collagen – give the skin strength
Elastin – provide elasticity Three types of Hair:
— The number of fibers increases with
1. Lanugo
depth in the dermis.
very fine and unpigmented
3. Nerve Endings
forms on a fetus during the last 3 months
— serve as receptors
of its development
— these receptors include
usually replace by birth
warm receptors
2. Vellus
cold receptors
unpigmented and very fine
pain receptors
replaces lanugo hair around the time of
pressure receptor birth
4. Cutaneous Glands
ex. body hair on most women and
— are considered exocrine glands
children
— are located throughout the dermis 3. Terminal
— produce and secrete products that are thick, coarse, and heavily pigmented
delivered to the appropriate location forms the eyebrows, eyelashes, and hair
through ducts. on the scalp
— 2 types: Sebaceous glands and sweat
At puberty, forms in the axillary and
glands pubic regions
1. Sebaceous glands
forms on face and possibly on the trunk Skin-covered nail root
and limbs of men visible nail plate
o make up from the edge of the nail and
Three sections of all types of human hair
the nail body
Bulb – thickening of the hair at the end of hair Nail body – lies over the nail bed
follicle Nail bed – appears pink because of the dermis
Root – extends from the bulb to the skin’s numerous blood
surface The skin rises to form a nail fold over the nail’s
Shaft – section of the hair extending out form lateral edge
the skin’s surface Nail fits into a nail groove
Eponychium or cuticle – at the proximal edge
Cross section of a hair shows three layers:
of the nail body, is composed of stratum
Inner medulla – composed of soft keratin corneum cells extending onto the nail bed.
Middle cortex – composed of hard keratin Nail matrix (nails growth center) – root of the
outer cuticle – appear as interlocking scaly nail is composed of active keratinocytes in the
plates of dead keratinocytes stratum basale
Lunule or lunule
* The direction of cuticle plates resists the follicle’s o white crescent
cells, so the hair cannot be easily pulled from the o may be visible under the nail especially
follicle.
on the thumbs
*The hair texture depends on the shaft’s cross-sectional o where the nail matrix is thick enough to
shape. hide the blood vessels of the dermis
deep to it
Straight hair – round shaft
Wavy hair – oval shaft
Curly hair – flatter shaft
* Rate of growth within the follicle matter too
Straight hair grows evenly within the follicle
wavy and curly hair may grow alternately faster
on one side of the follicle
*Hair color depends on the amount and type of melanin
produced by the hair follicle’s melanocytes
Gray to white hair – lack of melanin in the hair’s
cortex and from the possible presence of air in
the medulla
Black – eumelanin
Blond – Pheomelanin
*Hair has a life cycle
Growing stage – half inch per month and last for
approximately 3 years
Resting stage – 1 to 2 year and then it falls out
Dying stage
NAILS
Structure of the nail
You might also like
- Human Body Workbook Jan 15 2018Document178 pagesHuman Body Workbook Jan 15 2018Crina Elena Andries89% (9)
- 5 - IntegDocument8 pages5 - IntegGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Functions and StructureDocument12 pagesIntegumentary System Functions and StructureLly Isidoro100% (2)
- Kettlebell Swing and Lumbar LoadsDocument12 pagesKettlebell Swing and Lumbar Loadsrearickstrength_comNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells in The EpidermisDocument13 pagesTypes of Cells in The EpidermisSairelle Sordilla Obang83% (6)
- Clinical PelvimetryDocument24 pagesClinical PelvimetryVictor-Gabriel Rugina100% (1)
- BOOTY BY BRET MONTH 19 - January/February 2020: Week 1: Day 1 Set 1 Set 2 Set 3Document8 pagesBOOTY BY BRET MONTH 19 - January/February 2020: Week 1: Day 1 Set 1 Set 2 Set 3Diana CiupeiNo ratings yet
- Forward Head Posture Correction Versus Shoulder Stabilization Exercises Effect On Scapular Dyskinesia and Shoulder Proprioception in Athletes An Experimental StudyDocument7 pagesForward Head Posture Correction Versus Shoulder Stabilization Exercises Effect On Scapular Dyskinesia and Shoulder Proprioception in Athletes An Experimental StudyInternational Journal of PhysiotherapyNo ratings yet
- A. I. Ii. Iii.: Protection. Serving As The Covering of The Body, ItDocument9 pagesA. I. Ii. Iii.: Protection. Serving As The Covering of The Body, ItFrancis100% (1)
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument7 pagesSkin and Its AppendagesSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab QuizDocument12 pagesAnaphy Lab QuizScout Beauty JHOINo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture (Reviewer)Document4 pagesZoology Lecture (Reviewer)Maria GrasyaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan - Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan - Skeletal SystemMaria Danica89% (36)
- Auriculotherapy For Respiratory DisordersDocument3 pagesAuriculotherapy For Respiratory DisordersCarissa Nichols100% (3)
- Anaphy - IntegumentaryDocument4 pagesAnaphy - IntegumentaryYo1No ratings yet
- Chap3 Integ Anaphy NotesDocument11 pagesChap3 Integ Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- Integumentary & Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary & Skeletal SystemMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Layers of The SkinDocument5 pagesAnatomical Layers of The SkinRyzelle Louise SorianoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 & 6Document18 pagesTopic 5 & 6PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Integument System ActivityDocument5 pagesIntegument System ActivityeywatsarawatNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Epidermis Dermis: Stratum Corneum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Granulosum Papillary LayerDocument4 pagesIntegumentary System Epidermis Dermis: Stratum Corneum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Granulosum Papillary LayerNu Ri LeeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Functions and AnatomyDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System Functions and AnatomyAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemOddysa EstorqueNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab IntegDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lab IntegPhoemela Reign GregorioNo ratings yet
- BIO101 Student Notes PRELIM Integumentary System1Document4 pagesBIO101 Student Notes PRELIM Integumentary System1Kirstine Valerie MandalonesNo ratings yet
- Cells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDocument5 pagesCells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDimple Lexiry GloriaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary SystemwannabeeurzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- Skin and Its Appendages: Lectured By: Dr. Ed Gonzales Transcribed By: Gio PinedaDocument8 pagesSkin and Its Appendages: Lectured By: Dr. Ed Gonzales Transcribed By: Gio PinedaFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Skinbody MemranesDocument3 pagesModule 3 Skinbody MemranesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- IntegumentaryDocument5 pagesIntegumentaryNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PDF 2Document8 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PDF 2thyezlianNo ratings yet
- 5 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pages5 Integumentary SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Analysis of The Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesMicroscopic Analysis of The Integumentary SystemAgatha joy MadrazoNo ratings yet
- Midterm AnaphyDocument19 pagesMidterm AnaphywannabeeurzNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesIntegumentary SystemCelyn DeañoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemAliyah ZalzosNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 (Integumentary) - AnaphyDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 4 (Integumentary) - AnaphylalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 IntegumentaryDocument2 pagesChapter 5 IntegumentaryElle UgaddanNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of the Skin ExplainedDocument9 pagesStructure and Function of the Skin Explainednh2411No ratings yet
- Anaphy MidtermsDocument28 pagesAnaphy MidtermsxeanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3-4Document13 pagesAnatomy 3-4Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntegumentary SystemALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- What Is The Integumentary System?Document6 pagesWhat Is The Integumentary System?Jerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM OVERVIEWDocument5 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM OVERVIEWFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Reviewer PDF Skin Nail (Anatomy) 2Document1 pageIntegumentary System Reviewer PDF Skin Nail (Anatomy) 2Shiem TrabocNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyFaithNo ratings yet
- MOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Document41 pagesMOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Suez AyomNo ratings yet
- Topical Corticosteroids BinderDocument108 pagesTopical Corticosteroids BinderElena DragomirNo ratings yet
- Rift IntDocument32 pagesRift IntAnonymous bkn6BruPNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Functions of Human SkinDocument7 pagesThe Anatomy and Functions of Human SkinPau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System TransesDocument5 pagesIntegumentary System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary SystemCriscia Lene OlatNo ratings yet
- Intergumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntergumentary SystemAkihiro FurukawaNo ratings yet
- Happ Chapter 5 TransesDocument7 pagesHapp Chapter 5 TransesFrencess Kaye SimonNo ratings yet
- Skin, Hair, and NailsDocument9 pagesSkin, Hair, and NailsJustine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Mia Rev4Document4 pagesAnaphy Mia Rev4antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Integumentary System IncludesDocument29 pagesIntegumentary System IncludesRhena TogoresNo ratings yet
- Body MembranesDocument10 pagesBody MembranesCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- The SkinDocument2 pagesThe SkinIsabela Jelian AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesIntegumentary SystemChan TalNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body Membranes HahaDocument6 pagesSkin and Body Membranes Hahaقى قىNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Integumentary DigestiveDocument11 pagesReviewer Integumentary DigestiveMariah Alexa LibaoNo ratings yet
- Autosomal Dominant Inheritance HH HH: Huntington'S DiseaseDocument2 pagesAutosomal Dominant Inheritance HH HH: Huntington'S DiseaseVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytesVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- Draft Synovial FLuidDocument11 pagesDraft Synovial FLuidVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- After The Execution of DRDocument2 pagesAfter The Execution of DRVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- After The Execution of DRDocument2 pagesAfter The Execution of DRVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- DUR - Fracture of The Shaft Radius and UlnaDocument55 pagesDUR - Fracture of The Shaft Radius and UlnaM. Abdurrahman Al-HaraaniNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 - CONTROL OF BODY MOVEMENT (Akdemics)Document6 pagesCHAPTER 10 - CONTROL OF BODY MOVEMENT (Akdemics)Ivy CustodioNo ratings yet
- OSCE Neurologic TestDocument4 pagesOSCE Neurologic TestChristopher WuNo ratings yet
- Bnorton Soap NotesDocument2 pagesBnorton Soap Notesapi-285530156No ratings yet
- Male and Female Anatomy GuideDocument11 pagesMale and Female Anatomy GuideQwer TyNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing ConceptsDocument139 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing ConceptsGodfrey FrancoNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument7 pagesHealth AssessmentKaye Sheena B. MoncanoNo ratings yet
- I - Oral and Maxillofacial ExaminationDocument52 pagesI - Oral and Maxillofacial ExaminationLarisa Caliman OncuNo ratings yet
- Nexgen Complete Knee Solution Epicondylar Instrumentation Surgical Technique For Legacy Posterior Stabalized Knees Surgical TechniqueDocument32 pagesNexgen Complete Knee Solution Epicondylar Instrumentation Surgical Technique For Legacy Posterior Stabalized Knees Surgical TechniqueTudor MadalinaNo ratings yet
- Qééçxé Kééiéñ: DR - Ganesh NaikDocument9 pagesQééçxé Kééiéñ: DR - Ganesh NaikkgnaikNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System BrochureDocument2 pagesEndocrine System BrochureAldrin CortezNo ratings yet
- ICD 9 ProcedureDocument102 pagesICD 9 ProcedureChandra FerdianNo ratings yet
- Integrated Control of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesIntegrated Control of The Cardiovascular SystemPatricia SanchezNo ratings yet
- 10 Non-Anatomic Tooth Arrangement 1-16 at 96 DpiDocument89 pages10 Non-Anatomic Tooth Arrangement 1-16 at 96 Dpitrangy77No ratings yet
- Pernkopf Vol. 1 - DjvuDocument590 pagesPernkopf Vol. 1 - DjvuIsmael SalomónNo ratings yet
- Embryology of EyeDocument28 pagesEmbryology of Eyesamuelpnrj25100% (2)
- Supracondylar Humerus#Document56 pagesSupracondylar Humerus#Shisam PoudelNo ratings yet
- Kassiano Etal J Strength Cond Res 2023Document11 pagesKassiano Etal J Strength Cond Res 2023Edwin VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- B.SC Radiology Imaging Technology 1 2 Sem. SyllabusDocument33 pagesB.SC Radiology Imaging Technology 1 2 Sem. Syllabusالمدرب عمر عادلNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology GuideDocument57 pagesAnatomical Terminology GuideAlicina DaleNo ratings yet
- Physiology Essay 11: Sympathetic Nervous System in Stress ResponseDocument2 pagesPhysiology Essay 11: Sympathetic Nervous System in Stress ResponseNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Applications of Ilizarov Fixators To Fractures of The Tibia - A Practical Guide (Tech Ortho 17.1.2002) PDFDocument111 pagesApplications of Ilizarov Fixators To Fractures of The Tibia - A Practical Guide (Tech Ortho 17.1.2002) PDFBogdan IorgaNo ratings yet
- Applied Kinesiology and The Cervical SpineDocument5 pagesApplied Kinesiology and The Cervical SpineScott CuthbertNo ratings yet