Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy and Physiology - ACT1
Uploaded by
Mike Piche0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Anatomy and Physiology_ACT1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - ACT1
Uploaded by
Mike PicheCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
ACTIVITY NO.1
DIRECTIONAL TERMS
NAME:
GRADE AND SECTION:
1. The Language of Anatomy – Anatomical Positions and Directional Terms
a. _________________________ – body is erect with the feet
parallel and the arms hanging at the sides with the palms facing Right Left
forwards. Realize that pictures given in textbooks are “mirror
images”
b. Directional terms allow us to explain exactly where one body
structure is in relation to another.
1. _________________________ (cranial or cephalad) –
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the
body; above
2. _________________________ (caudal) – away from
the head end or toward the lower part of structure or
the body; below
3. _________________________ (ventral) – toward or at
the front of the body; in front of
4. _________________________ (dorsal) – toward or at
the backside of the body; behind
5. _________________________ – toward or at the
midline of the body; on the inner side of
6. _________________________ – away from the midline of the body; on
the outer side of
7. _________________________ – between a more medial and a more
lateral structure
8. _________________________ – close to the origin of the body part or the
point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
9. _________________________ – farther from the origin of a body part or
the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
10. _________________________ – toward or at the body surface
11. _________________________ – away from the body surface; more
internal
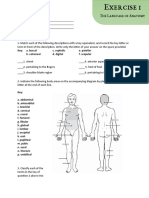
c. Anterior body landmarks
1. Abdominal – anterior body trunk; inferior to ribs
2. Acromial – point of shoulder
3. _________________________ – anterior surface of elbow
4. _________________________ – armpit
5. _________________________ – arm
6. Buccal – cheek area
7. Carpal – wrist
8. Cervical – neck region
9. Coxal – hip
10._________________________ – leg
11.Digital – fingers, toes
12._________________________ – thigh
13.Fibular – lateral part of leg
14._________________________ – area where thigh meets body trunk; groin
15.Nasal – nose area
16._________________________ – mouth
17._________________________ – eye area
18._________________________ – anterior knee
19.Pelvic – area overlying the pelvis anteriorly
20.Pubic – genital region
21._________________________ – breastbone area
22.Tarsal – ankle region
23._________________________ – chest
24.Umbilical – navel
d. Posterior body landmarks
1. _________________________ – head
2. Deltoid – curve of shoulder formed by large deltoid muscle
3. Gluteal – buttock
4. _________________________ – area of back between ribs and hips
5. Occipital – posterior surface of head
6. _________________________ – posterior knee area
7. Sacral – area between hips
8. Scapular – shoulder blade region
9. Sural – posterior surface of lower leg; the calf
10. _________________________ – area of spine
e. Body planes and sections
1. When preparing to look at the internal structures of the body, medical students
find it necessary to make a section, or cut. When the section is made through
the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary line called a
plane.
2. _________________________ section – cut made along the lengthwise, or
longitudinal, plane of the body, dividing the body into right and left parts. If
the cut is made down the median plane of the body and the right and left parts
are equal in size, it is called a midsagittal or median section.
3. _________________________section – cut made along a lengthwise plane
that the divides the body (or organ) into anterior and posterior parts. Also
called a coronal section.
4. _________________________ section – cut made along a horizontal plane,
dividing the body or organ into superior and inferior parts. Also called a cross
section.
f. Body cavities
1. _________________________ body cavity includes the cranial and spinal
cavity.
a. _________________________ cavity – space inside the skull.
Protects the brain.
b. _________________________ cavity – extends from the cranial
cavity nearly to the end of the vertebral column. The spinal cord,
which is a continuation of the brain, is protected by the vertebrae,
which surround the spinal cavity.
2. _________________________ body cavity is larger than the dorsal body
cavity and contains all the structures of the chest and abdomen.
a. _________________________ cavity – contains the lungs, heart. The
central region of the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart, is called
the mediastinum.
b. _________________________ cavity – separated from the thoracic
cavity by the diaphragm (layer of muscle underneath the lungs).
a. Abdominal cavity contains the liver, stomach, intestines
b. Pelvic cavity contains the reproductive organs, bladder, rectum.
c. No actual physical structure divides the abdominopelvic cavity
g. Body regions with the abdominopelvic cavity
1. _________________________ region – centermost region, deep to and
surrounding the umbilicus (navel)
2. _________________________ region – superior to the umbilical region
3. _________________________ (pubic) region – inferior to the umbilical
region
4. Right iliac or right _________________________ region – lateral to the
hypogastric region. Includes the superior part of the hip bone (known as the
ilium)
5. Left iliac or left inguinal region – lateral to the hypogastric region. Includes
the superior part of the hip bone
6. Right _________________________ region – lateral to the umbilical region,
on the right side
7. Left lumbar region – lateral to the umbilical region, on the left side
8. Right _________________________ region – flanks the epigastric region and
contains the lower ribs on the right side (chondro = cartilage)
9. Left hypochondriac region – flanks the epigastric region and contains the
lower ribs on the left side.
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology Lab Manual ReviewDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lab Manual ReviewJustine CarpioNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Garment-Pattern Making - A Textbook for Clothing Designers, Teachers of Clothing Technology, and Senior StudentsFrom EverandThe Theory of Garment-Pattern Making - A Textbook for Clothing Designers, Teachers of Clothing Technology, and Senior StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Anatomical Terms NotesDocument4 pagesAnatomical Terms NotesMicaela DavisNo ratings yet
- Ness Family History Part 1Document78 pagesNess Family History Part 1dbryant0101100% (1)
- Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-399404406100% (2)
- Savion Mitchell - SAP 1a LEQ 4 LanguageDocument4 pagesSavion Mitchell - SAP 1a LEQ 4 LanguageSavion MitchellNo ratings yet
- LAB Intro To AnatomyDocument8 pagesLAB Intro To AnatomynanaNo ratings yet
- Chapt01 Study OutlineDocument6 pagesChapt01 Study OutlineClaythie NicholasNo ratings yet
- Week1 PracticeDocument3 pagesWeek1 PracticeMarcus CarusoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1: Anatomy and Body PlanDocument2 pagesLaboratory Activity 1: Anatomy and Body PlanSamantha sanchezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology Notesapi-305436791No ratings yet
- Anatomy Language GuideDocument11 pagesAnatomy Language GuideKaye ViolaNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise No.1Document5 pagesLab Exercise No.1Maria Nyla ConsueloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter OverviewDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter OverviewJun ManNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Language Lab ManualDocument7 pagesAnatomical Language Lab ManualisahNo ratings yet
- Intro and Terminology WorksheetDocument6 pagesIntro and Terminology WorksheetYmme PalacNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Skeletal System Outline For Notes Health Care Careers NAMEDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Skeletal System Outline For Notes Health Care Careers NAMEEvi DousiaNo ratings yet
- Organization of The Human Body: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesOrganization of The Human Body: Learning ObjectivesDayceNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Organization of The Human BodyDocument8 pagesModule 6 - Organization of The Human Body10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Nucleus Anabolism Metabolism Histologist Genes: Pharynx Adipose Tissue Trachea Ureter Larynx Pleura Cartilage UrethraDocument6 pagesNucleus Anabolism Metabolism Histologist Genes: Pharynx Adipose Tissue Trachea Ureter Larynx Pleura Cartilage Urethrateemo no JutsuNo ratings yet
- English Homework 4Document2 pagesEnglish Homework 4Teodora TanaseNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2-The Language of MedicineDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 2-The Language of Medicineeddy surielNo ratings yet
- Exercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)Document7 pagesExercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)tomaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Pig Dissection GuideDocument8 pagesFetal Pig Dissection GuidedvinalNo ratings yet
- Human Movement Module 1Document10 pagesHuman Movement Module 1Paula Dimples SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 MC100Document2 pagesLab 1 MC100Aj MendozaNo ratings yet
- Exercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)Document7 pagesExercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)tomaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab ManualDocument9 pagesAnaphy Lab ManualKen KanekiNo ratings yet
- PERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 1.4-Learning TaskDocument9 pagesPERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 1.4-Learning TaskEmmalyn Perida100% (1)
- Body directional terms and regionsDocument8 pagesBody directional terms and regionsEuniece AnicocheNo ratings yet
- BI-124L-02 Exercises 1&2Document5 pagesBI-124L-02 Exercises 1&2camatangelleNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 6- 2nd quarter 1st summativeDocument10 pagesSUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 6- 2nd quarter 1st summativeJohn Cyrel MondejarNo ratings yet
- Produces Heat and MovementDocument15 pagesProduces Heat and MovementKeesha Mae Urgelles TimogNo ratings yet
- Anatomy QuestionDocument19 pagesAnatomy Questionstevanie WGNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - Introduction To Human Body - An OrientationDocument3 pagesWorksheet 1 - Introduction To Human Body - An OrientationJomari ManalansanNo ratings yet
- Anatomical directional terms and body regions quizDocument5 pagesAnatomical directional terms and body regions quizteachsanchezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 CHAPTER 2 Science Module Parts of BodyDocument8 pagesLesson 1 CHAPTER 2 Science Module Parts of BodyErving NuñezNo ratings yet
- Taller 8 Parts of The Body ActDocument1 pageTaller 8 Parts of The Body ActAndrés Felipe Jaramillo BertelNo ratings yet
- Body Parts Gr3Document2 pagesBody Parts Gr3uybuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 2-Organ-SystemsDocument5 pages2-Organ-SystemsBeaNo ratings yet
- MG II - TEMA 4 Limba EnglezaDocument3 pagesMG II - TEMA 4 Limba EnglezaGabriel IlinoiuNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TerminologyDocument12 pagesAnatomical Terminologysarped10No ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology WorksheetDocument5 pagesAnatomical Terminology WorksheetIzzy Dale Cagas SilangaNo ratings yet
- Self Study Handout - Medical Terminology - 2022Document14 pagesSelf Study Handout - Medical Terminology - 2022rhn 5b1coolNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TerminologyDocument11 pagesAnatomical TerminologyMartina SilerioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Axial SkeletonDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Axial SkeletonJustine May Balinggan DelmasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology WorksheetDocument2 pagesAnatomy & Physiology WorksheetMalyn DilagNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Assignment 2Document5 pagesMedical Terminology Assignment 2Beverly GraciousNo ratings yet
- 4 - Structure of The Human Skeleton WorksheetDocument9 pages4 - Structure of The Human Skeleton WorksheetJashneelNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument7 pagesManualsocimedia300No ratings yet
- Assignment No - 11 Digestive System (Alimentary System) Laboratory ProcedureDocument8 pagesAssignment No - 11 Digestive System (Alimentary System) Laboratory ProcedureRegina GambayanNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates: Fresh Water Oviparous Shells Small Skeleton SeaDocument3 pagesInvertebrates: Fresh Water Oviparous Shells Small Skeleton SeaanalazosNo ratings yet
- Surface Anatomy: The Language of AnatomyDocument5 pagesSurface Anatomy: The Language of AnatomyHitagi CrabNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM Notes WorksheetDocument2 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEM Notes WorksheetCarla MirandaNo ratings yet
- LSM Grade 4 Science 1st Trim Exam SY 2010 - 2011Document10 pagesLSM Grade 4 Science 1st Trim Exam SY 2010 - 2011Mauie Flores100% (1)
- SST6Document12 pagesSST6JT3No ratings yet
- Cell-Modification LectureDocument6 pagesCell-Modification LectureFiona LeeNo ratings yet
- Regions of The Dog's BodyDocument3 pagesRegions of The Dog's BodyNiel Bert Balios MonivaNo ratings yet
- Lebico Camille Sci 3a Act. 1Document3 pagesLebico Camille Sci 3a Act. 1wannieNo ratings yet
- Grade 2- READING - MT 1 - TERM 2Document6 pagesGrade 2- READING - MT 1 - TERM 2ruby Javaid21No ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- The Clinical Skull Manual: 1St EditionFrom EverandThe Clinical Skull Manual: 1St EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cell City AnalogyDocument1 pageCell City AnalogyMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Earth life quiz exposes geology dating techniquesDocument1 pageEarth life quiz exposes geology dating techniquesMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Mirror RayDocument1 pageMirror RayMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Finals ReviewDocument6 pagesInorganic Chemistry Finals ReviewMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Move It Like A NewtonDocument6 pagesMove It Like A NewtonMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Incident Report - AlisosoDocument3 pagesIncident Report - AlisosoMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Mirror Eq Copy 2Document3 pagesMirror Eq Copy 2Mike PicheNo ratings yet
- ANPH 4114 PHAP 4114: Graduate School of MedicineDocument8 pagesANPH 4114 PHAP 4114: Graduate School of MedicinelovelysyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Unfamiliar Words Activity 1Document1 pageUnfamiliar Words Activity 1Sharmaine Ann AustriaNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex Part 1 TranscriptDocument24 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex Part 1 Transcriptapi-273068056No ratings yet
- Belle Jacinthe DMCDocument6 pagesBelle Jacinthe DMCGrace Alejo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Answer Paper 2 PAP 1 2015Document7 pagesAnswer Paper 2 PAP 1 2015Nick LeeNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Activities Weeks 7 and 8Document11 pagesScience 10 Activities Weeks 7 and 8Kim CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Handouts Lymphatic System F11Document7 pagesHandouts Lymphatic System F11Kelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1qwer0909No ratings yet
- Review General & USMLE Microbiology MCQsDocument51 pagesReview General & USMLE Microbiology MCQsM7md AllahhamNo ratings yet
- Motivation: Understanding Needs, Drives and MotivesDocument48 pagesMotivation: Understanding Needs, Drives and MotivesRAVI THAKKARNo ratings yet
- Notes from Systematics Webinar Groups B and CDocument2 pagesNotes from Systematics Webinar Groups B and CYuki Ishida100% (1)
- SOL BIO Anatomical Evidence of Evolution Henry PriceDocument7 pagesSOL BIO Anatomical Evidence of Evolution Henry PriceHenry PriceNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument10 pages1 PBKevin MarbunNo ratings yet
- Soal PAT English Kelas 10 Edit1Document22 pagesSoal PAT English Kelas 10 Edit1Dony Petrus, S.Pd.No ratings yet
- REVIEW - The Origin and Nature of Life On Earth - The Emergence of The Fourth GeosphereDocument2 pagesREVIEW - The Origin and Nature of Life On Earth - The Emergence of The Fourth GeosphereLeonardoNo ratings yet
- CAPSTONE For Grade 12Document16 pagesCAPSTONE For Grade 12Rona RuizNo ratings yet
- Immunology For Pharmacy StudentsDocument199 pagesImmunology For Pharmacy StudentsPizzaChowNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Lab ReportDocument14 pagesExercise Physiology Lab ReportRomit Poddar0% (1)
- Mock NewDocument15 pagesMock NewHosni ShowikeNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet TemplateDocument1 pageLab Sheet TemplateKayleighGabrielleNo ratings yet
- Actor Si RizalDocument6 pagesActor Si RizalRezzmah Alicia Tomon KhadrawyNo ratings yet
- In This Phase, 2 ATP Are Used.: 1 Glucose Is Converted Into 2 Glyceraldehyde-3-PhosphateDocument8 pagesIn This Phase, 2 ATP Are Used.: 1 Glucose Is Converted Into 2 Glyceraldehyde-3-PhosphateGia HoàngNo ratings yet
- Phylogeny and Systematics: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument35 pagesPhylogeny and Systematics: Powerpoint Lectures ForDimo PratannaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Biosensors For DNA&Ndash Drug InteractionsDocument16 pagesElectrochemical Biosensors For DNA&Ndash Drug InteractionsGilson JúniorNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Organization of The Nervous SystemDocument66 pagesIntroduction and Organization of The Nervous SystemAlan MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Bab 3 Morfologi Polen 1Document13 pagesBab 3 Morfologi Polen 1Aped ChuaNo ratings yet
- Biocomputers: Using Biological Systems to Perform Computational CalculationsDocument3 pagesBiocomputers: Using Biological Systems to Perform Computational CalculationsAjinkyaJadNo ratings yet
- JuteDocument54 pagesJuteAkash BhowmikNo ratings yet