Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 6
Uploaded by
John Luis Bantolino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views1 pageOriginal Title
MATH 6 (4)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views1 pageMath 6
Uploaded by
John Luis BantolinoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
1. Other patterns in nature can also be seen in the ball move and jellyfish(dihedral-D4 symmetry).
Radial
of mackerel, the v-formation of geese in the sky and symmetry is also evident in different kinds of
the tornado formation of starlings. flowers.
PATTERNS AND REGULARITIES
Mathematics is all around us. As we discover
more about our environment, we can mathematically
describe nature. The beauty of a flower, the majestic
tree, even the rock formation exhibits nature’s sense of
symmetry.
Have you ever thought about how nature likes 2. FRACTALS – a curve or geometric figure, each part
to arrange itself in patterns in order to act efficiently? of which has the same statistical character as the
Nothing in nature happens without a reason, all of whole. A fractal is a never-ending pattern found in
these patterns have an important reason to exist and nature. The exact same shape is replicated in a
they also happen to be beautiful to watch. process called “self similarity.” The pattern repeats
itself over and over again at different scales. For
TYPES OF PATTERNS example, a tree grows by repetitive branching. This
1. SYMMETRY – a sense of harmonious and same kind of branching can be seen in lightning
beautiful proportion of balance or an object is bolts and the veins in your body. Examine a single
invariant to any various transformations fern or an aerial view of an entire river system and
(reflection, rotation or scaling.) you’ll see fractal patterns.
a.) Bilateral Symmetry: a symmetry in which the
left and right sides of the organism can be divided
into approximately mirror image of each other
along the midline. Symmetry exists in living things
such as in insects, animals, plants, flowers and
others. Animals have mainly bilateral or vertical
symmetry, even leaves of plants and some flowers
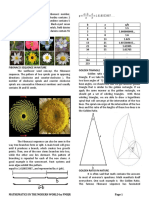
such as orchids. 3. SPIRALS - A logarithmic spiral or growth spiral is a
self-similar spiral curve which often appears in
nature. It was first describe by Rene Descartes and
was later investigated by Jacob Bernoulli. A spiral is
a curved pattern that focuses on a center point and
a series of circular shapes that revolve around it.
Examples of spirals are pine cones, pineapples,
hurricanes. The reason for why plants use a spiral
form is because they are constantly trying to grow
b.) Radial Symmetry ( or rotational symmetry ): a but stay secure.
symmetry around a fixed point known as the center
and it can be classified as either cyclic or dihedral.
Plants often have radial or rotational symmetry, as
to flowers and some group of animals. A five-fold
symmetry is found in the echinoderms, the group in
which includes starfish (dihedral-D5 symmetry), sea
urchins and sea lilies. Radial symmetry suits
organism like sea anemones whose adults do not
MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLD by PMSJR Page 1
You might also like
- Patterns in Nature: Why the Natural World Looks the Way It DoesFrom EverandPatterns in Nature: Why the Natural World Looks the Way It DoesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which: Patterns and RegularitiesDocument2 pagesA.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which: Patterns and RegularitiesNel BorniaNo ratings yet
- Math 6Document2 pagesMath 6John Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- LP1 - Patterns and Numbers in Nature and The WorldDocument21 pagesLP1 - Patterns and Numbers in Nature and The WorldphoebelazzyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Mathematics in Our WorldDocument12 pagesLesson 1 - Mathematics in Our Worldv89ymxbkmmNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World NotesDocument5 pagesMathematics in The Modern World NotesJeongguk KimNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Nature of MathematicsDocument9 pagesModule 1 Nature of Mathematicsstephen jude almeidaNo ratings yet
- Matm111 1st-SemesterDocument11 pagesMatm111 1st-SemesterLouise SantosNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheDocument1 pagePatterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Math 1Document10 pagesMath 1Leo John HinayasNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know: Concept BuildingDocument16 pagesWhat You Need To Know: Concept BuildingMilk BrotherNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument10 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldLeo John Hinayas100% (3)
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument8 pagesMathematics in The Modern Worldmyungsoo87% (120)
- Mathematics in The Modern World 7 PDF FreeDocument8 pagesMathematics in The Modern World 7 PDF FreeYvonne AlajarNo ratings yet
- Patterns: Quick TriviaDocument6 pagesPatterns: Quick TriviaNidaNo ratings yet
- 01 C1 Enhancement HandoutDocument8 pages01 C1 Enhancement HandoutHeart ChuaNo ratings yet
- Topic in Text MMWDocument9 pagesTopic in Text MMWEliana Uly HattoriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The WorldDocument3 pagesMathematics in The WorldKristine Anne IgotNo ratings yet
- Module 1. Lesson 2Document31 pagesModule 1. Lesson 2Rowena SuyatNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Mathematics in Our WorldDocument15 pages1.1 Mathematics in Our WorldBea Angelika Solomon100% (3)
- Module 1-2 Patterns and SequenceDocument10 pagesModule 1-2 Patterns and SequenceRonalyn CagueteNo ratings yet
- 1.1: Mathematics in Our WorldDocument4 pages1.1: Mathematics in Our WorldGlauis MadieNo ratings yet
- Math 101-PatternsDocument17 pagesMath 101-Patternsnathaniel montesNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 MMWDocument9 pagesLesson1 MMWkhlneNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheDocument2 pagesPatterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- GE 114 Module 2Document12 pagesGE 114 Module 2Marjorie GabrielesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1Avyanna XyrelleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MMWDocument6 pagesChapter 1 MMWKathyrine Claire EdrolinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Mathematics in Our WorldDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Mathematics in Our WorldEmmanuel Santos IINo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Nature of MathematicsDocument35 pagesLesson 1 The Nature of MathematicsARAGRACE REANO MalejanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 - The Mathematics in Our WorldDocument52 pagesLesson 1.2 - The Mathematics in Our WorldGuia CandelariaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Pattern and Numbers in NatureDocument10 pagesMathematical Pattern and Numbers in NatureFlehzy EstollosoNo ratings yet
- A - Chapter 1 Mathematics in Our WorldDocument49 pagesA - Chapter 1 Mathematics in Our WorldBrian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 5917603517600185137Document11 pagesInbound 5917603517600185137Erika Louisa Naingue PrejanNo ratings yet
- MMW ReviewwwweeDocument14 pagesMMW ReviewwwweeAcademic LifeNo ratings yet
- Nature of MathematicsDocument5 pagesNature of MathematicsMikaela Althea BorromeoNo ratings yet
- GE MMW MODULE 1 - Lesson 1Document11 pagesGE MMW MODULE 1 - Lesson 1Meah LabadanNo ratings yet
- MMW Second LectureDocument59 pagesMMW Second LectureJanine CrisoloNo ratings yet
- 2 Patterns MMWDocument6 pages2 Patterns MMWMcEddie Bagona67% (3)
- Unit I MMWDocument18 pagesUnit I MMWrpmananghayaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World: By: Janice A. HernandezDocument26 pagesMathematics in The Modern World: By: Janice A. HernandezZ e r oNo ratings yet
- Patterns in NatureDocument4 pagesPatterns in NatureNeveRed100% (2)
- 1.2 Mathematics in Our World PDFDocument11 pages1.2 Mathematics in Our World PDFVenus Abigail Gutierrez100% (1)
- Lesson 1.2 Ged 102 Mathematics in The Real WorldDocument29 pagesLesson 1.2 Ged 102 Mathematics in The Real WorldKim Ayron PasionNo ratings yet
- Kiwi SnowflakesDocument4 pagesKiwi SnowflakesMelanni InojalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1. Patterns in Nature and in The WorldDocument8 pagesLesson 1.1. Patterns in Nature and in The WorldMcdo JolibeeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World 1st Year 1st SemesterDocument46 pagesMathematics in The Modern World 1st Year 1st SemesterJhon Keneth Namias93% (14)
- Lesson 1 1Document8 pagesLesson 1 1neney maidenNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument10 pagesChapter IRr NgayaanNo ratings yet
- Ge 4Document13 pagesGe 4Hallel Jhon Blanza ButacNo ratings yet
- MMW - Lesson 1 MidtermDocument6 pagesMMW - Lesson 1 Midtermheartarances0214No ratings yet
- MATM Week 2-3Document5 pagesMATM Week 2-3Krisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Unit I. Mathematics in Our WorldDocument12 pagesUnit I. Mathematics in Our WorldRoanne FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World - Module 1Document4 pagesMathematics in The Modern World - Module 1Jasmine Monique CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Mathematics in Our World For PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Mathematics in Our World For PDFAnnikah Trizya FACTONo ratings yet
- 2ndSEM2021MMW W1PPT1Document55 pages2ndSEM2021MMW W1PPT1Glenn EscañanNo ratings yet
- GE105 - Chapter 1 ModuleDocument8 pagesGE105 - Chapter 1 ModuleVryll Lexa Casas DugadugaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Modern Worl1Document12 pagesMathematics in Modern Worl1Marls PantinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Prelim OpenDocument19 pagesChapter 1-Prelim OpenWild RiftNo ratings yet
- 1 Patterns in Nature and The WorldDocument4 pages1 Patterns in Nature and The WorldRafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- φ= a+b a a bDocument2 pagesφ= a+b a a bJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Our World Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)Document1 pageMathematics in Our World Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)John Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Golden Ratio in Nature: 1. Flower PetalsDocument2 pagesGolden Ratio in Nature: 1. Flower PetalsJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheDocument1 pagePatterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Shells: Applications of Mathematics in The WorldDocument1 pageShells: Applications of Mathematics in The WorldJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Golden Ratio in Nature: 1. Flower PetalsDocument2 pagesGolden Ratio in Nature: 1. Flower PetalsJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Shells: Golden Ratio in ArtsDocument1 pageShells: Golden Ratio in ArtsJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheDocument2 pagesPatterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheDocument2 pagesPatterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- φ= a+b a a bDocument3 pagesφ= a+b a a bJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- φ= a+b a a bDocument3 pagesφ= a+b a a bJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Shells: Golden Ratio in ArtsDocument1 pageShells: Golden Ratio in ArtsJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Our World Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)Document1 pageMathematics in Our World Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)John Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Golden Ratio in Nature: 1. Flower PetalsDocument2 pagesGolden Ratio in Nature: 1. Flower PetalsJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Our World Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)Document1 pageMathematics in Our World Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)John Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Chartres in Paris, France Also Exhibits The: Golden Ratio in ArchitectureDocument3 pagesChartres in Paris, France Also Exhibits The: Golden Ratio in ArchitectureJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Chartres in Paris, France Also Exhibits The: Golden Ratio in ArchitectureDocument3 pagesChartres in Paris, France Also Exhibits The: Golden Ratio in ArchitectureJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Applications of Mathematics in The World: in Fluid Dynamics, Engineers Use NumericalDocument1 pageApplications of Mathematics in The World: in Fluid Dynamics, Engineers Use NumericalJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Information Technology,: Applications of Mathematics in The WorldDocument2 pagesInformation Technology,: Applications of Mathematics in The WorldJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Mat 66Document2 pagesMat 66John Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Dendrochronology Which Is A Scientific Method ofDocument2 pagesDendrochronology Which Is A Scientific Method ofJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Mat 66Document2 pagesMat 66John Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- φ= a+b a a bDocument3 pagesφ= a+b a a bJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Information Technology,: Applications of Mathematics in The WorldDocument2 pagesInformation Technology,: Applications of Mathematics in The WorldJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Dendrochronology Which Is A Scientific Method ofDocument2 pagesDendrochronology Which Is A Scientific Method ofJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Applications of Mathematics in The World: in Fluid Dynamics, Engineers Use NumericalDocument1 pageApplications of Mathematics in The World: in Fluid Dynamics, Engineers Use NumericalJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Shells: Golden Ratio in ArtsDocument2 pagesShells: Golden Ratio in ArtsJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Golden Ratio in Nature: 1. Flower PetalsDocument3 pagesGolden Ratio in Nature: 1. Flower PetalsJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheDocument2 pagesPatterns and Regularities: A.) Bilateral Symmetry: A Symmetry in Which TheJohn Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Our World Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)Document1 pageMathematics in Our World Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)John Luis BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Invisible Rainbow A History of Electricity and LifeDocument17 pagesInvisible Rainbow A History of Electricity and LifeLarita Nievas100% (3)
- Week 1 Course Objectives and OutlineDocument15 pagesWeek 1 Course Objectives and Outlinechrisbourque13No ratings yet
- CabillanDocument12 pagesCabillanvivivioletteNo ratings yet
- Reading #2: Participatory Action ResearchDocument45 pagesReading #2: Participatory Action Researchapi-3723169100% (2)
- Investment Opportunities: Equity MarketsDocument38 pagesInvestment Opportunities: Equity MarketsRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Never Can Say Goodbye Katherine JacksonDocument73 pagesNever Can Say Goodbye Katherine Jacksonalina28sept100% (5)
- Comprehensive Compressed Air Assessments: The 5-Step ProcessDocument8 pagesComprehensive Compressed Air Assessments: The 5-Step ProcessANDRESNo ratings yet
- 07.03.09 Chest PhysiotherapyDocument10 pages07.03.09 Chest PhysiotherapyMuhammad Fuad MahfudNo ratings yet
- Fouts Federal LawsuitDocument28 pagesFouts Federal LawsuitWXYZ-TV DetroitNo ratings yet
- The 5 Basic Sentence PatternsDocument6 pagesThe 5 Basic Sentence PatternsShuoNo ratings yet
- Ready For First TB Unit3Document10 pagesReady For First TB Unit3Maka KartvelishviliNo ratings yet
- Stripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel PinDocument3 pagesStripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel Pinmuhamad laaliNo ratings yet
- Persuasive SpeechDocument2 pagesPersuasive SpeechAngel Zachary RayyanNo ratings yet
- Law On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesDocument3 pagesLaw On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesLenoel Nayrb Urquia Cosmiano100% (1)
- Working With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaDocument26 pagesWorking With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaAngela BeatriceNo ratings yet
- M40 Mix DesignDocument2 pagesM40 Mix DesignHajarath Prasad Abburu100% (1)
- 4complete The Min1Document3 pages4complete The Min1julia merlo vegaNo ratings yet
- Uttar Pradesh Universities Act 1973Document73 pagesUttar Pradesh Universities Act 1973ifjosofNo ratings yet
- CR Injector Repair Kits 2016Document32 pagesCR Injector Repair Kits 2016Euro Diesel100% (2)
- DBS AR 2019 Final Final PDFDocument371 pagesDBS AR 2019 Final Final PDFDevi Nurusr100% (1)
- Speakout Language BankDocument7 pagesSpeakout Language BankСаша БулуєвNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)Document28 pagesOrganisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)mahtaabkNo ratings yet
- Phrygian Gates and China Gates RecordingsDocument1 pagePhrygian Gates and China Gates RecordingsCloudwalkNo ratings yet
- Direct RetainerDocument186 pagesDirect RetainerAngkita KalitaNo ratings yet
- Niper SyllabusDocument9 pagesNiper SyllabusdirghayuNo ratings yet
- The Intelligent Investor NotesDocument19 pagesThe Intelligent Investor NotesJack Jacinto100% (6)
- Public ParticipationDocument17 pagesPublic ParticipationAinul Jaria MaidinNo ratings yet
- Chryso CI 550Document2 pagesChryso CI 550Flavio Jose MuhaleNo ratings yet
- Effect of Boron Content On Hot Ductility and Hot Cracking TIG 316L SSDocument10 pagesEffect of Boron Content On Hot Ductility and Hot Cracking TIG 316L SSafnene1No ratings yet
- AMBROSE PINTO-Caste - Discrimination - and - UNDocument3 pagesAMBROSE PINTO-Caste - Discrimination - and - UNKlv SwamyNo ratings yet