100% found this document useful (1 vote)
734 views7 pagesManagerial AccountingMid Term Examination (1) - CONSULTA
The document contains the mid-term examination questions and answers of Consulta, Eugenesis A. on Managerial Accounting. Some key details:
- Questions calculate break-even points, contribution margins, sales required to earn target profits, and effects of cost and price changes for two companies.
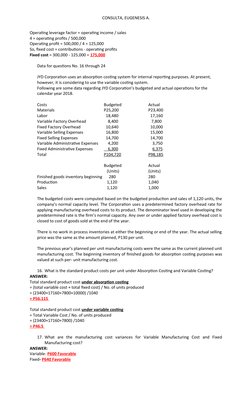
- Additional questions use data from Ethel Corp to calculate various metrics under absorption and variable costing, including standard costs, variances, operating income/loss, inventory values, and fixed costs expensed.
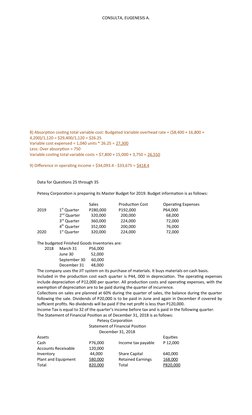
- JYD Corporation is considering a switch from absorption to variable costing. Questions analyze budgeted and actual data for JYD using both methods.
Uploaded by
May RamosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
734 views7 pagesManagerial AccountingMid Term Examination (1) - CONSULTA
The document contains the mid-term examination questions and answers of Consulta, Eugenesis A. on Managerial Accounting. Some key details:
- Questions calculate break-even points, contribution margins, sales required to earn target profits, and effects of cost and price changes for two companies.
- Additional questions use data from Ethel Corp to calculate various metrics under absorption and variable costing, including standard costs, variances, operating income/loss, inventory values, and fixed costs expensed.
- JYD Corporation is considering a switch from absorption to variable costing. Questions analyze budgeted and actual data for JYD using both methods.
Uploaded by
May RamosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Mid-term Examination Questions: This section contains multiple-choice questions focused on calculating company break-even points, margin of safety, and operating income leveraging financial formulas.
- Financial Accounting Examination: Exam problems related to absorption costing, inventory budgeting, and operating costs presented for evaluation and analysis.
- Budgeting Analysis Questions: Contains budget preparation questions focusing on sales, expenditures, and inventory projections for future financial periods.
- Variance Analysis Examination: This portion of the exam addresses variance evaluation concerning labor and material variances, highlighting favorable and unfavorable discrepancies.