0% found this document useful (0 votes)
763 views41 pagesCircular Motion 3
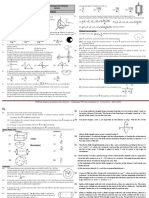
The document discusses various topics related to angular motion including angular displacement, velocity, acceleration, and their relationships. It provides examples of circular motion, centripetal force, and angular quantities. Key concepts covered include the definitions of angular displacement, velocity, acceleration, and their equations. Examples of problems calculate angular quantities like velocity and acceleration given information about circular motion and rotational dynamics.
Uploaded by
Raja BabuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
763 views41 pagesCircular Motion 3
The document discusses various topics related to angular motion including angular displacement, velocity, acceleration, and their relationships. It provides examples of circular motion, centripetal force, and angular quantities. Key concepts covered include the definitions of angular displacement, velocity, acceleration, and their equations. Examples of problems calculate angular quantities like velocity and acceleration given information about circular motion and rotational dynamics.
Uploaded by
Raja BabuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd