Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review-Module-13-Surveying-2-Part 1
Uploaded by
RamonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review-Module-13-Surveying-2-Part 1
Uploaded by
RamonCopyright:
Available Formats
MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila
CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City
Telephone Number: (02) 516-7559 (Manila) E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com
(032) 254-9967 (Cebu)
Review MODULE 13 – ROUTE SURVEYING – Part 1
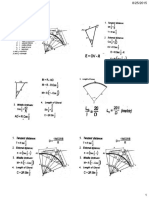
13.01 SIMPLE CURVES
SITUATION. SITUATION.
A simple curve has a degree of 6° and angle of intersection of 50°. The Azimuths of tangents through PC, PRC and PT are 240°,
270° and 250° respectively, the degree of the first curve is 1.5°
1. Calculate the distance from the midpoint of the curve to the and the stationing of PC is 10+800, the distance from PI of the first
point of intersection of the tangents. curve to the PI of the second curve is 300m.
2. Calculate the distance from the midpoint of the curve to the
midpoint of the long chord. 14. Determine the stationing of PRC.
3. If the stationing of PC is 50+160, determine the stationing at 15. Determine the Radius of the second Curve.
a point on the curve which intersects with the line making
deflection angle of 8° with the tangent through PC.
4. Compute the radius of curvature if we assume chord-basis. 13.04 TRANSITION CURVES
SITUATION.
SITUATION. The angle of intersection of a circular curve is 45 The design speed of a certain highway is 100kph, if the radius of
degrees 30 minutes and its radius is 198.17m. PI is at station the simple curve is 250m, and the allowable rate of change of
0+783.10. centrifugal acceleration is 0.5m/s3,
5. Compute the deflection angle of Sta. 0+736.58 from PC. 16. design the length of transition curve.
6. Compute the right angle offset from Sta. 0+736.58 on the SITUATION.
curve to tangent through PC. The tangent through TS and ST intersects at an angle of 40°, the
design speed of the highway is 90kph, if the radius of the of the
7. Degree of curve. Use chord basis. Assume 20 m length of simple curve is 200m. Determine the following.
chain.
17. The desirable length of spiral.
18. The spiral angle midway between TS and SC.
13.02 COMPOUND CURVES 19. The spiral angle at SC.
20. The offset distance of the point midway between TS and SC
SITUATION. and from tangent through TS.
The common tangent AB of a compound curve is 80m, with an 21. The offset distance of SC from tangent through TS.
azimuth of 270°. The azimuths of the tangents through PC and PT 22. The deflection angle midway between TS and SC.
are 250° and 280° respectively. The stationing of A is 100+210 23. The deflection angle at SC.
and the degree of the first curve is 6°. 24. The length of Short Tangent.
25. The length of Long Tangent.
8. Determine the stationing of PCC. 26. The length of Throw.
9. Determine the radius of the second curve. 27. The External Distance.
10. Determine the stationing of the PT. 28. The tangent distance for the spiral.
SITUATION.
A compound curve connects three tangents having bearings of
N70°E, Due East and S60°E respectively. The length of the chord
is 350 m long measured from the PC to the PT of the compound
curve and is parallel to the common tangent. If the stationing of
the PT is 3+450.
11. Determine the radii of the curves.
12. Determine the stationing of PCC and PC.
13.03 REVERSE CURVES
SITUATION.
The perpendicular distance between two parallel tangents of a
reversed curve is 35m. The azimuth of the back tangent of the
curve is 270 deg. And the azimuth of the common tangent is 300
deg. If the radius of the back curve is 160 m and the stationing of
P.R.C. is 10+140,
13. Find the station of P.T.
You might also like
- Spherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesFrom EverandSpherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesNo ratings yet
- Review Module 13 Route Surveying Part 1Document1 pageReview Module 13 Route Surveying Part 1YeddaMIlagan100% (1)
- Review ExercisesDocument68 pagesReview ExercisesDream Cafe0% (1)
- Problem Set 2Document1 pageProblem Set 2marcelinodennis1No ratings yet
- Review MODULE Surveying - (Curves) : Horizontal and Vertical Alignment of Highway Curves)Document2 pagesReview MODULE Surveying - (Curves) : Horizontal and Vertical Alignment of Highway Curves)TatingJainarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Part 2Document1 pageModule 3 Part 2Yang RhiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems SurveyingDocument2 pagesPractice Problems Surveyingptknm ptknmNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems SurveyingDocument2 pagesPractice Problems SurveyingYang RhiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems SurveyingDocument2 pagesPractice Problems SurveyingRitsu TainakaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems SurveyingDocument2 pagesPractice Problems SurveyingYang RhiaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets - Simple, Compound, Reverse Curved PDFDocument4 pagesProblem Sets - Simple, Compound, Reverse Curved PDFBeerRide50% (6)
- Surveying 2Document2 pagesSurveying 2haes.sisonNo ratings yet
- Reversed CurveDocument2 pagesReversed CurveMark Real Jubilo57% (7)
- Problem Set 2 Compound CurveDocument12 pagesProblem Set 2 Compound Curvezhwan Anwar nooriNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument3 pagesSurveyingMarc Dared Cagaoan50% (2)
- CurvesDocument6 pagesCurveschristian roy camasis0% (1)
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2jacob quizonNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam of Route Surveying QuestionnaireDocument1 pagePrelim Exam of Route Surveying QuestionnaireAnniesonNo ratings yet
- Simple Compound CurveDocument5 pagesSimple Compound CurveChristopher PojasNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument6 pagesSurveyingMARK KEVIN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Reversed CurveDocument7 pagesReversed CurveBenjo SantosNo ratings yet
- Plate3 4 2020Document2 pagesPlate3 4 2020Paolo Almazan Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Long Chord From TheDocument5 pagesThe Long Chord From TheCheska FernandezNo ratings yet
- BorderDocument11 pagesBorderasdsadsadsadas100% (1)
- Reversed CurvesDocument7 pagesReversed CurvesMarc Dared Cagaoan67% (9)
- Reversed CurveDocument3 pagesReversed CurveShaira Mae Cañedo0% (1)
- Module 3 Part 1Document2 pagesModule 3 Part 1Yang RhiaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Problem SetDocument2 pagesMidterm Problem SetJoylene Dayrit KIMNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 - Compound CurveDocument12 pagesProblem Set 2 - Compound CurveSitti Adelene Ahamad33% (6)
- 1 Simplecurve ProblemsDocument4 pages1 Simplecurve ProblemsSanderson BautistaNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Surveying - Set 6Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 - Surveying - Set 6Mark Lester LualhatiNo ratings yet
- Surveying PDFDocument3 pagesSurveying PDFMariah Kathleen LacsinaNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument2 pagesSurveyingKen FurioNo ratings yet
- Simple Compound CurveDocument5 pagesSimple Compound CurveEdenjade MacawiliNo ratings yet
- Compound CurvesDocument6 pagesCompound CurvesMycha Rose Aragon PalcoNo ratings yet
- Highway AnswerDocument2 pagesHighway AnswerDirect XNo ratings yet
- Simple CurvesDocument7 pagesSimple CurvesEunice EspirituNo ratings yet
- Plates PDFDocument13 pagesPlates PDFCRIISSY100% (1)
- Geometric CurvesDocument2 pagesGeometric CurvesMary Faith LopezNo ratings yet
- Route Surveying - Plate 1Document1 pageRoute Surveying - Plate 1Raymart BulagsacNo ratings yet
- Surveying - Transpo Engg (Refresher) PDFDocument2 pagesSurveying - Transpo Engg (Refresher) PDFDivine Joy Atractivo PinedaNo ratings yet
- Compound Curve PDF FreeDocument6 pagesCompound Curve PDF Freetewele brhaneNo ratings yet
- Plate 2 Compound CurveDocument1 pagePlate 2 Compound CurveRaymart BulagsacNo ratings yet
- Deflection, CompoundDocument27 pagesDeflection, CompoundNheilbertNo ratings yet
- GE 117 3B WF Problem Set 1Document3 pagesGE 117 3B WF Problem Set 1AndreaMiccaBautista0% (1)
- FinalDocument15 pagesFinalMeverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Surveying Lec2Document6 pagesSurveying Lec2hazelNo ratings yet
- Surveying CE Ref 4 & 5Document9 pagesSurveying CE Ref 4 & 5MARK KEVIN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- 2 Atpl NavDocument5 pages2 Atpl Navfebrianputra1818No ratings yet
- Q3Document4 pagesQ3Ritsu Tainaka0% (1)
- SURVEYING I and IIDocument10 pagesSURVEYING I and IIBer Ryl0% (1)
- NCE 322 - Quiz No. 1Document1 pageNCE 322 - Quiz No. 1Mark Lester Brosas TorreonNo ratings yet
- Lec # 03 Setting Out Simple CurveDocument25 pagesLec # 03 Setting Out Simple Curveata subhaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Simple CurvesDocument18 pagesLesson 11 Simple CurvesMANGABAT, KAREN JOY C.No ratings yet
- Problem Set in CEngr 320 (Simple Curves)Document20 pagesProblem Set in CEngr 320 (Simple Curves)Evaline Faith Tacadena Blanco44% (9)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Review Module 14 Basic Transportation Engineering Part 2Document1 pageReview Module 14 Basic Transportation Engineering Part 2RamonNo ratings yet
- 3 - Unsafe Acts and Unsafe Conditions - v.3Document34 pages3 - Unsafe Acts and Unsafe Conditions - v.3RamonNo ratings yet
- Value EngineeringDocument45 pagesValue EngineeringRamonNo ratings yet
- Value EngineeringDocument45 pagesValue EngineeringRamonNo ratings yet
- Fig.z 04 TTTG PN16 DN15-200 F4-F5Document1 pageFig.z 04 TTTG PN16 DN15-200 F4-F5d k70No ratings yet
- Ahern 1977Document9 pagesAhern 1977João VazNo ratings yet
- CE637A-Yield ConditionDocument24 pagesCE637A-Yield ConditionSanchita PaulNo ratings yet
- Fa37g - Sew-EurodriveDocument8 pagesFa37g - Sew-Eurodriveم بNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Final Coaching ShuffledDocument385 pagesMachine Design Final Coaching Shuffledkristan7No ratings yet
- ManualDocument10 pagesManualsayem biswasNo ratings yet
- Design of Portable EDM Machine ToolDocument4 pagesDesign of Portable EDM Machine Toolrakeshraki16600No ratings yet
- NOV Profab Daily Meeting - Kakinada Project STP For KG DWN-98/2 Kakinada FPSO Week-40Document28 pagesNOV Profab Daily Meeting - Kakinada Project STP For KG DWN-98/2 Kakinada FPSO Week-40Rendra Maha Putra JfNo ratings yet
- Orbital Motors Drawing: Reset Download 3D ModelDocument1 pageOrbital Motors Drawing: Reset Download 3D ModelaNKURNo ratings yet
- AGROINDUSTRIALA BREDAL K35-K165 - ENG - Until - 2018Document66 pagesAGROINDUSTRIALA BREDAL K35-K165 - ENG - Until - 2018PopSorinNo ratings yet
- Cameron Flange Slide Rule PDFDocument1 pageCameron Flange Slide Rule PDFcazaangelesNo ratings yet
- Multistage Multioutlet PumpDocument11 pagesMultistage Multioutlet Pumpmajortay100% (1)
- Product List Onetouch PDFDocument5 pagesProduct List Onetouch PDFGouse BujjiNo ratings yet
- 0008 Residential Tinsmithry 00Document2 pages0008 Residential Tinsmithry 00Jet ToledoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Laboratory Equipment and FacilitiesDocument17 pagesMechanical Engineering Laboratory Equipment and FacilitiesFrancis AlmiaNo ratings yet
- Intro To SRMDocument45 pagesIntro To SRMDorian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Dirving ToolsDocument3 pagesDirving ToolsAdeyemie Learhd JeywceeNo ratings yet
- ACMEE 2023 - 15th International Machine Tools ExhibitionDocument16 pagesACMEE 2023 - 15th International Machine Tools ExhibitionSandeep SNo ratings yet
- Kabeldon Cable AccessoriesDocument2 pagesKabeldon Cable AccessoriesVictor GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Factories Act, 1965 - 230918 - 112659Document124 pagesThe Factories Act, 1965 - 230918 - 112659rahman2011018No ratings yet
- 05-EL - FTR - Insulation & Continuity TestDocument3 pages05-EL - FTR - Insulation & Continuity Testben sullivanNo ratings yet
- Pump House DesignDocument33 pagesPump House DesignNeil AgshikarNo ratings yet
- Cartridge Filters: Technical Manual MT 080Document30 pagesCartridge Filters: Technical Manual MT 080abessiNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Allowable Load of Profile - Aluminium Profiles - PBA Leader Motion MalaysiaDocument3 pagesCalculation of Allowable Load of Profile - Aluminium Profiles - PBA Leader Motion MalaysiaSanket Ganesh PokharkarNo ratings yet
- EG Question BankDocument14 pagesEG Question BankRNo ratings yet
- 7 Frame Plunger Pump Models: SpecificationsDocument4 pages7 Frame Plunger Pump Models: SpecificationsFerdi PutraNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual: 0 Series PumpDocument31 pagesInstallation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual: 0 Series PumpTim WorkmanNo ratings yet
- Detonating Cord Booster L10A1: Energetic SystemsDocument1 pageDetonating Cord Booster L10A1: Energetic SystemsCorina RomanNo ratings yet
- Parallel Flange Channels (PFC)Document1 pageParallel Flange Channels (PFC)Eric S Y KwokNo ratings yet
- TD Esc 02 de en 11 023 Rev005 List of Limit Values E 26 To E 53Document21 pagesTD Esc 02 de en 11 023 Rev005 List of Limit Values E 26 To E 53Felipe SilvaNo ratings yet