Professional Documents
Culture Documents
International law of the sea provisions and fishing freedom
Uploaded by
Malavika SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
International law of the sea provisions and fishing freedom
Uploaded by
Malavika SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
INTERNATIONA LAW
THE LAW OF THE SEA
Q.1)Define High Seas. Discuss in brief the important provisions of the UNC on Law of Seas 1958 and
UNC 1982. Is the freedom of fishing on High Sea recognized?
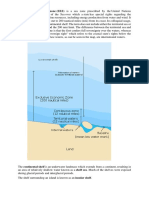
A. High seas- According to the International law, the term High seas means all the parts of the sea
that are not included in the territorial sea or inland waters of a country. It is the area beyond the
national jurisdiction.
This rule was formulated by Grotius in his maxim on “Mare Liberum” in 1609 and claimed that the
sea could not be owned by anyone.
As a result, all States supported that ships can go and use freedom of navigation, fight, fishing and
building artificial islands etc. But, the command has been considerably changed under the convention
on the Law of the sea of 1982.
Article 87(2) of the convention lays down the limitation of the general nature on the freedom of high
seas by stating that the freedom of the high seas “shall be exercised with due regard to the interests
of other States in their exercise of the freedom of high seas”.
UNC on Law of seas 1958
four conventions on the law of seas evolved in 1958, namely called Geneva convention on the law of
sea developed but the conventions failed to address several issues like the urgent need to regulate the
usage of minerals of the deep sea beds and high sea.
In 1982, the third UN conference adopted the Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
consisting of 320 articles and 9 Annexes, along with 4 resolution. A significant portion of the
convention was a replica of the old Geneva convention however several new factors were also
dictated which are as follows:
It expanded the scope regarding the matters of the new legal regime of the deep sea bed and
economic zones.
The territorial sea now extended up to 12 nautical miles limit.
In cases of dispute, the convention provides compulsory judicial settlement at the request of
one of the parties.
The convention also describes the formation of an international tribunal of the law of the sea
for helping in settlements of disputes.
The convention also deals with the regime of archipelagic states, the waters between the
islands are declared archipelagic waters, where ships of all States enjoy the right of innocent
passage.
Fishing on High Sea
Freedom of the high seas is now recognized to include freedom of navigation, fishing, the laying of
submarine cables and pipelines, and overflight of aircraft.
By the second half of the 20th century, demands by some coastal states for increased security and
customs zones, for exclusive offshore-fishing rights, for conservation of maritime resources, and for
exploitation of resources, especially oil, found in continental shelves caused serious conflicts. The
first United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea, meeting at Geneva in 1958, sought to codify
the law of the high seas but was unable to resolve many issues, notably the maximum permissible
breadth of the territorial sea subject to national sovereignty. A second conference (Geneva, 1960) also
failed to resolve this point; and a third conference began in Caracas in 1973, later convening in
Geneva and New York City.
You might also like
- River Flow Forecasting Through Conceptual Models Part I - A Discussion of PrinciplesDocument9 pagesRiver Flow Forecasting Through Conceptual Models Part I - A Discussion of Principlesmth2610No ratings yet
- ICJ Rules on Continental Shelf Delimitation Between Libya and MaltaDocument13 pagesICJ Rules on Continental Shelf Delimitation Between Libya and MaltaMercy NamboNo ratings yet
- Law of SeasDocument7 pagesLaw of SeasJanisar Ali BhuttoNo ratings yet
- INNOCENT PASSAGE THROUGH TERRITORIAL SEADocument65 pagesINNOCENT PASSAGE THROUGH TERRITORIAL SEARifasKochery100% (1)
- Public International LawDocument45 pagesPublic International LawNilesh TeloreNo ratings yet
- MSMA Chapter 6 - Rainwater HarvestingDocument20 pagesMSMA Chapter 6 - Rainwater HarvestingFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- Sources of international law - Custom and its elementsDocument5 pagesSources of international law - Custom and its elementsFarhat YunusNo ratings yet
- TTTT JJJJ: HE HE HE HE Udiciary Udiciary Udiciary UdiciaryDocument26 pagesTTTT JJJJ: HE HE HE HE Udiciary Udiciary Udiciary Udiciarywicked intentionsNo ratings yet
- SoftDocument2 pagesSoftJorge100% (1)
- Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. High CourtDocument3 pagesCode of Criminal Procedure, 1973. High CourtRASHMI KANSALNo ratings yet
- The Vienna Convention on the Law of TreatiesDocument10 pagesThe Vienna Convention on the Law of TreatiesJanisar Ali BhuttoNo ratings yet
- International LawDocument23 pagesInternational Lawrohanagarwal100% (1)
- International LawDocument11 pagesInternational Lawsandhya100% (1)
- Law Notes - Public International LawDocument17 pagesLaw Notes - Public International LawVenugopal MantraratnamNo ratings yet
- Case Book of International LawDocument41 pagesCase Book of International LawAngela ConejeroNo ratings yet
- As & A Level Geography Student Book - OxfordDocument508 pagesAs & A Level Geography Student Book - Oxford张楚涵No ratings yet
- Planning & Design of WCSDocument58 pagesPlanning & Design of WCSrajeevakumar100% (2)
- International Law of The Sea: 1.1. What Is It?Document21 pagesInternational Law of The Sea: 1.1. What Is It?Clark Kenntt50% (2)
- Significance of Formation Process of International Treaty Under International LawDocument18 pagesSignificance of Formation Process of International Treaty Under International LawmishraavneeshNo ratings yet
- Car Wash Water Reuse in BrazilDocument3 pagesCar Wash Water Reuse in BrazilJonatan Sovero BozaNo ratings yet
- Island of Palmas CaseDocument11 pagesIsland of Palmas CaseJesa FormaranNo ratings yet
- Public International Law WordDocument52 pagesPublic International Law Wordkounain fathimaNo ratings yet
- Anglo-Norwegian Fisheries Case establishes extra-territorial authorityDocument13 pagesAnglo-Norwegian Fisheries Case establishes extra-territorial authorityConie Novela100% (1)
- Grundfos A2 Water EngineeringDocument300 pagesGrundfos A2 Water EngineeringGrundfosEgypt100% (2)
- Municipal WaterDocument27 pagesMunicipal WaterRhea CelzoNo ratings yet
- 050 Sovereignty Over Pulau Ligitan and Pulau Sipadan (Indonesia-Malaysia) - ICJ Rep 202, P. 625 (SUMMARY)Document10 pages050 Sovereignty Over Pulau Ligitan and Pulau Sipadan (Indonesia-Malaysia) - ICJ Rep 202, P. 625 (SUMMARY)Yoshimata MakiNo ratings yet
- ELSI CaseDocument5 pagesELSI CaseBanana100% (1)
- Germany's Continental Shelf BoundariesDocument24 pagesGermany's Continental Shelf BoundariesAleezah Gertrude RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Taopa v. People of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageTaopa v. People of The PhilippinesChristine CaddauanNo ratings yet
- Continental Shelf Libya-Malta Case: FactsDocument2 pagesContinental Shelf Libya-Malta Case: FactsJessamine OrioqueNo ratings yet
- International Customs IndexDocument16 pagesInternational Customs IndexAparna SinghNo ratings yet
- International Law and Municipal LawDocument21 pagesInternational Law and Municipal LawveercasanovaNo ratings yet
- The Schooner Exchange v. McFaddonDocument3 pagesThe Schooner Exchange v. McFaddonbaird_taylorNo ratings yet
- Article 38 of The Statute of The ICJ Refers ToDocument3 pagesArticle 38 of The Statute of The ICJ Refers ToJanhvi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Law of the Sea ExplainedDocument22 pagesLaw of the Sea Explainedmansavi bihani100% (1)
- Oxford Dictionary of Law 7 EditionDocument9 pagesOxford Dictionary of Law 7 EditionManik Singh KapoorNo ratings yet
- Law of The Sea NotesDocument34 pagesLaw of The Sea NotesAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Icc, Icj, ItlosDocument1 pageIcc, Icj, ItlosmkbysNo ratings yet
- Right to Passage in Territorial WatersDocument27 pagesRight to Passage in Territorial WatersAshish RajNo ratings yet
- The Factory at Chorzow (Germany V. Poland) : TopicDocument4 pagesThe Factory at Chorzow (Germany V. Poland) : TopicJosiah BalgosNo ratings yet
- PERMANENT COURT OF INTERNATIONAL JUSTICE RULES ON CERTAIN GERMAN INTERESTS IN POLISH UPPER SILESIADocument80 pagesPERMANENT COURT OF INTERNATIONAL JUSTICE RULES ON CERTAIN GERMAN INTERESTS IN POLISH UPPER SILESIAorpeo InternationalNo ratings yet
- Developmental Phases Definitions of International LawDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Phases Definitions of International LawVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Territorial Sea Rules and SovereigntyDocument11 pagesTerritorial Sea Rules and SovereigntyDebson Martinet PahanguinNo ratings yet
- DiGEST FisheriesDocument2 pagesDiGEST FisheriesMitzi Caryl Encarnacion100% (1)
- EEZ, continental shelf, and territorial waters defined by UNCLOSDocument3 pagesEEZ, continental shelf, and territorial waters defined by UNCLOSlovehackinggalsNo ratings yet
- State ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesState Responsibilityjamot100% (1)
- UNCLOSDocument5 pagesUNCLOSjayant kashyapNo ratings yet
- Public International Law PDFDocument5 pagesPublic International Law PDFSankalp RajNo ratings yet
- Public International Law NotesDocument61 pagesPublic International Law NotesDatta JavalkarNo ratings yet
- RecognitionDocument15 pagesRecognitionNagalikar Law100% (1)
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia National Law University, LucknowDocument15 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohia National Law University, LucknowTulika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Pil (Notes On Extradition and Asylum)Document11 pagesSyllabus of Pil (Notes On Extradition and Asylum)Arshdeep Singh ChahalNo ratings yet
- International Law: Constitutionalism, Managerialism and The Ethos of Legal EducationDocument0 pagesInternational Law: Constitutionalism, Managerialism and The Ethos of Legal EducationAndreea PelinariNo ratings yet
- The Sources of International LawDocument1 pageThe Sources of International LawMika RainmanNo ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 2Document83 pages10 - Chapter 2AnantHimanshuEkka100% (1)
- Public International LawDocument133 pagesPublic International Lawtuff100% (1)
- International LawDocument201 pagesInternational LawApeksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Meaning of The State ResponsibilityDocument25 pagesMeaning of The State ResponsibilityKAYNATALINo ratings yet
- Updated Karina Rutledge 2Document22 pagesUpdated Karina Rutledge 2Anonymous RvItrLNo ratings yet
- The Codification of International Law 2Document40 pagesThe Codification of International Law 2doctrineNo ratings yet
- MCQ PDFDocument10 pagesMCQ PDFKim EstalNo ratings yet
- Guyana V SurinameDocument3 pagesGuyana V SurinameRic SaysonNo ratings yet
- Space Law: Exploring the Final FrontierDocument9 pagesSpace Law: Exploring the Final FrontierVishvas DeoNo ratings yet
- Human Rights: Previous Year's MCQs of Tripura University and Answers with Short ExplanationsFrom EverandHuman Rights: Previous Year's MCQs of Tripura University and Answers with Short ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- SEA Notes Module 3Document43 pagesSEA Notes Module 3amithamridhulanNo ratings yet
- SEA NotesDocument6 pagesSEA NotesamithamridhulanNo ratings yet
- Hydrogeology and Hydrochemistry of Shaqlawa AreaDocument11 pagesHydrogeology and Hydrochemistry of Shaqlawa AreawerewaroNo ratings yet
- Godavari (Janampet) Cauvery (Grand Anicut) Link Project EIA PDFDocument20 pagesGodavari (Janampet) Cauvery (Grand Anicut) Link Project EIA PDFsumitNo ratings yet
- Conservation Through Calibration and CommunicationDocument10 pagesConservation Through Calibration and Communicationyosi asterinaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Semester Mid Exams Multiple Choice Question PaperDocument7 pagesB.Tech Semester Mid Exams Multiple Choice Question Paperkatta vishodhanaNo ratings yet
- Urban Drought Bookchapt14 - Kapil Gupta and Vinay NikamDocument14 pagesUrban Drought Bookchapt14 - Kapil Gupta and Vinay NikamSameer PhadtareNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 0 - Part B Modelling Groundwater Flow Using FreewatDocument50 pagesTutorial 0 - Part B Modelling Groundwater Flow Using FreewatУрошМилићNo ratings yet
- Calculate RAS flow rate and ratio for wastewater treatmentDocument13 pagesCalculate RAS flow rate and ratio for wastewater treatmentAli AlibrahimiNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management in Kandy City, Sri Lankaarticle Solid WasteDocument20 pagesSolid Waste Management in Kandy City, Sri Lankaarticle Solid WastethangavelukumaranNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Law in IndiaDocument27 pagesGroundwater Law in IndiaZainy KhanNo ratings yet
- EM - 1110-2-1603 Hydraulic Design of Spillways PDFDocument170 pagesEM - 1110-2-1603 Hydraulic Design of Spillways PDFardi ainnurNo ratings yet
- SI 2020-053 Water (Subcatchment Councils) (Rates) (Amendment) Regulations, 2020 (No. 7)Document4 pagesSI 2020-053 Water (Subcatchment Councils) (Rates) (Amendment) Regulations, 2020 (No. 7)takudzwa92No ratings yet
- Automatic Sewage Cleaning MachineDocument7 pagesAutomatic Sewage Cleaning Machinevidyadhar GNo ratings yet
- Factsheet - Rebuilding After Aila Using Solar Pump Water Supply Resortation Banishanta, Dacope, KhulnaDocument2 pagesFactsheet - Rebuilding After Aila Using Solar Pump Water Supply Resortation Banishanta, Dacope, KhulnaCDMP BangladeshNo ratings yet
- 04-Water Quality and QuantityDocument46 pages04-Water Quality and QuantityAstra BeckettNo ratings yet
- World Water Day 2010 Presentation On OrissaDocument21 pagesWorld Water Day 2010 Presentation On OrissaPranab Ranjan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Atlc About UsDocument9 pagesAtlc About Usdigvijay singhNo ratings yet
- Palamuru Lift SchemeDocument2 pagesPalamuru Lift Schemevaranasirk1No ratings yet
- Low Impact Development Manual For Michigan September 2008Document512 pagesLow Impact Development Manual For Michigan September 2008Yadir Rodrìguez NùñezNo ratings yet
- DSSP Design GuidelinesDocument74 pagesDSSP Design GuidelinescherogonyaNo ratings yet
- Updated PFR 2feb After Correction SIngedDocument82 pagesUpdated PFR 2feb After Correction SIngednrks1karanpurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Integrated Water ManagementDocument10 pagesChapter 7 Integrated Water ManagementAmro HarasisNo ratings yet
- Exam Applied Hydro Geology 0405Document11 pagesExam Applied Hydro Geology 0405deshmukhgeolNo ratings yet
- CWC Hydro-Meteorological Observation ActivitiesDocument2 pagesCWC Hydro-Meteorological Observation ActivitiesHabeeb ShaikNo ratings yet
- Is 4558-1995Document11 pagesIs 4558-1995Pradeep S GowdaNo ratings yet