Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soil Mechanics - Lec 2 Symbols and Analytical Representation of The Basic Terms Related To Soil Composition and Condition
Uploaded by
ronnelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil Mechanics - Lec 2 Symbols and Analytical Representation of The Basic Terms Related To Soil Composition and Condition
Uploaded by
ronnelCopyright:
Available Formats
SOIL MECHANICS - LEC 2
SYMBOLS AND ANALYTICAL REPRESENTATION OF THE BASIC TERMS RELATED TO SOIL
COMPOSITION AND CONDITION
e = void ratio; the ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of solids
n = porosity; the ratio of the volume of voids to the total volume of soil
Dr = relative density; an index that quantifies the degree of packing between the loosest and the
densest possible state of coarse-grained soils as determined by experiments
Gs = specific gravity
ω = water/moisture content; the ratio of the weight of water to the weight of solids
S = degree of saturation; the ratio of the volume of water to the volume of voids
V = total volume of soil mass
Va = volume of air
Vs = volume of soil solids
Vw = volume of water
W = total weight of soil
Ws = weight of soil solids
Wω= weight of water
γd = dry unit weight
γm = moist/wet/bulk unit weight of soil mass
γs = unit weight of soil solids
γsat = saturated unit weight
γ = unit weight of soil per unit volume
γsub or γ' = effective/submerged/buoyant unit weight of soil mass
Table 1.0 Description based on Relative Density of Soil
Dr (%) Description
0-15 Very Loose
15-35 Loose
35-65 Medium Dense
65-85 Dense
85-100 Very Dense
Sample Problems:
1. Prove:
γd = (γ / 1 + ω)
2. A sample saturated clay was placed in a container and weighed. The weight was 6 N. The
clay in its container was placed in an oven for 24 hours at 100 °C. The weight was reduced to
a constant value of 5 N. The weight of the container is 1 N. If Gs = 2.7, determine the ff:
a. ω
b. e
c. γ
d. γd
e. γ'
You might also like
- Ground Floor Plan Second Floor Plan: Bedroom BedroomDocument1 pageGround Floor Plan Second Floor Plan: Bedroom BedroomronnelNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design: Presentation Sub TitleDocument20 pagesArchitectural Design: Presentation Sub TitleronnelNo ratings yet
- Islide Powerpoint ST Andard Template: Subtitle HereDocument39 pagesIslide Powerpoint ST Andard Template: Subtitle HereronnelNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law - How Voltage, Current, and Resistance RelateDocument7 pagesOhm's Law - How Voltage, Current, and Resistance RelateronnelNo ratings yet
- Department of Engineering Sciences: (Clsu-Cen: Bsce Program) 1Document10 pagesDepartment of Engineering Sciences: (Clsu-Cen: Bsce Program) 1ronnelNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument17 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningronnelNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mengr 3100 - Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument10 pages1 - Mengr 3100 - Basic Mechanical EngineeringronnelNo ratings yet
- I. Laplace TransformDocument35 pagesI. Laplace TransformronnelNo ratings yet
- Medicinal PlantsDocument14 pagesMedicinal Plantsronnel100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Basic (Edited)Document18 pagesThermodynamics Basic (Edited)ronnelNo ratings yet
- Computer HistoryDocument37 pagesComputer HistoryronnelNo ratings yet
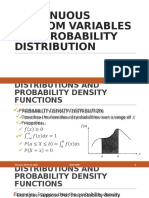
- ch4 Continuous RVDocument37 pagesch4 Continuous RVronnelNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)