Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Analysis-09-3-2021
Uploaded by
Christian John V. CamorahanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Analysis-09-3-2021
Uploaded by
Christian John V. CamorahanCopyright:
Available Formats
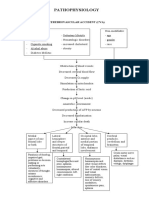
CASE ANALYSIS- SEPTEMBER 3, 2021
BERGER’S DISEASE / IgA NEPHROPATHY
Case:
§ A 15-year old SH student is suffering from recurring extremity numbness ad
hypothermic toes.
§ She is living with her father and three older brothers who are chronic smokers
§ On examination, the doctor noted no palpable pulses on the lower extremity
§ She also suffered from painful extremities for the past week. This pain goes away when
she is at rest.
§ Several open ulcers of the fingers and palms were also noted.
§ The following are significant lab results:
o Serum cholesterol: 340 mg/dL
o Platelet: 85 mg/dL
o Fibrinogen: 120 mg/dL
o A/G ratio: decreased
o Urine: Blood 3+
o Urine microscopy: Intact RBCs (12-16 hpf)
o GFR: decrased
Questions:
1. What is the patient's condition?
2. Provide the complete pathophysiology of the disease.
3. Explain the A/G ratio result and correlate it with the other signs/symptoms.
4. List 5 diagnostic tools a physician may use for diagnosis and provide a description for
each.
5. Provide medications that address not only the main cause but also the accompanying
disease manifestation.
Sir Jericho Case Questions:
What type of Gangrene is seen in this disease?
- ANSWER: Dry gangrene ( seen in arterial obstruction)
- Wet gangrene (Venous obstruction)
Why is there a need for COX (medication)?
- COX-2 inhibitors are NSAIDs that selectively block the COX-2 enzyme and not
the COX-1 enzyme. Blocking this enzyme impedes the production of prostaglandins
by the COX-2 which is more often the cause the pain and swelling of inflammation
and other painful conditions.
- Alleviate pain or suffering
Why is Codeine utilized as a medication for this condition?
- It works by changing the way the body senses pain and by cooling the body.
Codeine belongs to a class of medications called opiate (narcotic) analgesics and to a
class of medications called antitussives. When codeine is used to treat pain, it works
by changing the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain.
- It is the proform of MORPHINE
- Morphine is the best opiod analgesic
- Upon metabolism, it can be induced into an active morphine form which alleviates
pain
Leakage of albumin to other body sites. Is the decrease in A/G ratio only associated with
the leakage
- Due to the increase in IgA
- There is a decrease in ONCOTIC pressure (oncotic pressure is influenced by albumin)
What is the other name of Buerger disease?
- IgA Nepropathy
What is the end effect of albumin leakage?
- Edema
- Generalized edema (most tissues have edema): ANASARCHA
Explain positive or negative Allan’s Test.
- Allan’s test is used to determine if there is appropriate or adequate supply of blood
- The test is negative when there is a return of normal color to both hands
during occlusion of either artery alone. A positive test will be with persistent pallor
in the palm, indicating no collateral blood flow to the hand.
- Positive: No return of flushing after 10-15 seconds. No sufficient blood supply ( you
will know the patient is suffering from occlusion)
- Negative: return of flushing after 10-15 seconds. GOOD
- Simple Allen’s Test: only one hand or arm
- Modified Allen’s Test: Two hands or arm
What is the end effect of thrombosis why the patient suffered from gangrene?
- Embolus
Why are vasculatures occluded (what is the source of occlusion)?
- Embolus
- Embolism occurs when a piece of a blood clot, foreign object, or other bodily
substance becomes stuck in a blood vessel and largely obstructs the flow of blood.
Why PMNs predominate in this condition?
- Granulomas are formed in PMNs which lead to the formation of a thrombus, so ang
PMNs are part of a thrombus, pero ngaa may increase ka PMN before this ?
- The PMNs are the earliest repsonders to inflammation or damage, so may concurrent
damage sa blood vessels, so kay damage, ang PMNs ga respond which ingest materials
from the site of injury
- They are first responders! Together with the chemokines
- They become trap sa formation of thrombus
What condition is similar to Berger’s disease that is related to coldness or numbness together
with tingling sensation (Reynaud’s syndrome) and this syndrome is usually mistaken as
Berger’s due to these manifestations? (What condition is similar to Reynaud’s syndrome
phenomenon that may be mistaken as Berger’s, and what lab test is used to differentiate it?
- This test is positive for CAD but negative for Berger’s (ANSWER: CAT or Cold Agglutinin
Test)
What other APR is inversely proportional (the protein that decreases during inflammation)?
- This protein decreases together with albumin
- CRP is a positive ADR
- transferrin
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Main Topic - Heading 1: Clinical MicrosDocument23 pagesMain Topic - Heading 1: Clinical MicrosChristian John V. CamorahanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Immunology & Serology: Safety and Specimen PreparationDocument25 pagesImmunology & Serology: Safety and Specimen PreparationChristian John V. CamorahanNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- September - 6 - 2021-For - Students (HEMA)Document24 pagesSeptember - 6 - 2021-For - Students (HEMA)Christian John V. CamorahanNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- SEPTEMBER 6, 2021 Hematology Assessment: Characteristic FeaturesDocument23 pagesSEPTEMBER 6, 2021 Hematology Assessment: Characteristic FeaturesChristian John V. CamorahanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY PRETEST ReviewDocument10 pagesCLINICAL CHEMISTRY PRETEST ReviewChristian John V. CamorahanNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Coagulation and FibrinolysisDocument9 pagesMechanisms of Coagulation and FibrinolysisChristian John V. CamorahanNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologynitlihpNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument2 pagesNephrotic SyndromeAnnruby NefielNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Preoperative Assessment of The Patient With Heart Disease Case FileDocument2 pagesPreoperative Assessment of The Patient With Heart Disease Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Group 15 DM ModuleDocument38 pagesGroup 15 DM ModuleJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Central Auditory Processing DisordersDocument3 pagesCentral Auditory Processing DisordersGina Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Oxytocics: Adverse EffectsDocument3 pagesOxytocics: Adverse EffectsMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Tetanus: Guerrero, Djameica Danielle RDocument16 pagesTetanus: Guerrero, Djameica Danielle RDjameica GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Varicella Zoster VirusDocument13 pagesVaricella Zoster VirusyatikriyaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Need of Health Sector Indicators (Reviesd)Document11 pagesNeed of Health Sector Indicators (Reviesd)Sadikshya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- P1337420319157 Inda Helma YunitaDocument2 pagesP1337420319157 Inda Helma YunitaInda HelmaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- KI Health 75th FinalDocument127 pagesKI Health 75th FinalChandrimaChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument9 pagesAbdominal Aortic AneurysmIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Music and Art TherapyDocument6 pagesMusic and Art TherapyIanne Ranchez100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MICP211 Midterm ReviewerDocument39 pagesMICP211 Midterm ReviewerKrista CruzNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Skeletal Muscle System OSCE ExaminationDocument14 pagesSkeletal Muscle System OSCE ExaminationMaryam A Albalooshi100% (2)
- CIVIL SERVICE FORM 41 Medical CertificateDocument1 pageCIVIL SERVICE FORM 41 Medical CertificateElc Elc ElcNo ratings yet
- Sas 1 60 Multiple Choice Converted CompressedDocument153 pagesSas 1 60 Multiple Choice Converted CompressedRoswell Almodiel EscaranNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Contribution To SrinivasaDocument11 pagesMathematics - Contribution To SrinivasaSakshi RaniNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument56 pagesCase AnalysisTricia Denise EstabilloNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesQuestionnairevin_jai08100% (1)
- Laparaskopi PeritonitisDocument5 pagesLaparaskopi PeritonitisPutri RiszaNo ratings yet
- Edit NG Drug StudyDocument35 pagesEdit NG Drug StudyAlleinad BarracasNo ratings yet
- Handbook OHSDocument78 pagesHandbook OHSMiruna IliescuNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Disease Detectives Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDisease Detectives Cheat Sheetgolumnaa76% (58)
- Mapeh Performance Task Preventing Communicable DiseaseDocument1 pageMapeh Performance Task Preventing Communicable Diseasenina pascualNo ratings yet
- Lymphoma CancerDocument34 pagesLymphoma CancerwasihaiderkNo ratings yet
- Drugs Behaviour and Modern Society Canadian 1st Edition Hamilton Test BankDocument49 pagesDrugs Behaviour and Modern Society Canadian 1st Edition Hamilton Test Bankmichelleortizpxnzkycmbw100% (27)
- DD ShockDocument34 pagesDD Shockمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- Principles of Diuretic Therapy: Dr. Rania Magadmi, MBBS, PHDDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Diuretic Therapy: Dr. Rania Magadmi, MBBS, PHDمشاعرمبعثرةNo ratings yet
- Family MedicineDocument99 pagesFamily MedicineChris Jardine LiNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)