Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 3-5
Uploaded by
Madhuri MukherjeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 3-5
Uploaded by
Madhuri MukherjeeCopyright:
Available Formats
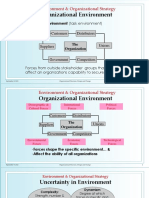
Environment & Organizational Strategy
Organizational Environment
Specific Environment (task environment)
Customers Distributors
The Unions
Suppliers
Organization
Government Competitors
Forces from outside stakeholder groups that directly
affect an organizations capability to secure resources
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 1
Environment & Organizational Strategy
Organizational Environment
Demographic & International Political
Cultural Forces Forces Forces
Customers Distributors
The Unions
Suppliers
Organization
Government Competitors
Environmental Economic Technological
Forces Forces Forces
-Forces shape the specific environment… &
-Affect the ability of all organizations
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 2
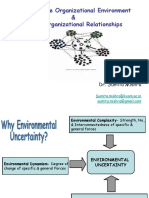
Environment & Organizational Strategy
Uncertainty in Environment
Dynamism:
Complexity: Degree at which
Strength, number & forces in specific and
Interconnectedness of generic environments
specific and change quickly
generic forces over time
Richness:
Amount of resources
available to support
an organization’s
domain
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 3
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 4
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 5
Organization & its Environment
Resource Dependence Theory
The goal of an organization is to minimize its
dependence on other organizations for the supply of
scare resources and to find ways of influencing them
to make resources available
− It has to exert influence over other organizations
so that it can obtain resources
− It must respond to the needs and demands of the other
organizations in its environment
Dependence on resource is determined by
• Criticality of the resource
• Scarcity of the resource
E.g.: CRY, Nuclear Agreement
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 6
Resource Dependence Theory
• Assume that your organization (XYZ) need a critical
input that is available from only one supplier (ABC,
which enjoys monopoly) & there is no substitute for it.
• More over there are at least four competing
organizations which are already getting the same
critical input from ABC and develop comparable and
competing products of your organization.
• It is impossible for you to diversify in the
short/medium term for multiple reasons.
You are expected to reduce the dependence of XYZ on
ABC; What are the possible options?
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 7
Organization & its Environment
Managing Resource Dependence
Two basic types of interdependencies to address
uncertainty
− Symbiotic interdependencies: interdependencies that
exist between an organization and its suppliers and
distributors (Vertical integration strategies)
− Competitive interdependencies: interdependencies that
exist among organizations that compete for scarce inputs
and outputs (Horizontal integration strategies)
Organizations aim to choose the interorganizational
strategy that offers the most reduction in uncertainty
with least loss of control
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 8
Environment & Organizational Strategy
Uncertainty in Environment
Symbiotic interdependence:
Informal Formal
Strategic Merger &
Reputation Co-optation
Alliance Takeover
Long-term Minority Joint
Networks
contracts Ownership Ventures
Competitive Interdependencies:
Collusion 3rd Party Strategic Merger &
and Cartels Linkage Alliance Takeover
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 9
Organization & its Environment
Transaction Cost Theory
• Transaction costs:
− The costs of
negotiating, monitoring, and governing
exchanges between people
• Transaction cost theory:
− A theory that states that
the goal of an organization is to minimize the costs of
a) exchanging resources in the environment and
b) managing exchanges inside the organization
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 10
Sources of Transaction Costs
Conditions wherein transaction cost is low/high..
Human & environmental factors
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 11
Organization & its Environment
Transaction Cost Theory
Bureaucratic costs: internal transaction costs
− Bringing transactions inside the organization minimizes
but does not eliminate the costs of managing transaction
• Managers deciding which strategy to pursue must take
the following steps:−
− Locate the sources of transaction costs that may affect an
exchange relationship and decide extent of transaction costs
− Estimate the transaction cost savings from using different
linkage mechanisms
− Estimate the bureaucratic costs of operating the linkage
mechanism
− Choose the linkage mechanism that gives the most transaction
cost savings at the lowest bureaucratic cost
December 11, 2020 Organizational Structure, Design and Change 12
Evolving Design of Organizations
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 13
Figure 4.1: Design Challenge (cont.)
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 14
Figure 4.1: Design Challenge (cont.)
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 15
Figure 4.1: Design Challenge (cont.)
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 16
Figure 4.1: Design Challenge (cont.)
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 17
Differentiation
• The process by which an organization allocates
people and resources to organizational tasks
• Establishes the task and authority relationships
that allow the organization to achieve its goals
Division of labor: the degree of specialization in the
organization
• In a simple organization, differentiation is low
because the division of labor is low
− Individuals typically perform all organizational
tasks
• In a complex organization, differentiation is high
because the division of labor is high
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 18
Organizational Chart of the B.A.R. and Grille
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 19
Balancing Differentiation and Integration
• Horizontal differentiation is supposed to enable
people to specialize and become more productive
− Specialization often limits communication between
subunits
− People develop subunit orientation
• Subunit orientation: a tendency to view one’s role in
the organization strictly from the perspective of the
time frame, goals, and interpersonal orientations of
one’s subunit
Integration: the process of coordinating various tasks,
functions, and divisions so that they work
together and not at cross-purposes
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 20
Organizational Structure: Introduction…
Concept of Integration
Integrating Mechanisms
− Hierarchy of authority
− Direct Contact
− Liaison Role
− Task Force
− Team
− Integrating Role
− Integrating Department
Choose the best integrative mechanism… (Group Activity)
Conflict between Finance and HR department (pay roll processing)
Pollution control board certificate
Hiring a supervisor to handle conflict between cooks and waiters
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 21
Balancing Centralization and Decentralization
Centralized organization: the authority to make important
decisions is retained by top level managers
− Top managers able to coordinate activities to keep the
organization focused on its goals
Decentralized organization: the authority to make important
decisions is delegated to managers at all levels in the
hierarchy
− Promotes flexibility and responsiveness
Ideal balance entails:
− Enabling middle and lower managers who are at the scene
of the action to make important decisions
− Allowing top managers to focus on long-term strategy
making
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 22
Balancing Standardization and
Mutual Adjustment
• Standardization: conformity to specific models or
examples that are considered proper in a given
situation
− Defined by rules and norms
• Mutual adjustment: the process through which
people use their judgment rather than standardized
rules to address problems, guide decision making, and
promote coordination
− Formalization: the use of rules and procedures to
standardize operations
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 23
Organizational Structure: Introduction…
Organizational Design Challenges
1) How to Differentiate (and reporting relations)
2) Balancing Differentiation & Integration
3) Balancing Centralization & Decentralization
4) Balancing Standardization & Mutual
Adjustment
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 24
Mechanistic and Organic Structures
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 25
Task and Role Relationships
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 26
Functional Differentiation in Uncertain
Environment
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 27
Environmental Uncertainty and Structure
Burns and Stalker
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 28
Organizational Design: Authority and Control
Authority: Origin of Vertical Differentiation
Structure in laymen’s language
To deal with coordination and motivation problems, the
organization can:
− Increase the number of managers it uses to
monitor, evaluate, and reward employees
− Increase the number of levels in its managerial
hierarchy
• Size and height limitations
− Tall organization:
− Flat organization:
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 29
Organizational Structure: Authority and Control
No. of Hierarchical Levels
Ideal number of hierarchical levels determined by:
− Principle of minimum chain of command: an organization
should choose the minimum number of hierarchical levels
consistent with is goals and the environment in which it
operates
− Span of control: the number of subordinates a manager
directly manages
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 30
Organizational Structure: Authority and Control
No. of Hierarchical Levels
Factors that determine the appropriate span of control
− Manager’s ability for adequate supervision of increasing
number of subordinates
− Complexity and interrelatedness of the subordinates’ tasks
• Complex, dissimilar, interrelated tasks – small span of control
• Routine, similar, unrelated tasks – large span of control
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 31
Organizational Structure: Authority and Control
Factors Affecting the Shape of the Hierarchy
12/11/2020 2:40 PM Organizational Structure, Design and Change 32
You might also like
- Reimagining Industry Growth: Strategic Partnership Strategies in an Era of UncertaintyFrom EverandReimagining Industry Growth: Strategic Partnership Strategies in an Era of UncertaintyNo ratings yet
- Environment & Organizational StrategyDocument41 pagesEnvironment & Organizational StrategyBhargav D.S.No ratings yet
- A Guide to Collaboration: Working Models of Comprehensive Community ProjectsFrom EverandA Guide to Collaboration: Working Models of Comprehensive Community ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SlidesDocument15 pagesChapter 3 SlidesShivamNo ratings yet
- Empirical Note on Debt Structure and Financial Performance in Ghana: Financial Institutions' PerspectiveFrom EverandEmpirical Note on Debt Structure and Financial Performance in Ghana: Financial Institutions' PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document17 pagesCH 3Sampurna SenNo ratings yet
- Managing The Organizational EnvironmentDocument19 pagesManaging The Organizational EnvironmentAmit BeheraNo ratings yet
- Organizational EnvironmentDocument14 pagesOrganizational Environmentsanjay28382No ratings yet
- Managing The Organizational EnvironmentDocument28 pagesManaging The Organizational EnvironmentSHUBHRANSHU SAHOONo ratings yet
- Table Ga LengkapDocument17 pagesTable Ga Lengkapnining zebuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6. Interorganizational RelationshipsDocument49 pagesLecture 6. Interorganizational Relationshipschiarazando34No ratings yet
- Business Environment: Management ExtraDocument30 pagesBusiness Environment: Management ExtraAmit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Resource Dependency and Transaction Cost Economics TheoriesDocument34 pagesResource Dependency and Transaction Cost Economics TheoriesMuhammad Waqar KhanNo ratings yet
- 19 - Competitive and Collaborative StrategiesDocument16 pages19 - Competitive and Collaborative StrategiesShweta BatraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2ShivamNo ratings yet
- Lavie 2006 - The Competitive Advantage of Interconnected FirmsDocument22 pagesLavie 2006 - The Competitive Advantage of Interconnected FirmsRodolfo StraussNo ratings yet
- Learning Leading To Creation of Solutions: Illustration Using Stakeholder TheoryDocument12 pagesLearning Leading To Creation of Solutions: Illustration Using Stakeholder TheoryMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- L2 - CSR Collaboration PDFDocument26 pagesL2 - CSR Collaboration PDFCLNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Business Environment - RDocument44 pages1 Introduction To Business Environment - RRupesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Stakeholders-Ethics Governance Social Responsibility-SustainabilityDocument25 pagesStakeholders-Ethics Governance Social Responsibility-Sustainabilityfirman prabowoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organizations Management - Session 1 & 2Document67 pagesIntroduction To Organizations Management - Session 1 & 2Keshi SavindraniNo ratings yet
- Hospitality Strategic ManagementDocument21 pagesHospitality Strategic ManagementNIK MOHAMAD ZULFADLI NIK MOHD FAHMINo ratings yet
- CH 1, Star Model, Competing Value FrameworkDocument22 pagesCH 1, Star Model, Competing Value FrameworkMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- b820 Strategy SlidesDocument99 pagesb820 Strategy Slidesmanny100100% (1)
- BUS 516 - Chapter 3 - IS, Organizations and StrategyDocument60 pagesBUS 516 - Chapter 3 - IS, Organizations and StrategyArju LubnaNo ratings yet
- Ma WebDocument14 pagesMa WebabhirejanilNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management BooksDocument24 pagesEngineering Management BooksFurqan RazaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0925527322003036 MainDocument22 pages1 s2.0 S0925527322003036 MainCat Minh HaNo ratings yet
- 5 Interorganizational RelationshipsDocument5 pages5 Interorganizational RelationshipsNamir RafiqNo ratings yet
- MIT Open Courseware Project Management - 2009Document186 pagesMIT Open Courseware Project Management - 2009Illyanna FoxNo ratings yet
- CH-2envronment &cultureDocument23 pagesCH-2envronment &cultureAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- MP06B0000025Document17 pagesMP06B0000025Alehegn ZurbetNo ratings yet
- CBCI Follow Up - Extra SlidesDocument80 pagesCBCI Follow Up - Extra SlidesSelim NalbantNo ratings yet
- Week 12 Organizational Structure, System ProcessDocument58 pagesWeek 12 Organizational Structure, System ProcessAngeline TanriNo ratings yet
- Marketin Management IIDocument13 pagesMarketin Management IILilla OroviczNo ratings yet
- Stakeholders in Corporate Governance (CG) and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)Document28 pagesStakeholders in Corporate Governance (CG) and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)Ruwan DileepaNo ratings yet
- 6 Sector Comparison WorksheetDocument6 pages6 Sector Comparison Worksheetapi-720147459No ratings yet
- Stakeholder Management & CommunicationDocument35 pagesStakeholder Management & CommunicationalbertNo ratings yet
- IBM - Week 3Document27 pagesIBM - Week 3Pranav TatavarthiNo ratings yet
- Week 12 Decision Making and Strategy ApplicationDocument22 pagesWeek 12 Decision Making and Strategy ApplicationKimemia KimothoNo ratings yet
- AMS IB 2023 - Session 09 Cooperation and MMCDocument31 pagesAMS IB 2023 - Session 09 Cooperation and MMCtommeastridNo ratings yet
- AIBE 2020 Stakeholders CC v1Document22 pagesAIBE 2020 Stakeholders CC v1Kenny MakNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure & HR Alignment: Managing StakeholdersDocument17 pagesOrganizational Structure & HR Alignment: Managing StakeholdersBhargav D.S.No ratings yet
- Topic 7 - STRATEGIC RELATIONSHIPSDocument17 pagesTopic 7 - STRATEGIC RELATIONSHIPSsara6anneNo ratings yet
- Designing Organization Project: BPCL: A Fortune 500, Maharatna Oil & Gas CompanyDocument15 pagesDesigning Organization Project: BPCL: A Fortune 500, Maharatna Oil & Gas CompanyAtul MishraNo ratings yet
- The Environment of Management: Management Dynamics Prof. Joy PollosoDocument52 pagesThe Environment of Management: Management Dynamics Prof. Joy PollosoCuster CoNo ratings yet
- MBA Strategic Management Unit IIDocument16 pagesMBA Strategic Management Unit IImansi_veerwal0% (1)
- Organization & Principles: "It's All About WorkingDocument41 pagesOrganization & Principles: "It's All About WorkingEVISHA SONI 1927233No ratings yet
- Integrated Reporting (IR)Document6 pagesIntegrated Reporting (IR)Iron PatriotNo ratings yet
- 3 Cultures, Ethics and Corporate GovernanceDocument25 pages3 Cultures, Ethics and Corporate GovernanceMY TRAN THI TRANo ratings yet
- Interorganisational Strategies For Managing Resources: Anu JoyDocument9 pagesInterorganisational Strategies For Managing Resources: Anu JoyjoyanuNo ratings yet
- Institution Building For Sustainable Development Learning BookletDocument37 pagesInstitution Building For Sustainable Development Learning BookletRajiv RanjanNo ratings yet
- Organization 1Document1 pageOrganization 1laobianxxNo ratings yet
- Internal Environment: Capabilities and Competencies: Chapter FiveDocument33 pagesInternal Environment: Capabilities and Competencies: Chapter FiveHammar Bokingo100% (1)
- AB3602 Week 9 - Cooperative StrategyDocument55 pagesAB3602 Week 9 - Cooperative StrategyxcjkxcjkNo ratings yet
- Strategic Relationship 1Document7 pagesStrategic Relationship 1Risma SylvaraniNo ratings yet
- Session 2.5 Two Areas of Underdeveloped Potential - Tald JakartaDocument9 pagesSession 2.5 Two Areas of Underdeveloped Potential - Tald JakartaMark Jonathan SacataniNo ratings yet
- The Environmental Context of ManagementDocument16 pagesThe Environmental Context of ManagementOm Prakash BhandariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Stakeholder Relationships, Social Responsibility, and Corporate GovernanceDocument20 pagesChapter 2 - Stakeholder Relationships, Social Responsibility, and Corporate GovernanceAisa TriNo ratings yet
- HRM in Business PerspectiveDocument15 pagesHRM in Business PerspectiveMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-8Document32 pagesChapter 6-8Madhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- List of Resources Against Assignment Class Participation - 1Document12 pagesList of Resources Against Assignment Class Participation - 1Madhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- CH 1, Star Model, Competing Value FrameworkDocument22 pagesCH 1, Star Model, Competing Value FrameworkMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Learning Leading To Creation of Solutions: Illustration Using Stakeholder TheoryDocument12 pagesLearning Leading To Creation of Solutions: Illustration Using Stakeholder TheoryMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- OB13 - TIF16 - Foundations of Organization StructureDocument26 pagesOB13 - TIF16 - Foundations of Organization StructureMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- OB13 TIF17 Organizational CultureDocument28 pagesOB13 TIF17 Organizational CultureMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Walt Disney To Restructure India Operations..: The Elements of The Star Model Mentioned in The ArticlesDocument2 pagesWalt Disney To Restructure India Operations..: The Elements of The Star Model Mentioned in The ArticlesMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Walt Disney: Organizational Design Considering STAR Model 1. ANALYSIS MATRIX For Identifying Elements of STAR ModelDocument2 pagesWalt Disney: Organizational Design Considering STAR Model 1. ANALYSIS MATRIX For Identifying Elements of STAR ModelMadhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Structural Changes at Mahindra (Feb 2016 To Dec 2019)Document3 pagesStructural Changes at Mahindra (Feb 2016 To Dec 2019)Madhuri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- OPHRM - Session 1-10 Notes - MMDocument35 pagesOPHRM - Session 1-10 Notes - MMMadhuri Mukherjee100% (8)
- Integrated Chinese Vol 4 TextbookDocument444 pagesIntegrated Chinese Vol 4 Textbookcuriousbox90% (10)
- Language and The Pursuit of Hap - Chalmers BrothersDocument1,184 pagesLanguage and The Pursuit of Hap - Chalmers BrothersGeorge Adrian Oprea100% (2)
- Experiment 3: Illumination Design of Dental Clinic: B. Lighting StandardDocument16 pagesExperiment 3: Illumination Design of Dental Clinic: B. Lighting StandarderizaNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Yaw Rate Estimation Using A Virtual SensorDocument14 pagesVehicle Yaw Rate Estimation Using A Virtual Sensorbnc1No ratings yet
- 8 GraphsFundamentalsDocument28 pages8 GraphsFundamentalsguptharishNo ratings yet
- The Future of Humanity ProjectDocument8 pagesThe Future of Humanity Projectapi-563597519No ratings yet
- Weekly Progress Report PDFDocument7 pagesWeekly Progress Report PDFHeak Hor50% (2)
- Les Lac Inset Monitoring FormDocument57 pagesLes Lac Inset Monitoring FormKim Sang AhNo ratings yet
- Contoh Teks HortatoryDocument4 pagesContoh Teks HortatoryZonia AlqanitaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics DPPDocument10 pagesElectrostatics DPPhimesh2006hNo ratings yet
- 312 Full-3Document8 pages312 Full-3Le TrungNo ratings yet
- Literature & MedicineDocument14 pagesLiterature & MedicineJoyce LeungNo ratings yet
- Route TrainingDocument14 pagesRoute Trainingjohn100% (1)
- General Education Final CoachingDocument22 pagesGeneral Education Final CoachingRochelle ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Watson SPEECH TO TEXT Code Snippet.rDocument2 pagesWatson SPEECH TO TEXT Code Snippet.rLucia Carlina Puzzar QuinteroNo ratings yet
- PH G12 S1Document9 pagesPH G12 S1mahmoudNo ratings yet
- How To Disassemble Dell Inspiron 17R N7110 - Inside My LaptopDocument17 pagesHow To Disassemble Dell Inspiron 17R N7110 - Inside My LaptopAleksandar AntonijevicNo ratings yet
- 20years Cultural Heritage Vol2 enDocument252 pages20years Cultural Heritage Vol2 enInisNo ratings yet
- Purple Futuristic Pitch Deck PresentationDocument10 pagesPurple Futuristic Pitch Deck PresentationRidzki F.RNo ratings yet
- Environmental Accounting From The New Institutional Sociology Theory Lens: Branding or Responsibility?Document16 pagesEnvironmental Accounting From The New Institutional Sociology Theory Lens: Branding or Responsibility?abcdefghijklmnNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes AJk 9th Class Chap6Document3 pagesPhysics Notes AJk 9th Class Chap6Khizer Tariq QureshiNo ratings yet
- Part 6 CapacitorWorksheetDocument2 pagesPart 6 CapacitorWorksheetMARIANNE ALEXIE DIAZNo ratings yet
- Courses Offered in Spring 2015Document3 pagesCourses Offered in Spring 2015Mohammed Afzal AsifNo ratings yet
- Course Reader For Chapter IiiDocument33 pagesCourse Reader For Chapter Iiipau baniagaNo ratings yet
- BE Physics-Solution PDFDocument235 pagesBE Physics-Solution PDFRajeev PaudelNo ratings yet
- Owner's Manual Pulsar NS160Document52 pagesOwner's Manual Pulsar NS160arNo ratings yet
- Sop 905Document10 pagesSop 905harryNo ratings yet
- Franchise Model For Coaching ClassesDocument7 pagesFranchise Model For Coaching ClassesvastuperceptNo ratings yet
- Software Lab Assignment 2Document4 pagesSoftware Lab Assignment 2atatsalamaNo ratings yet
- Financial and Economic Texts' Translation - 2 PGDocument2 pagesFinancial and Economic Texts' Translation - 2 PGbia1209No ratings yet