Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 3 (Diagnosis)
Uploaded by
zakaria hossainCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 3 (Diagnosis)
Uploaded by
zakaria hossainCopyright:
Available Formats
General Medicine
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
The term diagnosis is derived from Greek word 'dia' means through and 'gnosis' means
recognizing.
The art or act of recognization of the disease affecting the patient.
Field diagnosis /Presumptive diagnosis:
Based on
❖ Epidemiological data
❖ Clinical history
❖ Clinical findings
❖ Physical findings of specimen
❖ Results of rapid diagnostic test
❖ Necropsy findings
Clinical diagnosis
Based on
❖ Clinical history
❖ Clinical findings
Laboratory diagnosis
Based on
❖ Collection of samples
❖ Identification of the causative agents in the
collected samples
Confirmatory diagnosis / Final diagnosis / Definite diagnosis
Based on
❖ Interpretation of history and clinical findings
❖ Laboratory report of the tested samples
Clinical diagnosis:
Clinical diagnosis is a field diagnosis, is based on clinical findings such as clinical
characteristics.
Presumptive diagnosis
PD is a diagnosis which is assumed as true or valid until the contrary is proved. PD is based
on non-laboratory field based holistic data (animal reproduction, management data,
epidemiologic data, and etiologic data) and reductionistic data (signalment, anamnesis, clinical
Prepared by Dr. Md. Shamim Ahasan
General Medicine
signs, physical signs, physical findings of specimens, response to treatment or preventive
measures and necropsy data etc.)
Field diagnosis
A non-laboratory, presumptive diagnosis is based on interpretation of significant holistic
data (eg. Signalment, distribution), clinical data (clinical characteristics), response to treatment
and necropsy data and final diagnosis based on the interpretation of field and / or laboratory data.
Prepared by Dr. Md. Shamim Ahasan
General Medicine
Prepared by Dr. Md. Shamim Ahasan
General Medicine
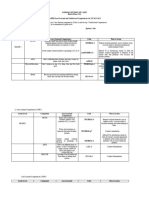
Steps Methods of examination Aims and objectives
Step 1:History taking
Clinical history Recording of: Patient data, Disease history, and
Management history
Step 2:Examination of the environment:
Indoor and outdoor environments Determines the relationship between environmental
factors and the incidence of disease.
Step 3:Examination of patient:
(A) General examination Determines the physical abnormalities and
(a) Distant inspection manifestations of diseases.
(b) Close examination of vital signs Records temperature, pulse and respiratory rates.
(c) Physical examination:
Palpation, Percussion & Determines the abnormalities in organs and systems.
Auscultation
(B) Special examination Determines the body regions and systems affected.
(a) Examination of body regions and systems
(b) Examination of identified system Determines the location of lesions in organs and
radiography and other techniques. systems.
(c) Examination of lesions‘ Biopsy and fluid’
Determines types of lesions.
Step 4:Laboratory examination of
specimens:
Blood, urine, feces, soils - Determines the specific cause of disease.
Micro-parasitological techniques
Prepared by Dr. Md. Shamim Ahasan
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Iap CoverDocument22 pagesIap CoverJeshella Roxas0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Global Pharmaceutical Industry Case Study Scenario PlanningDocument4 pagesThe Global Pharmaceutical Industry Case Study Scenario PlanningIke Ten100% (1)
- CP 102 Syllabus NWDocument4 pagesCP 102 Syllabus NWSarahLabadanNo ratings yet
- Endogenous Hyperthermia (Fever) &toxaemiaDocument9 pagesEndogenous Hyperthermia (Fever) &toxaemiazakaria hossainNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Imbalance - Powerpoint - LectureDocument53 pagesFluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Imbalance - Powerpoint - Lecturezakaria hossainNo ratings yet
- Immunology and Serology SolutionDocument17 pagesImmunology and Serology Solutionzakaria hossainNo ratings yet
- Protozoology PDFDocument27 pagesProtozoology PDFzakaria hossainNo ratings yet
- Care ReportDocument23 pagesCare ReportSindi Muthiah UtamiNo ratings yet
- Faktor Perilaku Dan Gaya Hidup Yang Mempengaruhi Status Prediabetes Pasien Puskesmas Pati IIDocument14 pagesFaktor Perilaku Dan Gaya Hidup Yang Mempengaruhi Status Prediabetes Pasien Puskesmas Pati IITinaNo ratings yet
- Caitlin Berge Resume and ReferencesDocument2 pagesCaitlin Berge Resume and Referencesapi-453476924No ratings yet
- Tormax United Kingdom - Imotion 2202 - Operations - Instructions For UseDocument20 pagesTormax United Kingdom - Imotion 2202 - Operations - Instructions For UseRico AndrianNo ratings yet
- 2022 Children's Month CelebrationDocument3 pages2022 Children's Month Celebrationjoemar cafrancaNo ratings yet
- Association of Thrombotic Markers With Severity of Pediatric-Onset Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument3 pagesAssociation of Thrombotic Markers With Severity of Pediatric-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosusalfaz zamzamiNo ratings yet
- Least Learned Skills in MapehDocument6 pagesLeast Learned Skills in MapehDiana ValienteNo ratings yet
- Tle 10 Workplace HazardsDocument35 pagesTle 10 Workplace HazardsXavierNo ratings yet
- English Resume (Circumcision)Document1 pageEnglish Resume (Circumcision)Siti WidyawatiNo ratings yet
- SAD Social Anxiety DisorderDocument5 pagesSAD Social Anxiety Disorderselina shakyaNo ratings yet
- Stramonium and Lyssinum - The Rabies Miasm 1Document34 pagesStramonium and Lyssinum - The Rabies Miasm 1Suriya OsmanNo ratings yet
- (M1-E1) Evaluación (Prueba) - r.19 - Inglés III CoaDocument6 pages(M1-E1) Evaluación (Prueba) - r.19 - Inglés III CoaBrujo Chilote SelknamNo ratings yet
- Drilling Report of Nov - Dec 2017 (PT - KMP)Document136 pagesDrilling Report of Nov - Dec 2017 (PT - KMP)Vicho RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 1.case Study in Canine Intestinal LymphangiectasiaDocument5 pages1.case Study in Canine Intestinal LymphangiectasiaIhda AdilaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus IOM B.pharmaDocument56 pagesSyllabus IOM B.pharmaks0259415No ratings yet
- MainDocument14 pagesMainAntikNo ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDocument6 pagesNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryQuennie AlamNo ratings yet
- Reviewer C AnswersDocument39 pagesReviewer C AnswersDavis WhiteNo ratings yet
- Change Theory Project: Exploring Lewin's Force-Field Model of ChangeDocument15 pagesChange Theory Project: Exploring Lewin's Force-Field Model of ChangeInna NaraievskaNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work in Grade IiiDocument47 pagesBudget of Work in Grade IiiGlenda Audije ApiagNo ratings yet
- Walia 2018Document56 pagesWalia 2018Andre Arcondo LopezNo ratings yet
- Master The Boards Usmle Step 2 CKDocument2 pagesMaster The Boards Usmle Step 2 CKmbehar090% (1)
- Colon CancerDocument17 pagesColon CancerYaska MusaNo ratings yet
- Lignana LinhacaDocument5 pagesLignana Linhacaclissia croelhasNo ratings yet
- Judicial Independence ZimDocument49 pagesJudicial Independence ZimColias DubeNo ratings yet
- MSC in Clinical Epidemiology Course Outline 2015Document24 pagesMSC in Clinical Epidemiology Course Outline 2015Neo Mervyn MonahengNo ratings yet
- God Created YouDocument232 pagesGod Created YouYayra De SouzaNo ratings yet