79% found this document useful (14 votes)
51K views19 pagesModern History Timeline
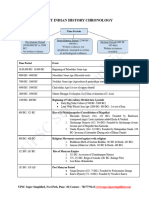
This is the timeline or a chronology of the British era when the control of India were there in the hands of British crown i.e., from 1857 to 1947 (Revolt of 1857 till India got Independence.
Uploaded by
Krishan JangidCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
79% found this document useful (14 votes)
51K views19 pagesModern History Timeline
This is the timeline or a chronology of the British era when the control of India were there in the hands of British crown i.e., from 1857 to 1947 (Revolt of 1857 till India got Independence.
Uploaded by
Krishan JangidCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Birth of Nationalism (1857 - 1885): Covers the events marking the beginning of Indian nationalism, including the 1857 Revolt and subsequent key reforms and movements.
- Moderate Phase of Indian Nationalism (1885 - 1905): Details the rise of moderate Indian nationalism with the formation of the Indian National Congress and other reform movements.
- Extremist Phase of Indian Nationalism (1906 - 1916): Describes the split in Congress and the rise of extremist factions advocating for more radical approaches.
- Gandhian Era (1917 - 1947): Chronicles the period of Mahatma Gandhi's influence over the Indian independence movement, including key campaigns and changes leading to independence.