Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study Materials For Rhythm II Presentation
Uploaded by
Dat Phan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesOriginal Title
19. Study Materials for Rhythm II Presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesStudy Materials For Rhythm II Presentation
Uploaded by
Dat PhanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Study Materials for Rhythm II Presentation
1. What is the cause of a heart block dysrhythmia?
a. An ectopic focus originates above the ventricle
b. The rhythm originates at the AV junctional tissue, producing retrograde depolarization.
c. The electrical current has difficulty traveling down the normal conduction pathway
d. An ectopic beat that originates in the right or left atria
2. People with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are born with an extra electrical pathway
between the upper chambers of the heart (atria) and the lower chambers (ventricles). This extra
pathway makes which of the following more likely to occur?
a. Abnormally fast heart rhythms
b. Myocardial Infarction
c. Hypertension
d. Cardiomyopathy
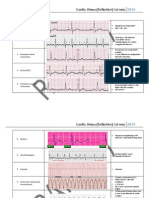
3. What is the key finding(s) on the ECG below?
a. Left ventricular hypertrophy
b. Right Ventricular hypertrophy
c. Sick sinus Syndrome
d. Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
4. A 5O-year-old woman with an ST-segment elevation MI is being prepared for transport to the
cardiac catheterization laboratory. Aspirin has been given, a heparin drip has been started, and a
portable cardiac monitoring device is attached. Vital signs are stable and within normal limits,
and there are no findings of heart failure, but she is still experiencing chest pain. A rhythm strip
is obtained (Figure below). What is the most appropriate next step?
a. Delay transport to administer an amiodarone drip
b. Delay transport to administer atropine and monitor the effects
c. Do not delay transport
d. Do not delay transport but prepare for possible transvenous pacemaker placement
5. A 42-year-old woman presents with progressive shortness of breath of 5 days' duration. She has
a history of chronic renal failure and is on hemodialysis Vital signs include blood pressure 95/50,
pulse 110, respirations 24, and oxygen saturation 95% on room air. An ECG is obtained (Figure
below). While waiting for chest radiography, she becomes increasingly pale and dusky, and her
systolic pressure progressively decreases to 70 mm Hg with only transient response to
intravenous fluid resuscitation. What is the most effective definitive treatment?
a. Calcium gluconate, sodium bicarbonate, insulin, and glucose
b. Dobutamine
c. Pericardiocentesis
d. Thrombolytic therapy
6. What is the likely interpretation of the rhythm strip below?
a. First-degree AV block
b. Second-degree AV block Type I
c. Second-degree AV block Type II
d. Third-degree AV block
e. Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
7. What is the likely interpretation of the rhythm strip below?
a. First-degree AV block
b. Second-degree AV block Type I
c. Second-degree AV block Type II
d. Third-degree AV block
e. Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
8. What is the likely interpretation of the rhythm strip below?
a. First-degree AV block
b. Second-degree AV block Type I
c. Second-degree AV block Type II
d. Third-degree AV block
e. Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
You might also like
- PANCE Prep Pearls Cardio Questions PDFDocument9 pagesPANCE Prep Pearls Cardio Questions PDFkat100% (3)
- Part 1 EP ClinicalDocument28 pagesPart 1 EP ClinicalHany100% (2)
- All Clinical CasesDocument118 pagesAll Clinical CasesMichael AbioyeNo ratings yet
- Heart EditDocument51 pagesHeart EditCoral Srinivasa Ramalu100% (1)
- 3 Heart InternetNewDocument55 pages3 Heart InternetNewCoral Srinivasa RamaluNo ratings yet
- 500 Sba NeurologyDocument437 pages500 Sba Neurologyمحمد القرنيNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics Round4Document3 pagesGeriatrics Round4MOHAMED HOSSAMNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument32 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionFaisal AwaluddinNo ratings yet
- 2021 April FCPS Cardiology SolvedDocument20 pages2021 April FCPS Cardiology SolvedMerab SyedNo ratings yet
- Heart SoundsDocument4 pagesHeart Soundsthakurnikhilkumar119No ratings yet
- Paper C 2019 With Key andDocument28 pagesPaper C 2019 With Key andaizaz100% (1)
- UntitledDocument135 pagesUntitledDr.younes95 RekaaneyNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment FinalDocument5 pagesFormative Assessment FinalJonathan YeohNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers: CardiologyDocument77 pagesQuestions & Answers: CardiologyDev Yadav100% (1)
- Chapter 24: Alterations of Cardiovascular Function Power-Kean Et Al: Huether and Mccance'S Understanding Pathophysiology, Second Canadian EditionDocument20 pagesChapter 24: Alterations of Cardiovascular Function Power-Kean Et Al: Huether and Mccance'S Understanding Pathophysiology, Second Canadian EditionmonicaNo ratings yet
- 70 Cardio Endo Rheum QuestionsDocument56 pages70 Cardio Endo Rheum QuestionslaralatifNo ratings yet
- Clinchers 100 Important PointsDocument21 pagesClinchers 100 Important PointsNeha GoelNo ratings yet
- MCQ PretestDocument3 pagesMCQ PretestKia AgusputraNo ratings yet
- Daftar Kelulusan MCQSCBT Periode Agustus 2018Document9 pagesDaftar Kelulusan MCQSCBT Periode Agustus 2018MH KurniawanNo ratings yet
- ... & More: ECG ChallengeDocument2 pages... & More: ECG ChallengehameunjungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document6 pagesChapter 13Teehee Jones100% (1)
- 50 Item MedicalDocument8 pages50 Item Medicalshark_tale04No ratings yet
- Im Boards Rationalized ExamDocument21 pagesIm Boards Rationalized Examesbat07No ratings yet
- ECG Handout 1Document26 pagesECG Handout 1Kyle LatayanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Problem 2Document8 pagesUnit 3 Problem 2Adoub AlderaziNo ratings yet
- CARDIOLOGY Notes by MeDocument33 pagesCARDIOLOGY Notes by MeJanie-Vi GorospeNo ratings yet
- Try Out NewDocument19 pagesTry Out NewIke AdrianaNo ratings yet
- فحص جراحة 11Document144 pagesفحص جراحة 11Ola AlaaNo ratings yet
- 1996 Bookmatter InternalMedicineDocument117 pages1996 Bookmatter InternalMedicineMenna GalalNo ratings yet
- Aortic StenosisDocument3 pagesAortic StenosisMaxine BaraquiaNo ratings yet
- 50 Item Medical-Surgical Nursing Practice TestDocument19 pages50 Item Medical-Surgical Nursing Practice TestsongkyoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Disease Flashcards PDFDocument52 pagesPathophysiology of Disease Flashcards PDFFlowerNo ratings yet
- Um MCQDocument4 pagesUm MCQWinnie WongNo ratings yet
- MCQs IN MEDICINEDocument150 pagesMCQs IN MEDICINERITESH SINGHNo ratings yet
- MCQ ArrhythmiaDocument5 pagesMCQ ArrhythmiaDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Medicine MCQS JULY 2023 SOLVEDDocument15 pagesMedicine MCQS JULY 2023 SOLVEDLijo JoNo ratings yet
- Final Cardiovascular Unhas 2013Document18 pagesFinal Cardiovascular Unhas 2013Habi Septiati MusinNo ratings yet
- Cardiology LastDocument101 pagesCardiology Lastxaltra100% (1)
- MCQs - CardiologyDocument16 pagesMCQs - CardiologyZach Elzwie100% (4)
- Cardio and Hema Super SamplexDocument24 pagesCardio and Hema Super SamplexMj Lina TiamzonNo ratings yet
- Andi 26-30Document6 pagesAndi 26-30Andi HidayatNo ratings yet
- مجد ٤Document13 pagesمجد ٤Mohammad AlrefaiNo ratings yet
- Materi Kardio 02 JanuariDocument57 pagesMateri Kardio 02 JanuariPutra AchmadNo ratings yet
- ECG QuestionsDocument4 pagesECG QuestionsWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Soal MAYO Yg KeluarDocument8 pagesSoal MAYO Yg KeluardoktersaktiNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: Dr. Asif WazirDocument21 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: Dr. Asif WazirHillary BushnellNo ratings yet
- Final Questions 2021Document8 pagesFinal Questions 2021PatrycjaSkierkaNo ratings yet
- Cvs Assesment 1 OrigkeyDocument5 pagesCvs Assesment 1 OrigkeydrashtisataNo ratings yet
- Uns 2017Document44 pagesUns 2017Roni ArmandaNo ratings yet
- Final Medical Examination 4 Year Medical Student:) Select ONE BEST Answer (Document10 pagesFinal Medical Examination 4 Year Medical Student:) Select ONE BEST Answer (Dhanoush MşđNo ratings yet
- Masterclass Book Part 2Document367 pagesMasterclass Book Part 2Eng Kian Ng100% (5)
- Group B Hypovolemic ShockDocument22 pagesGroup B Hypovolemic ShockPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- MCQ Cardiology 1Document7 pagesMCQ Cardiology 1Dian ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Critical CareDocument38 pagesCritical CareavisenicNo ratings yet
- Medicine - 1 Solved BCQS Final Year MBBS LumhsDocument20 pagesMedicine - 1 Solved BCQS Final Year MBBS LumhsShairy SohoNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment: BOFs for MRCP(UK) and MRCP(I) Part IFrom EverandSelf-Assessment: BOFs for MRCP(UK) and MRCP(I) Part INo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Klinik Bornmeds Stress Exercise Report: Stress ECG Analysis SystemDocument1 pageKlinik Bornmeds Stress Exercise Report: Stress ECG Analysis SystemMagenta GamingNo ratings yet
- DokumenDocument4 pagesDokumenFkep2015No ratings yet
- Nstemi (Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction)Document37 pagesNstemi (Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction)andi yusmawatiNo ratings yet
- A Head Nurse Oversees Nursing Activities in A Range of Health Care SettingsDocument8 pagesA Head Nurse Oversees Nursing Activities in A Range of Health Care SettingsMitch MaLagambaNo ratings yet
- Heart Sound .Mid Systolic Click-Mitral ProlapseDocument2 pagesHeart Sound .Mid Systolic Click-Mitral ProlapseTeti AndriNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Emgerencies 2021Document19 pagesHypertensive Emgerencies 2021Faranitach AiniNo ratings yet
- Atrial Septal DefectDocument7 pagesAtrial Septal DefectRose WidantiNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation - Geeky MedicsDocument10 pagesAtrial Fibrillation - Geeky MedicsJahangir AlamNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps To Rhythm Strip InterpretationDocument2 pages5 Steps To Rhythm Strip Interpretationjosh082572No ratings yet
- Tabel Severitas BPJS Tindakan JantungDocument9 pagesTabel Severitas BPJS Tindakan JantungTeduh ParamadinaNo ratings yet
- 01 Cir 22 3 385Document20 pages01 Cir 22 3 385Diana AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument11 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PDFpriyanka bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Role in ManagementDocument6 pagesEchocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Role in Managementjk045413No ratings yet
- Is There Benefit From Stenting On Cognitive Function in Intracranial AtherosclerosisDocument5 pagesIs There Benefit From Stenting On Cognitive Function in Intracranial AtherosclerosisAlexandru MartisNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument39 pagesCongestive Cardiac Failurezacks nyirongoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument13 pagesCongestive Heart Failureali alrashediNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument2 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromemoen bonNo ratings yet
- PATHODocument3 pagesPATHODr-Irfan Habib100% (1)
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesIschemic Heart Diseaseborn_321118403100% (1)
- Right + Increased Vascularity + Fixed S2 / Widely Split Austin-Flint (Chronic) Graham Steele MurmurDocument14 pagesRight + Increased Vascularity + Fixed S2 / Widely Split Austin-Flint (Chronic) Graham Steele MurmurRojales FrancisNo ratings yet
- Criteria For The Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument20 pagesCriteria For The Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial InfarctionalexandraossesNo ratings yet
- QUIZ AfibDocument3 pagesQUIZ AfibDomingo, Viella Clarisse S.No ratings yet
- Transient Ischemic AttackDocument19 pagesTransient Ischemic Attackjoshua sondakhNo ratings yet
- Revista Médica de ChileDocument8 pagesRevista Médica de ChileLudwigPlateBargielaNo ratings yet
- Auscultation of The HeartDocument84 pagesAuscultation of The HeartASTOASTONo ratings yet
- Result Analysis Date: November 22, 2017 Conclusion: V. Laboratories and Diagnostic ExamsDocument7 pagesResult Analysis Date: November 22, 2017 Conclusion: V. Laboratories and Diagnostic ExamsEllaine Joy Mesina PadizNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument18 pagesEcgDelyn Gamutan MillanNo ratings yet
- Zero To Finals MedicineDocument352 pagesZero To Finals MedicinePlay100% (23)
- ECG Rhythm Interpretation: Module IV CDocument18 pagesECG Rhythm Interpretation: Module IV CsrimatsimhasaneshwarNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument55 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseMimi Morallos-EspirituNo ratings yet