Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Effect of Training in The Improvement of Emplo
Uploaded by
Ossama allamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Effect of Training in The Improvement of Emplo
Uploaded by
Ossama allamCopyright:
Available Formats
ARTICLE Asia-Pacific Management
and Business Application
1(2) 129 – 139
Training’s Effect and Application To Improve ©UB 2012
University of Brawijaya
Employee Efficiency In Pharmaceutical Industry Malang, Indonesia
http://apmba.ub.ac.id
Sinem Aydoğdu
Okan University, Institute of Social Sciences, Management and Organization
Abstract
Globalization affects businesses, especially in this rapid changes of the business environment
forces organizations to change their operations and structures. To be accomplished in a
competition, companies need well trained and well developed employees from front
employees to the top level managers in the executive suite. In Pharmaceutical Industry in
Turkey, due to the fast and rapid changes and improvements concerning the regulations
and procedures of Ministery of Health, guidelines such as GMP (Good Manufacturing
Practises), GLP (Good Laboratory Practises), GDP (Good Documentation Practises),
employees at work should be trained and updated about the current knowledge to increase
the efficiency in the organization.The main purpose of this study is to investigate the effect
of training on employee efficiency. Research was carried out with 74 employees from a
pharmaceutical company in İstanbul, Turkey. The data was collected due to convenience
sampling method. For assesing the collected data, the packaged statistical data analysis tool
SPSS 15.0 was used. Initially, all instruments’ reliability was tested. To ensure the items’
internal consistency, reliability was assessed by Cronbach Alpha and Factor analysis, the
hypotheses were tested by One-Way Anova. The results of study support the hypotheses.
There is a significant difference between white collar and blue collar employees on the idea
of training’s efficiency in the area of career development, that of productivity, professional
growth and customer satisfaction.
Keywords
Training, Employee Efficiency, Pharmaceutical Industry
Received: 26 November 2012; Accepted: 14 December 2012; Publised Online: 31 December 2012
Introduction organizations to reach the set goals, to
develop themselves and to survive in the
Businesses faces important and rapid
competitive market. To be accomplished in
changes. These fast, rapid changes
a competition, companies need employees
and improvements happen because
who are well-trained and well-adopted in
of globalization and technological
their companies.
changes. In the business environment,
forces the organizations to change their In Pharmaceutical Industry, due to the fast
operations and structures. Fast adoption changes and improvements concerning
of these changes and contionus renewal the regulations and procedures of
of both employees and organizations help Ministery of Health, guidelines such as
Corresponding author Email: sinemaydogdu@yahoo.com
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139 ISSN : 2252-8997
130 Sinem Aydoğdu
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practises), white collar and blue collar employees
GLP (Good Laboratory Practises), GDP on the idea of efficiency and of career
(Good documentation Practises) etc. development, productivity, professional
employees at work should be updated to growth and customer satisfaction.
increase the efficiency of the organization.
Otherwise, organizations can not raise Literature Review
their competition power to exist and
develop themselves. Training
A traditional management theory has Physical, social, intellectual, and mental
suggested that to increase the efficiency trainings are very essential in facilitating
of our companies we need a division of not only the level of efficiency but also
labour. Adam Smith first suggested this in the development of personnels in any
1700s arguing that by dividing labour and organizations. Dessler (2003) describes
allowing them to specialise in a specified the term of training as ‘the methods used
area, an organization would be able to to give employees the skills they need
increase efficiency and therefore prices to perform their jobs more effectively.
were lower and competitiveness was Shortly, it is a learning process that involves
gained in the market. This concept was the acquisition of skills, knowledge,
further developed by Frederick Taylor a concepts or attitudes to increase employee
hundred and fifty years later through his performance (Sözer, 2004).
concepts of scientific management. Taylor
The main objective of training is to
went one step further by developing
improve the qualities of a trainee, to
principles asserting that work methods
formulate objectives for different needs
were needed to be studied scientifically in
and ways of achieving it. The training
order to train and develop each employee
objective is very important because it
actively instead of passively.
determines the designed and content of
Today, organizations should give more the training programmes. Contents of the
importance to training. Physical, social, training remain the same no matter the
intellectual, and mental trainings are very type of training involved. It is to increase
essential in facilitating not only the level personnel efficiency, professional growth,
of efficiency but also the development smooth and more effective organization’s
of personnels in any organizations. A operations. (Olaniyan & Ojo, 2008).
training provides specific knowledge,
The driving factors of training can be
skills and abilities to employees which are
described as compounds of structural
necessary to perform specific activities for
characteristics, labor demand dynamics,
specific jobs. Providing those necessary
human resource management practices,
skills make employees improve their
workforce features, and firm performances.
qualifications. In other words, by training,
We observe that training activities
employees have the chance to upgrade
emerge positively associated with high-
their efficiency.
performance practices, innovative
This paper builds on the literature on labor demand features, workforce skill
training and employee efficiency and the level, firm size, and are affected by labor
main purpose of this study is to investigate flexibility in various directions. (Guidetti
the effect of training on employee and Mazzanti, 2007). In order to develop
efficiency. It tries to explore whether an effective training program, which is
there is a significant difference between going to be described more specifically
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
Training’s Effect And Application To Improve Employee Efficiency In Pharmaceutical Industry 131
and clearly in “the process of training” part power. Therefore, this capital needs to be
below- there should be a need analysis of improved, refreshed and upgraded with
both employees and organization. Once the help of training activities. To sum up,
the minimum training needs of each in a strategic perspective, training is the
employee have determined, the next platform of organizational transformation,
move is to establish training goals. Goals, the mechanism of both individual and
as declared on Payroll Manager’s Report, organizational renewal and the instrument
need to be specific, clear, precise and of global information (Bingöl, 2010).
measurable. (Payroll Manager’s Report,
2007). With the help of need analysis, the Determining Training Needs
targeted problems of workers, departments
Determining training needs typically
or organizations can be solved since need
involves generating answers to several
analysis is formed on the basis of both
questions which demonstrate the close
performance appraisal of employees and
link between employment planning and
the information received from interviews
determining training needs. Based on our
conducted by their managers about their
determination of organization’s needs, the
performance. (Sözer, 2004).
work to be done, and the skills necessary
to complete this work, our training
The Importance of Training programs should follow naturally. Once
The importance of training lies in the we identify where deficiencies lie, we
fact that the function of human resource have a grasp of the extent and nature of
management prepares employees to be our training needs. The leading questions
ready for rapidly changing environments in Table 1 suggest the kinds of signals
and enlarging organizations (Smith, 1999). that can warn a manager when training
will be necessary. The most obvious ones
In other words, training is driven by relate directly to productivity. Indications
organizational change which includes that job performance is declining may
investments of new technology, include production decreases, lower
implementation of quality assurance quality, more accidents, and higher scrap
programs and new management practices. or rejection rates. Any of these outcomes
This fact provides organizations such might suggest that worker’s skills need to
employees with improved motivation. be fine-tuned. We are assuming that the
Having these types of employees is a employee’s performance decline is in no
strategic aim of organizations. This means way related to lack of effort. Managers,
training constitutes the key factor of an too, must also recognize that a constantly
organization in achieving its strategic evolving workplace may require training.
targets. In addition, it plays a crucial Changes imposed on employees as a
role in defining organizations’ efficiency result of job redesign or a technological
and productivity. As it is said before, breakthrough also require training.
training activities help employees to
learn all needed behaviors which are Once it has been determined that training
related to their work. Moreover, with the is necessary, training goals must be
help of training, an employee is able to established. Management should explicitly
improve his awareness of responsibilities state its desired results for each employee.
and roles in an organization. By this It is not adequate to say we want change
way, his motivation improves as in employee’s knowledge, skills, attitudes,
well. Additionally, the human capital or behaviors; we must clarify what is to
of a company is its main competency change and by how much. These goals
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
132 Sinem Aydoğdu
Figure 1: Determining training needs.
What deficiencies,
if any do incumbents have in the Is there a
skills knowledge, or abilities What are the organization's
need for goals?
required to exhibit the necessary training?
job behaviors?
What behaviors are necessary
for each job incumbent What tasks must be completed
to complete his or her to achieve its goals?
arranged tasks?
should be tangible, verifiable, timely, and • Apprenticeships: are frequently used
measurable. They should be clear to both to combine classroom instructions
the supervisor and the employee. (De with working alongside a seasoned
Cenzo, & Robbins (2010). veteran, coach, or mentor. The
combination of hands-on and
Training Methods classroom learning compliments each
A training can be initiated for a variety other. Apprenticeships are frequently
of reasons for an employee or group of used in skill trade or craft jobs such as
employees, e.g.,:When a performance building trades.
appraisal indicates performance
• Internships: are opportunities for
improvement is needed , to "benchmark"
students in higher education to utilize
the status of improvement so far in a
their instruction and training in a
performance improvement effort , and to
chosen proffession as a part of their
train a specific topic (see below) (http://
education. Internships vary from very
managementhelp.org/trng_dev/basics/
unstructured to highly structured and
reasons.htm)
may include college credit.
On-the-Job Training Methods
Off-the-Job Training Methods
Several methods exist in the literature
as the approaches on-the-job training Approaches in the angle of off-the-job
methods, such as: training are also described in thes paper,
such as :
• Job Rotation: has long been considered
as a valuable tool to increase • Classroom Lectures: Many
employee’s motivation. It involves organizations use classroom
lateral transfers that allow employes instructions along with other methods
to work at different jobs and provides to provide a great deal of information
exposure to a variety of tasks. As with in a limited timeframe. Instructors
any training, HRM should ensure the need to understand the different
trainers not only know the job, but learning charactericstics of adult
also how to train others as well. learners and the variety of instruction
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
Training’s Effect And Application To Improve Employee Efficiency In Pharmaceutical Industry 133
types that create interest in specific employee’s efficiency. For instance, a
technical, interpersonal, or problem training motivates employees so turnover
solving skills they are teaching. rate and absenteeism decrease while
performance and organizational and also
• Multimedia Learning: can demonstrate customer relations increase (Özveren,
technical skills not easily presented by 1990).
other training methods.
According to a study which done by
• Simulations: involve learning a job by Drahani (2004), 75% of respondents
actually performing the work (or its indicated that they were highly satisfied
stimulation). Simulation methods may or satisfied with the content and relevance
include case analyses, experimental of the training to their individual
exercises, computer simulations, effectiveness and development; and
virtual reality, role playing, and group 85% of the respondents indicated
interaction. they were highly satisfied or satisfied
• Vestibule Training: facilitates learning with the relevance of the training to their
by using the same equipment that professional development.
one actually will use on the job but Bentley describes training as ‘an
in a stimulated work environment. investment for success’ in the book called
(DeCenzo, Robbins & Stephen ‘the Business of Training’ (Bentley,
(2010)). 1991). Despite the fact that training seems
like it only operates for corporations’
The Role of Training in Improving success and investment, it also operates
Employee Efficiency for individual’s success and investment.
Training provides specific knowledge, Without employee’s investments, no one
skills and abilities for employees and are will be able to gain corporate’s success.
necessary to perform specific activities for The CEO of the Motorola Company
specific jobs. Providing those necessary mentioned the relation of employee and
skills makes employees improve their organizational success by saying that
qualifications. In other words, by training, ‘… we use training not just about the
employees have the chance to upgrade success of the company but about success
their efficiency. Furthermore, according of employees and so the success of total
to a meta-analysis conducted by Hysong organization. (Howard, 1993) Therefore,
and Quinones (1997), there is a positive investment in employees becomes an
relationship between self-efficacy and essential part of organizational future
performance. strategy. (Bentley, 1991) .
Moreover, self-efficacy has also been According to a research, made by
found to be positively related to subsequent Erdoğan Taşkın, in Turkey, nearly 50%
job attendance and ability to cope with job of organizations perform training in order
demands. (Frayne & Latham, 1987). With to improve employee’s effectiveness
the help of training, employees are able to and organizational commitment (Taşkın,
raise their self-efficacy and their standard 2001). The other 50 % of organizations’
performance and reflect their performance reasons to perform training are to provide
increase to the overall performance of motivation, improve employee skills,
the organization. (Swart, Mann, Brown raise the culture level of employees,
and Price, 2005) Performing an effective improve the communication skills
training program is the key to increae between employees, make labor force be
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
134 Sinem Aydoğdu
professional in their fields and improve Methodology
employees’ knowledge. Moreover,
nearly 30% of the organizations declare Sample
the topics of their training programs The sample of this study is conducted
such as productivity, communication, from a pharmaceutical company in private
motivation, customer information, sector, İstanbul. The sample consists of 74
customer relations, self development, individuals from different departments of
behavior development, human relations, the organization.
time management, skill improvement and
technological innovations. Furthermore,
Hypotheses
organizations list the areas on which
training improves the employees, such Hypothesis 1: There is a significant
as raising communication, developing difference between white collar and
employees, developing skills, following blue collar employees on the idea of
innovations, providing self-confidence training’s efficiency in the area of career
and self-consciousness, improving human development.
relations, raising performance, providing
Hypothesis 2: There is a significant
responsibility, procuring organizational
difference between white collar and blue
commitment, providing job satisfaction,
collar employees on the idea of training’s
progressing in career and procuring
efficiency in the area of productivity.
employee’s productivity and efficiency.
(Taşkın, 2001) As it can be understood Hypothesis 3: There is a significant
from the results of the research, among difference between white collar and blue
these organizations in Turkey, the main collar employees on the idea of training’s
aim of training is to supply employee’s efficiency in the area of professional
development and efficiency. growth.
As mentioned in the previous chapter, Hypothesis 4: There is a significant
an effective training not only gives job difference between white collar and blue
related information but also provides collar employees on the idea of training’s
behavioral changes. Additionally, training efficiency in the area of customer
means providing skills and knowledge by satisfaction.
which people can perform in the changed
situation. (Colin, 1993) Analysıs Method
To sum up, having the most suitable The statistical procedures used to analyze
employees at your company, especially if the collected data are explained in this
the company is in pharmaceutical sector, section. For assesing data, the packaged
which is audited often and the regulations statistical data analysis tool SPSS 15.0 was
and procedures change frequently, is as used. Initially, all instruments’ reliability
important to the success of the business was tested. To ensure the items’ internal
as your finances and product. Moreover, consistency, reliability was assessed by
human capital needs continuous nurturing. Cronbach Alpha and Factor analysis,
To nurture it, workers need to be well- the hypotheses were tested by One-Way
trained to reach their full potential and Anova.
performance (Employee Training &
Development, Finweek, 2006).
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
Training’s Effect And Application To Improve Employee Efficiency In Pharmaceutical Industry 135
Research Fındıngs 32 participants (43%) are university
graduates, 10 participants (14%) have a
According to the Descriptive Statistics,
Master’s Degree. 17 participants (23%)
the sample consists of 74 individuals. The
have a tenure in the organization between
sample consists of 12 women (16%) and
0-5 years, 44 participants (59%) have a
62 men (84%). 31 % (23 participants)
tenure in the organization between 6-10
of the sample is between the ages of 20-
years, 13 participants (18%) have a tenure
30, 51% (38 participants) of the sample
in the organization more than 10 years.
is between the ages of 31-40 and 12%
(9 participants) of the sample is between
the ages of 41- 50, 5% (4 participants) of Reliability Analysis
the sample is higher than 50. 57% (42 Reliability analysis was conducted for
participants) is white- collar employee, training. Cronbach α score of the measure
43% (32 participants) are blue-collar is 0.8963. The reliability coefficients,
employee. 9 participants (12%) are means, standart deviations for each
primary school graduates, 23 participants variable were reported in Table 2.
(31%) are high school graduates,
Table 2 Means, Standard Deviations and Reliability Coefficients of Training.
Scale N Mean Std.Dev. Cronbach α
Training Effectiveness (overall) 74 3,7421 1,1845 0,8963
- Career Development 74 3,6791 1,0974 0,8521
- Area of Productivity 74 4,0973 1,0168 0,8873
- Professional Growth 74 3,5690 1,1683 0,8632
- Customer Satisfaction 74 3,3782 1,1739 0,8792
Factor Analysis One-Way Anova T-Test
In order to find the structures of training, The relationship between four factors of
factor analysis using principal components training and the position of employees
solution with varimax rotation was were analyzed through Independent
conducted. Factors with eigenvalues 1.00 Sample T-Tests, then Scheffe Post Hoc
or more were taken into consideration Multiple Comparisons was conducted to
and total variance explained. Kaiser- establish the direction of differences in
Meyer-Olkin (KMO) value was found perception to the position. The results are
.923 Bartlett Test of Sphericity (.000, shown in Table 3.
Chi- Square: 3715,881, df: .190) showed
that the variables were suitable for factor According to the results in Table 3, there are
analysis. The factors items loaded under significant differences between position
the first factor was named as “career and career development (F= 6.352, t=
development” having a variance of -.944 and p= .000< .05), position and area
45.791%. The second factor was named as of productivity (F=5.541, t= -.879 and
“ area of productivity” having a variance p= .000< .05), position and professional
of 13.876%. The third factor was named growth (F= 5.136, t= -.945 and p= .000<
as “professional growth” having a .05), position and customer satisfaction
variance of 6.659%. The fourth factor was (F= 3.116, t= -.769 and p= .000< .05 ).
named as “customer satisfaction” having According to Sceffe Post Hoc Multiple
a variance of 5.894%. All of the factors Comparisons Results of career
had a total of 72.22%.
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
136 Sinem Aydoğdu
Table 3: Independent Sample T-Tests Result
Factor Position N Mean Std.Dev. F Sig. t
Blue-collar 32 3,4872 1,87454
Career Development 6,352 0,000 -.944
White-collar 42 4,5953 1,67079
Blue-collar 32 3,3056 0,51308
Area of Productivity 5,541 0,000 -.879
White-collar 42 3,4797 0,69381
Blue-collar 32 3,1134 1,34218
Proffesional Growth 5,136 0,000 -.945
White-collar 42 3,4892 1,25452
Blue-collar 32 3,557 0,99660
Customer Satisfaction 3,116 0,000 -.769
White-collar 42 3,9663 0,97215
development, there is a significant satisfaction, there is a significant
difference between blue-collar employees difference between blue-collar employees
(Mean= 3.4872) and white-collar (Mean= 3.557) and white-collar employees
employees (Mean=4.5953 and p= .005< (Mean=3.9663 and p= .000< .05), so it
.05), so it can be said that a significant can be said that a significant difference
difference between white- collar between white-collar employees and blue-
employees and blue collar employees collar employees and the idea of training’s
and the idea of training’s efficiency occurs efficiency occurs in the area of customer
in the area of career development. satisfaction.
According to Sceffe Post Hoc Multiple
Discussion
Comparisons Results of area of
productivity, there is a significant This study has concerned with
difference between blue-collar employees exploring the effects of training on
(Mean= 3.3056) and white-collar improving employee’s efficiencies in
employees (Mean=3.4797 and p= .000< pharmaceutical industry. The significant
.05), so it can be said that a significant difference between white-collar
difference between white-collar employees and blue-collar employees
employees and blue-collar employees and and the idea of training’s efficiency occurs
the idea of training’s efficiency occur in in the area of career development. It is
the area of productivity. known that job rotation and coaching are
managerial training technics. Therefore,
According to Sceffe Post Hoc Multiple they are not generally used for blue-collar
Comparisons Results of professional employees. Moreover, training technics
growth, there is a significant difference for improving leadership skills and time
between blue-collar employees (Mean= management skills are called personal
3.1134) and white-collar employees development trainings, which are not
(Mean=3.4892 and p= .000< .05), so it generally used for blue-collar employees
can be said that a significant difference either. Being deprived of those trainings
between white-collar employees and makes employees think that trainings
blue-collar employees and the idea of they took are not able to satisfy their
training’s efficiency occurs in the area of career developments. To sum up, all of
professional growth. those differentiations make blue- collar
According to Sceffe Post Hoc Multiple employees think in a way that training
Comparisons Results of customer does not help their career improvement
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
Training’s Effect And Application To Improve Employee Efficiency In Pharmaceutical Industry 137
and that they do not have the adequate performing problem solving training, of
amount of training. increasing self confidence and professional
growth because of performing training
In regards to the productivity, it can and of performing adequate amount of
be said that a significant difference training. Problem solving training is
between white-collar employees and another technic of personal development
blue-collar employees and the idea of training, which means it is not generally
training’s efficiency occurs in the area of applied to blue-collar workers. Because
productivity. White-collar employees and of not performing personal development
blue-collar employees are different from training technics, blue-collar employees
each other in respect of having trainings may feel that they do not have adequate
that improve their communication, amount of training and not improve
motivation, performance, conflict their professions as well as their self
management, stress management confidence. Therefore, in this research it
and problem solving skills. Like the becomes a significant difference between
trainings for improving leadership and white-collar employees and blue-collar
time management skills, technics called employees on perceiving the efficiency of
communication, motivation, performance, training in professional growth area.
conflict management, stress management
and problem solving skills are personal In regards to customer satisfaction, it
development trainings too. Therefore, can be said that a significant difference
these technics do not generally applied between white-collar employees and
to blue-collar employees. In other blue-collar employees and the idea of
words, an employee may not able to training’s efficiency occurs in the area
have an enough productivity when he of customer satisfaction. White-collar
does not know how to manage stress, employees and blue-collar employees
problems or conflicts that often happen are different from each other in respect
in workplace. Therefore, in this research of related feature sector about having
it becomes a significant difference successful communication to customers,
between white-collar employees and taking orders right and helping undecided
blue-collar employees in perceiving the customers to give orders. Moreover,
efficiency of training in productivity because of globalization, cruel and strict
area. The other possible reason of this competition conditions and rapid change,
differentiation may be that employees companies take customer needs, opinions
who are working for managerial positions and demands into account seriously
are more likely to experience personal in order to cope with the difficulties,
development trainings rather than basic gain competitive advantage and to be
training technics. Therefore, they become successful in such competitive market.
personally developed, which may lead Hence, all of the main philosophy
them to have a higher productivity. underlying training technics and training
subjects provide customer satisfaction.
Accroding to the results in professional
growth, it can be said that a significant In spite of the fact that productivity and
difference between white-collar employees customer satisfaction are inevitable parts
and blue-collar employees and the idea of pharmaceutical industry and most of the
of training’s efficiency occurs in the area trainings concern this, there is a significant
of professional growth. White-collar difference between white-collar and blue-
employees and blue-collar employees are collar employees in respect of those two
different from each other in respect of areas. Moreover, blue-collar employees
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
138 Sinem Aydoğdu
working for pharmaceutical industry in pharmaceutical industry. However,
believe that their companies do not there are some limitations of the study
generally make investments about their that needs to be mentioned. One of the
career developments and professional limitations of this study is the sample size.
growth. Additionally, they also believe The sample of the study consisted of only
that they do not have enough amount of one firm from pharmaceutical industry.
training. The research could be carried out in
different production or service provider
Conclusion sectors; and it is obvious that the results
would be different.
According to the results of the study,
blue-collar employees are aware of not The second limitation of this study is the
performing managerial training subjects time. If this study could be performed
and technics such as job rotation, coaching, in wider time period, the results would
communication training, conflict be different; because of the changes
management training, stress management in business environment. Another
training, leadership training, teamwork consideration involves the demographic
training, time management training, variables. Results might have been
problem solving training and motivation different if percentages of the demographic
training. Hence, having non-managerial variables were different.
training technics and subjects make them
feel in a way that they have inadequate
amount of training and scarcity in career Notes of Contributor
development as well as professional Sinem Aydoğdu is PhD candidate at Okan
growth and productivity. University, Institute of Social Sciences,
The present study is expected to contribute Management and Organization. She is
to the literature since it provides basis to currently working as Chief of Controlling
reveal the effects of training on employees & Reporting di PharmaVision San. ve Tic.
A.Ş. in Istambul, Turkey.
References
Bentley, T. (1991). “The Business of Dessler, G. (2003). “Human Resource
Training”. 1st edition. London: Management”, 9th edition, New
McGraw Hill, p.33 Jersey: Prentice Hall,2003, p.187.
Colin, T. (1993). “Strategic Change Drahani, K. (2004). “Professional
Management and Training: Training Programs as Tools for
Adaptive, Adoptive and Innovative Effective Staff Development: A
Roles”, Journal of European Case Study”, Academy of Human
Industrial Training, Vol.17, No.5, Resource Development International
p.26. Conference (AHRD), pp.1146-1147.
Journal of European Industrial Training, Dursun, B. (2010). “İnsan Kaynakları
Vol.17, No.5, (June 1993), p.26. Yönetimi”, Beta Yayınevi, 7. Baskı
DeCenzo A David, Robbins P., Stephen, p.239- 240
A. (2010). “Human Resources Employee Training & Development,
Management”, Wiley, 10th Edition., Finweek, (2006 July), p.44.
p. 190- 192
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
Training’s Effect And Application To Improve Employee Efficiency In Pharmaceutical Industry 139
Frayne, Latham G. (1987). “Application Özevren, M. (1990). “The Benefit and
of Social Learning Theory to Cost Analysis of Recruitment and
Employee Self-management of Training”, 1st Edition, İstanbul:
Attendance”, Journal of'Applied Bilim Teknik Press, p.82.
Psychology, Vol.72, No.3, p.389. Payroll Manager's Report, (2007).
Giovanni G., Mazzanti, M. (2007). “Firm- “Establishing Training Goals for
level Training in Local Economic You and Your Staff for 2008”, Vol.7,
Systems Complementarities in No.12, pp.4-5.
Production and Firm Innovation Smith, A. (1999). “ International Briefing
Strategies”, Journal of Socio- 4 Training and Development in
Economics, Vol.36, No.6, p.875 Australia”, International Journal of
http://managementhelp.org/trng_ Training and Development, Vol.3,
dev/basics/reasons.htm No. 4, p.308.
Howard, R. (1993). “The Learning Sözer, S. (2004). “An Evaluation of current
Imperative- Managing People for Human Resource Management
Continuous Innovation” Boston: Practices in The Turkish Private
Harvard Business School Press Sector”, Master Thesis, Middle
Hysong S. J., Quinones, M. A. (1997). East Technical University Social
“The Relationship Between Self Sciences Institute, p.11, p.26.
efficacy and Performance: A Meta- Swart, J., Mann, C., Brown, S. and
analysis”, 12th Annual Conferance Price, A. (2005). ”Human Resource
of the Society for Industrial and Development Strategyand Tactics”,
Organizational Psychology, St. 1st Edition, Oxford: Elsevier, p195.
Louis.
Taşkın, E. (2001). ”İşletme Yönetiminde
Olaniyan D.A., Ojo B. L. (2008). “Staff eğitim ve Geliştirme”, 3rd Edition,
Training and Development: A İstanbul: Papatya, pp.185, 199,205-
Vital Tool for Organisational 215.
Effectiveness”, European Journal of
Scientific Research, 2008, p.328
Asia-Pacific Management and Business Application, 1, 2 (2012):129 – 139
You might also like
- Interpreting Movements in Broad MoneyDocument13 pagesInterpreting Movements in Broad MoneyOssama allamNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Access To and Usage of Financial Services in EthiopiaDocument10 pagesBarriers To Access To and Usage of Financial Services in EthiopiaOssama allamNo ratings yet
- Ijs Ron 2013489Document12 pagesIjs Ron 2013489Ossama allamNo ratings yet
- Lagged Effects of Training On Financial Performance: Evidence From Longitudinal DataDocument12 pagesLagged Effects of Training On Financial Performance: Evidence From Longitudinal DataOssama allamNo ratings yet
- Impact of Training and Development On Financial Performance Case Study: Kosovo EnterprisesDocument8 pagesImpact of Training and Development On Financial Performance Case Study: Kosovo EnterprisesOssama allamNo ratings yet
- The Roleof Trainingand Developmentin Enhancing Employees PerformanceDocument11 pagesThe Roleof Trainingand Developmentin Enhancing Employees PerformanceOssama allamNo ratings yet
- The Influenceof Trainingon Employees Performance OrganizationalDocument12 pagesThe Influenceof Trainingon Employees Performance OrganizationalOssama allamNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Agile Leadership Workbook 3 CollaborationDocument12 pagesAgile Leadership Workbook 3 CollaborationGaryNo ratings yet
- IIMBx BusMgmtMM AAMP FAQ v3 PDFDocument2 pagesIIMBx BusMgmtMM AAMP FAQ v3 PDFAnirudh AgarwallaNo ratings yet
- Module Rizal 1Document60 pagesModule Rizal 1theotherivy5No ratings yet
- Field Report Tanzania Revenues AuthorityDocument26 pagesField Report Tanzania Revenues AuthorityFlorence Hiza100% (14)
- (As Per Deped Reg'L Memo No. 027, S. 2018) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 pages(As Per Deped Reg'L Memo No. 027, S. 2018) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayJanelkris PlazaNo ratings yet
- Details To Process My OfferDocument8 pagesDetails To Process My OfferSairamTirumalaiGovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Uki Nupasari Lab Inggris (Ikut Ujian Hari Senin)Document9 pagesUki Nupasari Lab Inggris (Ikut Ujian Hari Senin)UkinupasariNo ratings yet
- Alabama State University: Montgomery, ALDocument14 pagesAlabama State University: Montgomery, ALSaddam HossainNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7ppt.Document16 pagesCHAPTER 7ppt.JOMARI DL. GAVINONo ratings yet
- Theories of Nursing PracticeDocument98 pagesTheories of Nursing PracticeshebaNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence For Effective Classroom Management - Handout-FinalDocument21 pagesEmotional Intelligence For Effective Classroom Management - Handout-FinalBhanu Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- 271 - Pages 4 2007Document10 pages271 - Pages 4 2007Joanna AngelopoulouNo ratings yet
- Blakemore Frith 2005 The Leaning BrainDocument221 pagesBlakemore Frith 2005 The Leaning BrainVictor MN100% (2)
- Hand Book of SMART DAYDocument27 pagesHand Book of SMART DAYMenurseto MawaddahNo ratings yet
- 2003 CUREE ExcerptDocument24 pages2003 CUREE ExcerptFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- In Medias Res 2017Document76 pagesIn Medias Res 2017MIT Comparative Media Studies/Writing100% (1)
- Craft Techniques in Conductive Education To Support The Employment 2022 HeliDocument3 pagesCraft Techniques in Conductive Education To Support The Employment 2022 HeliMixa TekluNo ratings yet
- 01 Delegate Workbook RMG02101ENME v3 (AD02) Nov2019Document5 pages01 Delegate Workbook RMG02101ENME v3 (AD02) Nov2019Nizar EnnettaNo ratings yet
- Re Lesson Plan Pre-Primary/ PrimaryDocument10 pagesRe Lesson Plan Pre-Primary/ Primaryapi-398083288No ratings yet
- NBT BrochureDocument2 pagesNBT BrochureAsiphe BiyoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Women's Empowerment Captured in The Movie Wonder Woman 1984 (A Feminism Study)Document12 pagesAnalysis of Women's Empowerment Captured in The Movie Wonder Woman 1984 (A Feminism Study)Linguapreneur IndonesiaNo ratings yet
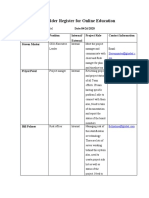
- Stakeholder Register For Online EducationDocument2 pagesStakeholder Register For Online EducationjonNo ratings yet
- Early Learning FrameworkDocument48 pagesEarly Learning FrameworkNguyen Duy ThaoNo ratings yet
- EsaiDocument3 pagesEsaiFebry PutriNo ratings yet
- Baloi West District: 1 Quarter District Monitoring Evaluation & Adjustments (DMEA)Document17 pagesBaloi West District: 1 Quarter District Monitoring Evaluation & Adjustments (DMEA)Raima CABARONo ratings yet
- Essay StructureDocument16 pagesEssay StructureCònGìBằngNo ratings yet
- Tamil NaduDocument255 pagesTamil NaduSiva PrakashNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT Math Q2 W5 Lesson 39Document23 pagesGrade 5 PPT Math Q2 W5 Lesson 39Bernadine Jacob TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University: S O A RDocument12 pagesBulacan State University: S O A REmerson Cruz100% (2)
- Introduction To PEDDocument9 pagesIntroduction To PEDprabhaakarNo ratings yet