Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm
Uploaded by
Mau MauOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midterm
Uploaded by
Mau MauCopyright:
Available Formats
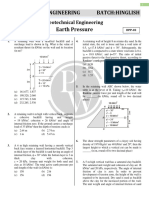
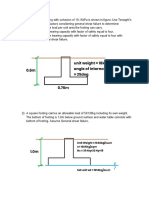
FOUNDATION ENGINEERING - Midterm Exam 6. A sheet pile is shown in the figure. 8. A square footing with dimension of 1.3 x 1.
3
a. Determine the minimum value of embedment m has its bottom 1.5 m below the ground
1. A direct shear test is performed on a depth d for stability, in meters. (Ans: 4.347m) surface. The groundwater table is expected to
specimen of dry sand. The shear box is circular in b. Using the minimum value of d, determine the exist during the life of the structure. The unit
cross-section with a diameter of 50 mm. The Soil 1:
H1 tension in the tie rod per meter length of pile. weight of soil above the water table is 17.20
γ1, φ1
normal force imposed on the specimen is 250 N. (Ans: T = 171.77 kN) kN/m3 and that below the water table is 19.60
The shear force is 150 N. Determine the angle of kN/m3. The angle of internal friction is 20° and
internal friction of this sand. (Answer: φ=30.96°) γm = 19.62 kN/m3 cohesion is 15 kPa. Using general shear failure
Ka = 0.3
and a factor of safety of 3.0. For angle of internal
2. A triaxial test on a saturated soil has the Soil 2: friction of 20°, the bearing capacity factor are Nc
γ2, φ2 H2
following results: = 17.69; Nq=7.44; Nγ=3.64.
Cell Pressure Deviator Pore Pressure a. Calculate the gross allowable bearing capacity
(kPa) Stress (kPa) (kPa) if the water table is 4 m below the ground
200 119 142.5 surface. (Ans: 189.821 kPa)
400 143 275.5 a. Determine the total lateral pressure at the Ka = 0.3 b. Calculate the gross allowable bearing capacity
γsat = 19.49 if the water table is 2 m from the ground surface.
600 178 396 base of the wall. (Ans: 88.25 kPa) kN/m3
a. Determine the drained angle of internal b. Determine the total active force acting on the (Ans: 186.944 kPa)
friction of the soil. (Ans: φ=8.737°) wall. (Ans: 331.61 kN) c. Calculate the gross allowable bearing capacity
b. Determine the cohesion of the soil in drained c. Determine the total active moment acting on if the water table is at the embedment of the
condition. (Ans: 42.22 kPa) the wall. (Ans: 884.85 kN-m) Kp = 3
foundation. (Ans: 185.146 kPa)
γsat = 19.49 d. Calculate the gross allowable bearing capacity
kN/m3
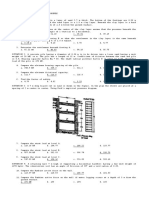
3. The results of a consolidated-drained triaxial 5. A retaining wall is shown in the figure. if the water table is 1.0 m from the ground
test conducted on a normally consolidated clay, a. Determine the total active pressure before surface. (Ans: 175.957 kPa)
are as follows: tensile crack occurs. (Ans: 76 kN)
Chamber confining 250 kPa b. Determine the total active pressure after
stress, σ3 tensile crack occurs. (Ans: 79.45 kN) 7. A square foundation is shown in the figure.
Deviator stress at 350 kPa The footing will carry a gross mass of 30,000 kg.
q = 15 kN/m2
failure Using a factor of safety of 3, determine the size
a. Calculate the angle of friction of the soil of the footing - that is the size of B. Assume
sample. (Ans: φ=24.316°) general shear failure. For φ=35°, Nc=57.75,
b. Calculate the shear stress on the failure plane. Nq=41.44 and Nγ=45.51.
(Ans: τ = 159.5 kPa)
c. Calculate the effective normal stress on the
plane of maximum shear. (Ans: σ = 425 kPa) γ = 16.5 kN/m3 “Wala dito si Chito.
φ = 26° Wala din si Kiko.
H = 6m c = 10 kN/m2
4. From the figure shown: Surcharge load is Wala din si Cloc 9.
applied at the ground surface qo = 40 kPa. Pero…
H1 = 3m, ɣ1 = 17 kN/m3, φ1 = 22° May MAGBABAGSAKAN DITO.”
H2 = 4m, ɣ2 = 21 kN/m3, φ2 = 28°
You might also like
- Soil 1: γ, φ 3 3: K = 0.3 γ = 19.49 kN/mDocument1 pageSoil 1: γ, φ 3 3: K = 0.3 γ = 19.49 kN/msenior highNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document1 pageQuiz 2senior highNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- Geotechnic 2Document2 pagesGeotechnic 2Faez El-NinoNo ratings yet
- Geo - 3Document2 pagesGeo - 3SamNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Mm/s .106 Cm/s 0.750 Cm/s .106 Mm/s 0.750 Mm/s .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Cm/sDocument2 pages.0106 Mm/s 0.075 Mm/s .106 Cm/s 0.750 Cm/s .106 Mm/s 0.750 Mm/s .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Cm/sReech Aerol AlmendralNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics IIDocument2 pagesSoil Mechanics IIqwfqefwqefgefqeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Exam 04Document10 pagesAssessment Exam 04TachooNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Assessment ExamDocument7 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Assessment ExamAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Soil 6 Ap (Ril 2023Document2 pagesSoil 6 Ap (Ril 2023Nica SudamaNo ratings yet
- Consolidation of SoilDocument8 pagesConsolidation of SoilRay JillNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartDocument4 pagesQuiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartBenjamin Benicarlo Juanillo IIINo ratings yet
- CE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Document21 pagesCE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Irmak ÜnalNo ratings yet
- 2 BAA3513 Lateral Earth Pressure (Part 2)Document42 pages2 BAA3513 Lateral Earth Pressure (Part 2)احمد يوسفNo ratings yet
- Ass2 SoilMech UAEU Fall2023Document4 pagesAss2 SoilMech UAEU Fall2023mouazam KhalidNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Nov 2023 - GEO 1 - DONEDocument2 pagesCE Refresher Nov 2023 - GEO 1 - DONEengr.jaysoncapadosamariNo ratings yet
- CE Module 28 - Rigid Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Document3 pagesCE Module 28 - Rigid Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Final ExaminationDocument1 pageFinal ExaminationJam Arambala AbelloNo ratings yet
- Ce l3t1-1Document24 pagesCe l3t1-1marfu-um AbidNo ratings yet
- CE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Document21 pagesCE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2mahavir damakaleNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5Anonymous Vx9KTkM8n67% (3)
- Module 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressDocument12 pagesModule 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressShane IsorenaNo ratings yet
- 99.earth Pressure - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03 & 04)Document3 pages99.earth Pressure - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03 & 04)wikita4906No ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering Refresher ModuleDocument5 pagesFoundation Engineering Refresher ModuleTaki Tachibana100% (1)
- Foundation Engineering Refresher Module Problems and SolutionsDocument5 pagesFoundation Engineering Refresher Module Problems and SolutionsLYNSER CORONEL ABANZADONo ratings yet
- FDocument5 pagesFKrisangel AbletesNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering Refresher ModuleDocument5 pagesFoundation Engineering Refresher ModuleJunar AmaroNo ratings yet
- Hge Pre-Board QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesHge Pre-Board QuestionnairegregNo ratings yet
- Tugas Akhir Teknik Pondasi IiDocument3 pagesTugas Akhir Teknik Pondasi IiOkha JuliansyahNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Mid 1Document9 pagesAssignment For Mid 1Vũ Thị Hà TrangNo ratings yet
- Rasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Document3 pagesRasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Greg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsDocument18 pagesSoil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsBemzar SamsonNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument3 pagesLateral Earth PressureDupio German IINo ratings yet
- Critical State Soil Mechanics Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesCritical State Soil Mechanics Exam QuestionsHari RamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial A7 & A8 Earth Pressure & Retaining WallsDocument3 pagesTutorial A7 & A8 Earth Pressure & Retaining WallsSaiful Azhar Ahmad TajudinNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 2Document3 pagesCE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 2rando12345No ratings yet
- p&B-m2 Earth Pressure TheoDocument8 pagesp&B-m2 Earth Pressure TheoChetan PatilNo ratings yet
- P&B m2Document8 pagesP&B m2kuchNo ratings yet
- Math 1Document1 pageMath 1adonis bibatNo ratings yet
- Review Module 62 (GH10) Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDocument2 pagesReview Module 62 (GH10) Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsJoenem AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 8Document8 pagesEvaluation Exam 8Michael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Review Module 27 - Part 1 and Part 2Document3 pagesReview Module 27 - Part 1 and Part 2Angelie RemediosNo ratings yet
- 3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering 8Document2 pages3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering 8JuDeNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation, Slope Stability & Braced CutsDocument25 pagesPile Foundation, Slope Stability & Braced CutsJommarVocalTagalogNo ratings yet
- Soil 7 April 2023 1 of 2Document1 pageSoil 7 April 2023 1 of 2Nica SudamaNo ratings yet
- Basement Wall SPR NewDocument12 pagesBasement Wall SPR NewAnonymous O404LiV4CNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems in Lecture File For Bearing CapacityDocument4 pagesSample Problems in Lecture File For Bearing CapacityJemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Bolton paper analyzes soil properties and earth pressure designDocument1 pageBolton paper analyzes soil properties and earth pressure designdaylight888No ratings yet
- Assessment Exam 04: Geotechnical EngineeringDocument7 pagesAssessment Exam 04: Geotechnical EngineeringAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- 3) Bearing CapacityDocument19 pages3) Bearing CapacityhaftamuTekle100% (1)
- Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering ECADocument24 pagesSoil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering ECADebasis MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Foundation EngineeringDocument5 pagesProblem Set Foundation EngineeringJohn Mathew BrionesNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 3: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 3: Eview NnovationsKian InductivoNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Problems2Document3 pagesMiscellaneous Problems2Jesus Ray M. MansayonNo ratings yet
- Seatwork-2 2Document2 pagesSeatwork-2 2JhettNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT For Final Exam 2022Document5 pagesASSIGNMENT For Final Exam 2022Vũ Thị Hà TrangNo ratings yet
- Soil Settlement Activity SolutionsDocument5 pagesSoil Settlement Activity Solutionssenior highNo ratings yet
- Special Topic Assign Men 14Document1 pageSpecial Topic Assign Men 14Mau MauNo ratings yet
- Specialtopicassignment 13Document1 pageSpecialtopicassignment 13Mau MauNo ratings yet
- Ce 23Document1 pageCe 23Mau MauNo ratings yet
- Prelim ExamDocument1 pagePrelim ExamMau MauNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 10 01465Document18 pagesSustainability 10 01465Mau MauNo ratings yet
- SPECIALTOPICASSIGNMENT23Document1 pageSPECIALTOPICASSIGNMENT23Mau MauNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms 08 01941 v2Document14 pagesMicroorganisms 08 01941 v2Mau MauNo ratings yet
- A y C 3 3 DL LL DL LL C Y: Section For Moment Is Halfway Between Middle and Edge of WallDocument1 pageA y C 3 3 DL LL DL LL C Y: Section For Moment Is Halfway Between Middle and Edge of WallMau MauNo ratings yet
- Defining Publics in Public Relations: The Case of A Suburban HospitalDocument12 pagesDefining Publics in Public Relations: The Case of A Suburban HospitalLexy DappyNo ratings yet
- Energy and Entropy (Alekseev, G. N.) (1986) (208p)Document208 pagesEnergy and Entropy (Alekseev, G. N.) (1986) (208p)Lucas Kiel100% (2)
- Jadual Waktu SPM 2010Document2 pagesJadual Waktu SPM 2010sallehGNo ratings yet
- Ad 304Document1 pageAd 304srinimehaNo ratings yet
- Minerals Engineering: Duncan M. Smythe, Annegret Lombard, Louis L. CoetzeeDocument10 pagesMinerals Engineering: Duncan M. Smythe, Annegret Lombard, Louis L. Coetzeefaouzi rachidNo ratings yet
- Caracteristicas Del Conocimiento Cientifico CreencDocument20 pagesCaracteristicas Del Conocimiento Cientifico CreencLiana PichardoNo ratings yet
- 24160-Article Text-39228-1-10-20220603Document10 pages24160-Article Text-39228-1-10-20220603pandji pridjantoNo ratings yet
- Logical FallaciesDocument15 pagesLogical FallaciesLouis Marvil AbalaNo ratings yet
- SchimmentiDevelopmentalrootsofdissociationpre PrintDocument42 pagesSchimmentiDevelopmentalrootsofdissociationpre PrintZeynep ÖzmeydanNo ratings yet
- Definition of FamilyDocument6 pagesDefinition of FamilyKeana DacayanaNo ratings yet
- Production of Phenol Via Chlorobenzene and Caustic ProcessDocument1 pageProduction of Phenol Via Chlorobenzene and Caustic ProcessPatricia MirandaNo ratings yet
- Empirical Correlation Between CaliforniaDocument94 pagesEmpirical Correlation Between CaliforniaRefilwe MoorosiNo ratings yet
- Change MGMT ExamplesDocument19 pagesChange MGMT Examplesjyoti chauhanNo ratings yet
- Essence of Indian Traditional KnowledgeDocument2 pagesEssence of Indian Traditional KnowledgePavan KocherlakotaNo ratings yet
- Bacon on Marriage and Single LifeDocument2 pagesBacon on Marriage and Single LifeLijimol GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Listening skills practice: Living online – exercisesDocument2 pagesListening skills practice: Living online – exercisesnavasfernando75100% (1)
- Water Budget Equation Exercise Problems SolvedDocument10 pagesWater Budget Equation Exercise Problems SolvedSheeraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Research 3Document76 pagesResearch 3Jackson IbascoNo ratings yet
- IISER Aptitude Test 2013: Syllabus ForDocument1 pageIISER Aptitude Test 2013: Syllabus ForSanthoshkumar RayavarapuNo ratings yet
- (Cambridge Studies in Italian History and Culture) Anthony L. Cardoza-Aristocrats in Bourgeois Italy - The Piedmontese Nobility, 1861-1930-Cambridge University Press (1998)Document263 pages(Cambridge Studies in Italian History and Culture) Anthony L. Cardoza-Aristocrats in Bourgeois Italy - The Piedmontese Nobility, 1861-1930-Cambridge University Press (1998)agalassiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Input Components: Operación de SistemasDocument5 pagesElectrical Input Components: Operación de Sistemasgalvis1020No ratings yet
- Learning Task Part 1Document7 pagesLearning Task Part 1Francia Neil BasilioNo ratings yet
- Pravesh 5Document3 pagesPravesh 5VIVEK SHAKYANo ratings yet
- CE Declaration of ConformityDocument2 pagesCE Declaration of Conformitymaria cristina ristagnoNo ratings yet
- API 579 FFS in CodeCalc/PVEliteDocument4 pagesAPI 579 FFS in CodeCalc/PVEliteSajal Kulshrestha100% (1)
- The No Cry Sleep Solution PDFDocument273 pagesThe No Cry Sleep Solution PDFanastaufan MrNo ratings yet
- 002 SillitoeDocument14 pages002 Sillitoesebastian tiriraNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4067211Document53 pagesSSRN Id4067211mnpxzdsqs8No ratings yet
- SASA ReviewerDocument4 pagesSASA ReviewerMia FayeNo ratings yet
- 15.production and Productivity Improvement Measures at MOIL-MOILDocument8 pages15.production and Productivity Improvement Measures at MOIL-MOILkatta_sridharNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Blending and MixingFrom EverandPharmaceutical Blending and MixingP. J. CullenRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Understanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersFrom EverandUnderstanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsFrom EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyFrom EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignFrom EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Operational Excellence: Journey to Creating Sustainable ValueFrom EverandOperational Excellence: Journey to Creating Sustainable ValueNo ratings yet
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyFrom EverandGuidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Vapor Cloud Explosion, Pressure Vessel Burst, BLEVE, and Flash Fire HazardsFrom EverandGuidelines for Vapor Cloud Explosion, Pressure Vessel Burst, BLEVE, and Flash Fire HazardsNo ratings yet