0% found this document useful (0 votes)
568 views5 pagesTextile Production Process
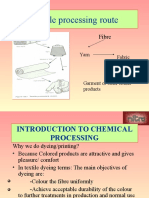
The document describes the key processes involved in producing cotton, leather, and silk fabrics. For cotton, the main steps are ginning to separate fibers from seeds, spinning yarn, and weaving cloth. Leather production involves cleaning, tanning, dyeing, and finishing animal hides. Silk fabrication starts with unravelling cocoons to extract fibers, weaving yarn into cloth, and dyeing, printing, and finishing the material. Each material undergoes several processing stages to transform raw materials into finished fabrics.
Uploaded by
tharanshinningCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
568 views5 pagesTextile Production Process
The document describes the key processes involved in producing cotton, leather, and silk fabrics. For cotton, the main steps are ginning to separate fibers from seeds, spinning yarn, and weaving cloth. Leather production involves cleaning, tanning, dyeing, and finishing animal hides. Silk fabrication starts with unravelling cocoons to extract fibers, weaving yarn into cloth, and dyeing, printing, and finishing the material. Each material undergoes several processing stages to transform raw materials into finished fabrics.
Uploaded by
tharanshinningCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5