Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PEDIA Typhoid-Fever
Uploaded by
iSmayli (smyle-smayl)Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PEDIA Typhoid-Fever
Uploaded by
iSmayli (smyle-smayl)Copyright:
Available Formats
TYPHOID/ENTERIC FEVER - Pedia
Potentially fatal multisystemic disease characterized by fever and abdominal
pain and caused by dissemination of S. typhi or S. paratyphi
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Asia
Highest in children younger than 5 yr of age
Human: only host
ETIOLOGY/ RISK FACTORS
S. enterica serovar Typhi (S. typhi)
Less severe: Salmonella paratyphi A, B (Schotmulleri), C
(Hirschfeldii)
Fecal-oral transmission
Infective dose: 105-109 organisms DIFFERENCTIAL DIAGNOSES (3)
Incubation period: 7-14 days to 3-30 days, depending on the Malaria
inoculum size Acute gastroeneteritis
Direct or indirect contact with an infected person (sick or chronic Dengue fever
carrier): prerequisite for infection.
MC MOT: Ingestion of foods or water contaminated with S. Typhi DIAGNOSIS
from human feces
Waterborne outbreaks: 2’ to poor sanitation or contamination
Oysters and other shellfish cultivated in water contaminated by
sewage
Night soil as fertilizer
SALIENT FEATURES
High-grade fever with a wide variety of associated features, such as
generalized myalgia, abdominal pain, hepatosplenomegaly, and
anorexia
Fever may rise gradually; classic stepladder rise of fever is rare MANAGEMENT
Rose spots (maculopapular rash) -7th -10th day of illness Adequate rest, hydration; correct fluid and electrolyte imbalance.
Coated tongue, diarrhea, pallor, constipation, headac, jaundice, Antipyretic therapy (acetaminophen 10-15 mg/kg every 4-6 hr PO)
obtundation, ileus, intestinal perforation A soft, easily digestible
Diet - continued unless with abdominal distention or ileus
You might also like
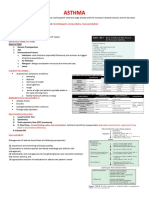
- Asthma: Bronchospasm, Airway Edema, Mucus ProductionDocument2 pagesAsthma: Bronchospasm, Airway Edema, Mucus ProductioniSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Case For RCPCC 2Document4 pagesCase For RCPCC 2iSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Pedia: 4 Criteria (Including at Least 1 Clinical and 1 Immunologic Criterion)Document1 pageSystemic Lupus Erythematosus-Pedia: 4 Criteria (Including at Least 1 Clinical and 1 Immunologic Criterion)iSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- PEDIA aPSGNDocument2 pagesPEDIA aPSGNiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Pedia MeningitisDocument1 pagePedia MeningitisiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guidelines PSOHNS2016Document45 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines PSOHNS2016Jan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Home Care For CovidDocument18 pagesHome Care For CovidiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Pathophy Miliary TBDocument5 pagesPathophy Miliary TBiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- PMA Code of EthicsDocument7 pagesPMA Code of EthicskaliyasaNo ratings yet
- Research - Rev Lit BseDocument7 pagesResearch - Rev Lit BseiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Eye Chart Template 17Document2 pagesEye Chart Template 17iSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- PMA Code of EthicsDocument7 pagesPMA Code of EthicskaliyasaNo ratings yet
- Ob BioethicsDocument1 pageOb BioethicsiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- LECTURER: Alizza Love F. Velasco, MD, FPAFP, FPSHPM: WellnessDocument6 pagesLECTURER: Alizza Love F. Velasco, MD, FPAFP, FPSHPM: WellnessiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Note To SelfDocument1 pageNote To SelfiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- YohimbimeDocument13 pagesYohimbimeiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Para Cestode TableDocument3 pagesPara Cestode TableiSmayli (smyle-smayl)100% (1)
- Chemotherapy For MalariaDocument5 pagesChemotherapy For MalariaiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- PemphigusDocument1 pagePemphigusiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Epidemiology Distribution of Diseases Caused by AnimalDocument1 pageEpidemiology Distribution of Diseases Caused by AnimaliSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Valgancyclovir MOA: Uses Pharmacokinetics Dosage Side Effects ContraindicationsDocument2 pagesValgancyclovir MOA: Uses Pharmacokinetics Dosage Side Effects ContraindicationsiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Superficial MycosesDocument2 pagesSuperficial MycosesiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- In The EastDocument2 pagesIn The EastiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Real-World Examples: Data AnalysisDocument6 pagesReal-World Examples: Data AnalysisiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Nelson Tools For Space Analysis and Design 050211Document11 pagesNelson Tools For Space Analysis and Design 050211iSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Maricris Joy L. CaoileDocument1 pageMaricris Joy L. CaoileiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)