Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COVID ADVISORY What To Do To Keep Yourself and Others Safe From COVID
Uploaded by
william penalverOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COVID ADVISORY What To Do To Keep Yourself and Others Safe From COVID
Uploaded by
william penalverCopyright:
Available Formats
What to do to keep yourself and others safe from
COVID-19
Maintain at least a 1-metre distance between yourself and others to
reduce your risk of infection when they cough, sneeze or speak. Maintain an
even greater distance between yourself and others when indoors. The further
away, the better.
Make wearing a mask a normal part of being around other people. The
appropriate use, storage and cleaning or disposal are essential to make
masks as effective as possible.
Here are the basics of how to wear a mask:
Clean your hands before you put your mask on, as well as before and after
you take it off, and after you touch it at any time.
Make sure it covers both your nose, mouth and chin.
When you take off a mask, store it in a clean plastic bag, and every day either
wash it if it’s a fabric mask, or dispose of a medical mask in a trash bin.
Don’t use masks with valves.
For specifics on what type of mask to wear and when, read our Q&A and
watch our videos. There is also a Q&A focused on masks and children.
Find out more about the science of how COVID-19 infects people and our
bodies react by watching or reading this interview.
For specific advice for decision makers, see WHO’s technical guidance.
How to make your environment safer
Avoid the 3Cs: spaces that are closed, crowded or involve close
contact.
o Outbreaks have been reported in restaurants, choir practices, fitness
classes, nightclubs, offices and places of worship where people have
gathered, often in crowded indoor settings where they talk loudly,
shout, breathe heavily or sing.
o The risks of getting COVID-19 are higher in crowded and inadequately
ventilated spaces where infected people spend long periods of time
together in close proximity. These environments are where the virus
appears to spread by respiratory droplets or aerosols more efficiently,
so taking precautions is even more important.
Meet people outside. Outdoor gatherings are safer than indoor ones,
particularly if indoor spaces are small and without outdoor air coming in.
o For more information on how to hold events like family gatherings,
children’s football games and family occasions, read our Q&A on small
public gatherings.
Avoid crowded or indoor settings but if you can’t, then take precautions:
o Open a window. Increase the amount of ‘natural ventilation’ when
indoors.
o WHO has published Q&As on ventilation and air conditioning for both
the general public and people who manage public spaces and
buildings.
o Wear a mask (see above for more details).
Don’t forget the basics of good hygiene
Regularly and thoroughly clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand
rub or wash them with soap and water. This eliminates germs including
viruses that may be on your hands.
Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth. Hands touch many surfaces
and can pick up viruses. Once contaminated, hands can transfer the virus to
your eyes, nose or mouth. From there, the virus can enter your body and
infect you.
Cover your mouth and nose with your bent elbow or tissue when you
cough or sneeze. Then dispose of the used tissue immediately into a closed
bin and wash your hands. By following good ‘respiratory hygiene’, you protect
the people around you from viruses, which cause colds, flu and COVID-19.
Clean and disinfect surfaces frequently especially those which are
regularly touched, such as door handles, faucets and phone screens.
What to do if you feel unwell
Know the full range of symptoms of COVID-19. The most common
symptoms of COVID-19 are fever, dry cough, and tiredness. Other symptoms
that are less common and may affect some patients include loss of taste or
smell, aches and pains, headache, sore throat, nasal congestion, red eyes,
diarrhoea, or a skin rash.
Stay home and self-isolate even if you have minor symptoms such as
cough, headache, mild fever, until you recover. Call your health care
provider or hotline for advice. Have someone bring you supplies. If you need
to leave your house or have someone near you, wear a medical mask to
avoid infecting others.
If you have a fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical
attention immediately. Call by telephone first, if you can and follow the
directions of your local health authority.
Keep up to date on the latest information from trusted sources, such as
WHO or your local and national health authorities. Local and national
authorities and public health units are best placed to advise on what people in
your area should be doing to protect themselves.
You might also like
- 7-Step Meeting Process AgendaDocument2 pages7-Step Meeting Process Agendawilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- Meeting 6 Books and Records RequiredDocument1 pageMeeting 6 Books and Records Requiredwilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- Meeting 3 Model Order of BusinessDocument1 pageMeeting 3 Model Order of Businesswilliam penalverNo ratings yet
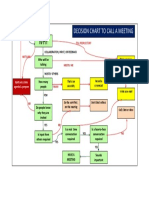
- Meeting 1 Chart - Decision To Call A MeetingDocument1 pageMeeting 1 Chart - Decision To Call A Meetingwilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- Model Minutes of Meeting: Call To OrderDocument2 pagesModel Minutes of Meeting: Call To Orderwilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Federation and UnionDocument2 pagesDifference Between Federation and Unionwilliam penalver0% (1)
- How To Write Effective Meeting MinutesDocument6 pagesHow To Write Effective Meeting Minuteswilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 AgendaDocument1 pageMeeting 2 Agendawilliam penalverNo ratings yet
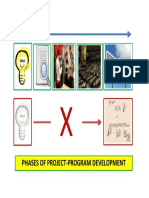
- Phases of Project-Program DevelopmentDocument1 pagePhases of Project-Program Developmentwilliam penalverNo ratings yet
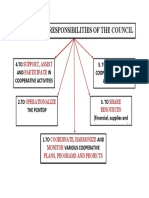
- 2a3 Mandate and Responsibilities of The CouncilDocument1 page2a3 Mandate and Responsibilities of The Councilwilliam penalverNo ratings yet
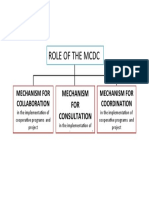
- 2a2 Role of MCDCDocument1 page2a2 Role of MCDCwilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- 2a2 Role of MCDCDocument1 page2a2 Role of MCDCwilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- 2a2 Role of MCDCDocument1 page2a2 Role of MCDCwilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of CooperativeDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Cooperativewilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- Candidate Forum: April 27, 2019 1:00pm - 5:pm Municipal Gymnasium LGU Makilala, Makilala, CotabatoDocument41 pagesCandidate Forum: April 27, 2019 1:00pm - 5:pm Municipal Gymnasium LGU Makilala, Makilala, Cotabatowilliam penalverNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Pre Travel Mosquitos SnakesDocument59 pagesPre Travel Mosquitos SnakesIsrael EspinNo ratings yet
- The History and Scope of EpidemiologyDocument40 pagesThe History and Scope of EpidemiologyMike LorenaNo ratings yet
- FlagellatesDocument35 pagesFlagellatesblue_blooded230% (1)
- Whocdscsreph200212 PDFDocument72 pagesWhocdscsreph200212 PDFIcaii InfotechNo ratings yet
- National Antibiotic Guideline 2014 Full VersionDocument246 pagesNational Antibiotic Guideline 2014 Full Versionevonnecheah100% (2)
- Biochemistry of AIDS - HIVDocument6 pagesBiochemistry of AIDS - HIVEdward XiamNo ratings yet
- Influenza and Public Health: Learning From Past PandemicsDocument156 pagesInfluenza and Public Health: Learning From Past PandemicsmoralelesmoraisNo ratings yet
- Alternative Second-Line Drugs For TuberculosisDocument42 pagesAlternative Second-Line Drugs For TuberculosisAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Dental Laboratory Infection ControlDocument6 pagesDental Laboratory Infection ControlDrShweta SainiNo ratings yet
- Hemophilia, meningitis, and shunt care nursing questionsDocument5 pagesHemophilia, meningitis, and shunt care nursing questionsSherilNo ratings yet
- CoverDocument613 pagesCoverRobert MicuNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Pablo Borbon Main II Batangas CityDocument75 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Pablo Borbon Main II Batangas CityklareNo ratings yet
- Gdocs Trans TemplateDocument3 pagesGdocs Trans TemplateshichiNo ratings yet
- BAI Annual Report 2013Document62 pagesBAI Annual Report 2013Anton Cornel0% (1)
- Safety and quality assessment in clinical laboratoriesDocument2 pagesSafety and quality assessment in clinical laboratoriesRicardo Lorenzo AlasNo ratings yet
- AF SeedingDocument6 pagesAF SeedingdonkeyendutNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - 4th - EdDocument35 pagesRespiratory System - 4th - EdJen100% (1)
- Pediatrics RemarksDocument62 pagesPediatrics RemarksGÖKSU SAYGILINo ratings yet
- QAC Evolution of Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Compounds 2Document8 pagesQAC Evolution of Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Compounds 2Jennifer VelascoNo ratings yet
- Vaginal MicrobiomeDocument9 pagesVaginal MicrobiomeRika Yulizah GobelNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Gram Negative Rods FlowchartDocument1 pageAerobic Gram Negative Rods FlowchartKeithNo ratings yet
- Medical and Veterinary Entomology 3rd Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesMedical and Veterinary Entomology 3rd Edition Ebook PDFvicki.raio639100% (42)
- Communicable Diseases ReviewerDocument13 pagesCommunicable Diseases ReviewerMarivic Salcedo McCreaNo ratings yet
- Job Responsibilities of Health Assistant (Male &female)Document8 pagesJob Responsibilities of Health Assistant (Male &female)Kailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Isaac Press ConferenceDocument2 pagesJonathan Isaac Press ConferenceThe FederalistNo ratings yet
- Severe Sepsis Screening Tool NhsDocument2 pagesSevere Sepsis Screening Tool NhsDavide Antonelli LaghiNo ratings yet
- Utbk Level 4Document4 pagesUtbk Level 4Charisa MarthaNo ratings yet
- Arachnids of Medical Importance (Ticks and MitesDocument26 pagesArachnids of Medical Importance (Ticks and MitesCLEMENT100% (1)
- CHN Lec FinalsDocument14 pagesCHN Lec FinalsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Trypanosomiasis in CamelsDocument20 pagesTrypanosomiasis in CamelsAnugat Jena0% (1)