Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gayorgor Case Study
Gayorgor Case Study
Uploaded by
Xepher Amador0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views7 pagesThe patient, a 45-year-old male smoker with a stressful job, presented with chest pain and pressure. Assessments found elevated blood pressure and a family history of hypertension and diabetes. Nursing diagnoses included ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased cardiac output. Planned interventions included establishing a quiet environment, elevating the head of the bed and legs, repositioning every 2 hours, instructing on small frequent feedings, teaching relaxation techniques, providing oxygen as ordered, and collaborating with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care. The expected outcomes were for the patient to display stable vital signs, reduced episodes of dyspnea and angina, and participation in activities to reduce heart workload within 8 hours.
Original Description:
Original Title
Gayorgor-Case-Study (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient, a 45-year-old male smoker with a stressful job, presented with chest pain and pressure. Assessments found elevated blood pressure and a family history of hypertension and diabetes. Nursing diagnoses included ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased cardiac output. Planned interventions included establishing a quiet environment, elevating the head of the bed and legs, repositioning every 2 hours, instructing on small frequent feedings, teaching relaxation techniques, providing oxygen as ordered, and collaborating with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care. The expected outcomes were for the patient to display stable vital signs, reduced episodes of dyspnea and angina, and participation in activities to reduce heart workload within 8 hours.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views7 pagesGayorgor Case Study
Gayorgor Case Study
Uploaded by
Xepher AmadorThe patient, a 45-year-old male smoker with a stressful job, presented with chest pain and pressure. Assessments found elevated blood pressure and a family history of hypertension and diabetes. Nursing diagnoses included ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased cardiac output. Planned interventions included establishing a quiet environment, elevating the head of the bed and legs, repositioning every 2 hours, instructing on small frequent feedings, teaching relaxation techniques, providing oxygen as ordered, and collaborating with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care. The expected outcomes were for the patient to display stable vital signs, reduced episodes of dyspnea and angina, and participation in activities to reduce heart workload within 8 hours.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
III. Among the five (5) nursing problems, create a nursing care plan (based on the scenario).
Limit assessments from the
scenario. Provide realistic nursing care (Philippine setting) and jive your assessments to desired outcome and nursing
intervention.
Name: Malcolm Winchester Sex: Male
Age: 45 Years old Chief complaint: Chest pain and pressure
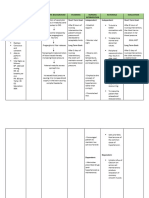
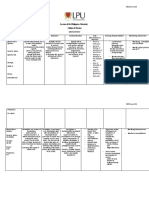
Assessment Nursing Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis
Subjective: After 8 hours of - Establish a quiet A quiet environment Goal met.
- Patient nursing environment reduces the patient's Patient was
verbalized that intervention, the energy demands. able too
his blood patient will be manifest
pressure was a able to: regular heart
“little high” Ineffective - Elevate the head of the Elevation aids in chest rate and
- Patient reports a Tissue - Display vital bed expansion and rhythm.
stressful job. Perfusion signs within oxygenation.
- Patient related to acceptable limits,
expresses that he Decreased dysrhythmias
does not have a Cardiac absent/controlled - Check for calf With forced bed rest,
formal exercise Output ,and no tenderness, diminished decreased cardiac
regimen symptoms of pedal pulses, swelling, output, and venous
- Patient is a failure. local redness, or pallor pooling, the risk of
smoker. of extremity. thrombophlebitis rises.
- Patient Specifically, the
complained of patient will be
chest pain. able to: - Elevate legs, avoiding Reduces venous
pressure under the knee return and preload and
Objective: - demonstrate or in a position may lower the risk of
- HPN and type 2 adequate cardiac comfortable to the thrombus or embolus
diabetes run in output as patient. formation.
the family. evidenced by
vital signs within
acceptable limits, - Reposition patient Prolonged immobility
dysrhythmias every two (2) hours. should be avoided for
absent/controlled patients on bed rest
, and no due to deconditioning
symptoms of effects and risks such
failure (e.g., as pressure ulcers,
hemodynamic especially in patients
parameters with edema. In
within acceptable edematous areas,
limits, urinary decreased circulation
output increases the risk of
adequate). pressure ulcers.
- report
decreased
episodes of - Instruct patient on In order to avoid
dyspnea, angina. eating small frequent heartburn and acid
- take part in feedings indigestion,
activities that
reduce the - Teach the patient Anginal pain is
workload on the relaxation techniques frequently caused by
heart. and how to use them to emotional stress,
reduce stress. which can be
alleviated with
non-pharmacological
measures such as
relaxation.
- Provide oxygen and Oxygenation
monitor oxygen increases the amount
saturation via pulse of oxygen circulating in
oximetry, as ordered. the blood, increasing
the amount of
available oxygen to
the myocardium and
thus reducing
myocardial ischemia
and pain.
Collaborative:
- Collaborate with other To provide a holistic
healthcare professionals care for the patient
You might also like
- Classifications of Heart MurmursDocument2 pagesClassifications of Heart MurmursVS100% (2)
- Cardiac Disease in PregnancyDocument21 pagesCardiac Disease in PregnancyRenata CilestrinaNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drug Study...Document6 pagesDrug Study...Johanz PacrisNo ratings yet
- CPR NewDocument37 pagesCPR NewNur Hazimah100% (1)
- The Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaFrom EverandThe Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanAsylla PajijiNo ratings yet
- NCP For Dizziness and HeadacheDocument4 pagesNCP For Dizziness and Headachekarthi karthi100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputHope TomeNo ratings yet
- Anemia NCPDocument5 pagesAnemia NCPMel Christian Baldoz100% (2)
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Document70 pagesIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)Deborah AnnNo ratings yet
- NCP (Rheumatic Heart Disease)Document2 pagesNCP (Rheumatic Heart Disease)Jenny Ajoc75% (4)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To Cardiomyopathywen_pil75% (8)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathySoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- NCP For CHFDocument11 pagesNCP For CHFqingwen100% (5)
- NCP 2 and Soapie 1Document5 pagesNCP 2 and Soapie 1narsD100% (1)
- Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Margaret Macasaet0% (1)
- Case Study Myocardial InfarctionDocument23 pagesCase Study Myocardial InfarctionJester GalayNo ratings yet
- NCP - MIDocument3 pagesNCP - MILlena Grace NatividadNo ratings yet
- Organization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and NeurotransmittersDocument3 pagesOrganization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.No ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypertension Nursing Care Plangeng gengNo ratings yet
- Esophageal AtresiaDocument70 pagesEsophageal Atresiahayssam rashwan100% (1)
- Rex Final Coaching MSDocument6 pagesRex Final Coaching MSRayden BarridaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument10 pagesPulmonary HypertensionqingwenNo ratings yet
- NCP Chest PainDocument2 pagesNCP Chest PainLinsae Troy50% (2)
- NCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument22 pagesNCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeAnnNo ratings yet
- NCP Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesNCP Dengue Feveralfonselay63% (8)
- 1-!nursing Diagnosis:: Myocardial Infarction As Evidenced by Reports of Chest Pain With Radiation in Bilateral ArmDocument3 pages1-!nursing Diagnosis:: Myocardial Infarction As Evidenced by Reports of Chest Pain With Radiation in Bilateral Armون توNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressLeticia ElricNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document4 pagesNCP 1Jezrale FameNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81No ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Nursing Management: Patients With Coronary Vascular DisordersDocument13 pagesChapter 14: Nursing Management: Patients With Coronary Vascular DisorderskingNo ratings yet
- NCP Chest PainDocument2 pagesNCP Chest PainCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Kiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- NCP BeeaDocument3 pagesNCP BeeaKiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation IndependentLau100% (1)
- NCP SGHDocument2 pagesNCP SGHdaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Revised NCP 1-3Document6 pagesRevised NCP 1-3MarcieNo ratings yet
- NCP SGH DianaDocument2 pagesNCP SGH Dianadaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention : Been Experiencing Chest Pains)Document3 pagesNursing Intervention : Been Experiencing Chest Pains)Czynna Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MCN Lab NCP - Varicose VeinsDocument1 pageMCN Lab NCP - Varicose VeinsJenine OquendoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Palliative Care Nursing NotesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Palliative Care Nursing NotesblaireNo ratings yet
- MS CompreDocument25 pagesMS CompreJhonny pingolNo ratings yet
- NREMT Practice Test Bank - 4q Multiple Choice-9Document1 pageNREMT Practice Test Bank - 4q Multiple Choice-9Dickson Kuria MburiNo ratings yet
- Coronary AtherosclerosisDocument3 pagesCoronary AtherosclerosisGwyn Oona Florence ForroNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document4 pagesActivity 5AngieNo ratings yet
- Caro NCPDocument17 pagesCaro NCPAbegail PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Hematologic Acute or Chronic Problems: ScenarioDocument36 pagesHematologic Acute or Chronic Problems: ScenariobhavanaNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Venous ReturnDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Venous ReturnFloramae LosaritaNo ratings yet
- Tabije, Arvie Jayselle PDocument6 pagesTabije, Arvie Jayselle PJayselle ArvieNo ratings yet
- Group-5 - NCP - Ges HypDocument2 pagesGroup-5 - NCP - Ges HypWallen Jey VelascoNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Document3 pagesAcute Pain!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!ahz_kerian2No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management of Altered Acute Biologic CrisisDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Management of Altered Acute Biologic CrisisSam Abduhassan SaidNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1 OB High Risk Grp.1Document15 pagesAssignment No.1 OB High Risk Grp.1YongNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPdimple caspilloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationSharmaine Camille de LeonNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Lorma Medical Center Carlatan, San Fernando City, La Union Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageLorma Medical Center Carlatan, San Fernando City, La Union Nursing Care PlanKenmiharu SorianoNo ratings yet
- Identify Non-Modifiable and Modifiable Risk Factors For HypertensionDocument3 pagesIdentify Non-Modifiable and Modifiable Risk Factors For HypertensionwokorowNo ratings yet
- Hyper Vole MiaDocument7 pagesHyper Vole MiaMICHELLE BIANCA PATRICE CRUZNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular ContinuumDocument229 pagesCerebrovascular ContinuumFiizhda BaqarizkyNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot SP B.inggrisDocument19 pagesTetralogy of Fallot SP B.inggrisSoraya VerinaNo ratings yet
- What Is A StrokeDocument10 pagesWhat Is A StrokeRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Screening For Microalbuminuria in Patients With Diabetes: How? Why?Document2 pagesScreening For Microalbuminuria in Patients With Diabetes: How? Why?Abhishek SenNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure: Protocol About Blood PDocument2 pagesBlood Pressure: Protocol About Blood PconheoconNo ratings yet
- Q - A Random 8Document5 pagesQ - A Random 8Yuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument13 pagesHypertensionAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of HeartDocument20 pagesBlood Supply of HeartPraneethaNo ratings yet
- Pattern of Drug Prescribed and Drug Related Problems Among Hospitalized Elderly PatientsDocument13 pagesPattern of Drug Prescribed and Drug Related Problems Among Hospitalized Elderly PatientsMediterr J Pharm Pharm SciNo ratings yet
- Lyceum of The Philippines University College of Nursing: MCN Form 014Document3 pagesLyceum of The Philippines University College of Nursing: MCN Form 014twinkleNo ratings yet
- Penicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPenicillin Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Villelabeitia Jaureguizar 2016 Journal of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation and PreventionDocument10 pagesVillelabeitia Jaureguizar 2016 Journal of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation and PreventionPablo Damian LeivaNo ratings yet
- DNB QUESTION PAPER-topic Wise2017Document42 pagesDNB QUESTION PAPER-topic Wise2017VinayNo ratings yet
- Nclex Test 04Document47 pagesNclex Test 04Humberto RussoNo ratings yet
- Intensive Care Unit Issues in Eclampsia and HELLP SyndromeDocument2 pagesIntensive Care Unit Issues in Eclampsia and HELLP SyndromeYoga Maulana HernowoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2-Final-June 2023Document9 pagesAnatomy 2-Final-June 2023Douaa lkNo ratings yet
- Causes Signs and Symptoms of Hemolytic AnemiaDocument1 pageCauses Signs and Symptoms of Hemolytic AnemiaJeki BongNo ratings yet
- Thorax To RectumDocument35 pagesThorax To RectumdhaineyNo ratings yet
- First Year MBBSDocument25 pagesFirst Year MBBSTofik MohammedNo ratings yet
- Curofy Best ECG CasesDocument26 pagesCurofy Best ECG Casescnshariff@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1.4 Circulation of Blood in The BodyDocument13 pagesScience 9 1.4 Circulation of Blood in The BodyChad Kirsten Mier LustreNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiology (EP) Study and Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)Document3 pagesElectrophysiology (EP) Study and Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)Jesmine KonnaeckalNo ratings yet