100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views58 pagesCB Testing SCOPE Compatibility Mode
The document discusses condition monitoring of circuit breakers. It covers various offline and online testing methods for different components of circuit breakers, including contact resistance testing, time testing, travel mechanism testing, and coil current testing. Maintaining and monitoring the condition of circuit breakers is important for safety and protecting electrical equipment.
Uploaded by
Vepty whoopsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views58 pagesCB Testing SCOPE Compatibility Mode
The document discusses condition monitoring of circuit breakers. It covers various offline and online testing methods for different components of circuit breakers, including contact resistance testing, time testing, travel mechanism testing, and coil current testing. Maintaining and monitoring the condition of circuit breakers is important for safety and protecting electrical equipment.
Uploaded by
Vepty whoopsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Welcome and Introduction
- Program Overview
- Importance of Circuit Breaker
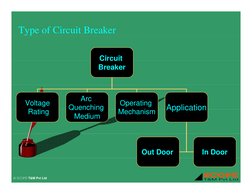
- Types of Circuit Breaker
- Condition Monitoring Need
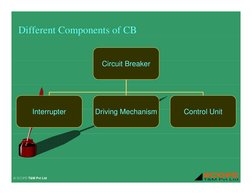
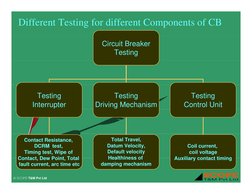
- Components and Testing Techniques
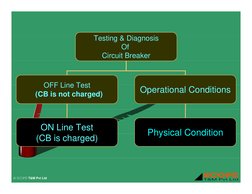
- Testing Detailed Procedures
- Off Line Testing Process
- Contact Resistance Tests
- Dynamic Contact Resistance Measurement
- Case Studies and Observations
- RTMon Field Unit
- SCHELOG Maintenance Manager