Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study Discussion (A)
Uploaded by
Bq dwi EvaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study Discussion (A)
Uploaded by
Bq dwi EvaCopyright:
Available Formats
CASE STUDY DISCUSSION (A)
Case 1.
A 28 year old man visits his physician complaining of an intense, sharp pain in his back and
side. In a conversation with his physician, the patient confesses to eating a diet high in animal
proteins such as meat, cheese, and fish. Results of a complete urinalysis are shown below.
Chemical/Physical Analysis
Color Yellow Glucose Negative Urobilinogen Normal
Appearance Clear Protein Trace Blood Large
Specific Gravity 1.025 Ketones 150mg/dL Nitrite Negative
pH 5.0 Bilirubin Negative Leukocyte Negative
Microscopic Analysis
>100 RBC/hpf
0-3 WBC/hpf
20-30 Bacteria/hpf
0-5 Squamous Epithelial Cells/hpf
Unidentified Crystals
Questions
1. Is there a discrepancy between the leukocyte and nitrite counts on the reagent stix compared
to the results reported in the microscopic analysis?
2. Is the presence of WBCs with bacteria clinically significant?
3. Suggest an explanation for blood in the urine.
Case 2.
A 10 year old boy, who recently recovered from a streptococcal infection, was taken to the
doctor with symptoms including fever, nausea, and malaise. Physical examination reveals
edema around the eyes and the knees. Blood tests reveal a decrease in serum complement. A
routine urinalysis reveals the following results.
Chemical/Physical Analysis
Color Yellow Blood Moderate
Clarity Hazy pH 6.5
Glucose Negative Protein 300mg/dL
Bilirubin Negative Urobilinogen Normal
Ketones Negative Leukocyte Esterase Small
Specific Gravity 1.015 Nitrite Negative
Microscopic Analysis
20-50 RBC/hpf
10-20 WBC/hpf
2-5 RBC casts/lpf
2-5 Granular casts/lpf
Questions
1. What is the significance of a positive leukocyte esterase?
2. How could there be a positive leukocyte esterase and a negative nitrite?
3. What is the significance of the presence of blood along with protein in the urine?
4. What disease are the results indicative of?
Case 3.
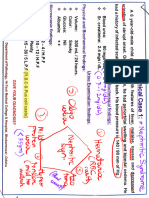
A 10-year old girl had a routine urine exam at the time of her school physical. Results follow:
Questions
1. Identify the abnormal test results highlighted
2. What is the most probable diagnosis for this patient? Support your answer (include in
your discussion the physical, chemical and microscopic findings).
3. Based on your diagnosis, what follow up testing should be done on this urine?
4. What single microscopic finding is most helpful in differentiating an upper UTI from a
lower UTI?
You might also like
- Diskusi Kasus Kelas ADocument4 pagesDiskusi Kasus Kelas ABangZayNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY DISCUSSION (A) Docx IsiDocument4 pagesCASE STUDY DISCUSSION (A) Docx IsiAmayliahNo ratings yet
- Case Study Discussion Blok Urin 2014-2015docxDocument5 pagesCase Study Discussion Blok Urin 2014-2015docxEdita DevanaNo ratings yet
- Diskusi Kasus Kelas B 1.: Characteristic ResultDocument6 pagesDiskusi Kasus Kelas B 1.: Characteristic ResultBagas aninditoNo ratings yet
- Case 1: HistoryDocument7 pagesCase 1: HistoryGold NajmNo ratings yet
- Kasus 1: Chemical/Physical AnalysisDocument5 pagesKasus 1: Chemical/Physical AnalysisMuhamad Chairul SyahNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Case StudiesDocument11 pagesUrinalysis Case Studiesdandooshe38% (13)
- CASE STUDY DISCUSSION (B) Docx IsiDocument3 pagesCASE STUDY DISCUSSION (B) Docx IsiAmayliah0% (1)
- (F3) Clinical Pathology DR KitsDocument15 pages(F3) Clinical Pathology DR KitsBryan Nartatez BautistaNo ratings yet
- Final Laboratory ProceduresDocument14 pagesFinal Laboratory ProceduresJosh BlasNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Presentation1Document25 pagesUrinalysis Presentation1OliviaLaneNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis CaseDocument3 pagesUrinalysis CaseAzriel Al MushoriNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document8 pagesCase Study 2Joanne Faith ManayagNo ratings yet
- Case Studies Chapter 5Document5 pagesCase Studies Chapter 5Len Abo Ashes100% (1)
- Havana CC1 Chon Tla3Document2 pagesHavana CC1 Chon Tla3Keannu HavanaNo ratings yet
- Reggie Fornolles MT 116 Activity 8Document3 pagesReggie Fornolles MT 116 Activity 8Reggie FornollesNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Cases (Revised)Document3 pagesUrinalysis Cases (Revised)Gold NajmNo ratings yet
- Course Case Studies - Viral HepatitisDocument5 pagesCourse Case Studies - Viral HepatitiswqmxmNo ratings yet
- Aubf Case Study AbcdefDocument9 pagesAubf Case Study AbcdefChiara Kate CodillaNo ratings yet
- Havana CC1 Chon Tla3Document4 pagesHavana CC1 Chon Tla3Keannu HavanaNo ratings yet
- Case ChartsDocument22 pagesCase ChartsFaiza HussainNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cases Patho With AnswersDocument32 pagesClinical Cases Patho With AnswersraviNo ratings yet
- CPC Compiled Report FinalDocument24 pagesCPC Compiled Report FinalNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Abnormal LTs 2014Document63 pagesAbnormal LTs 2014Robert G. Gish, MDNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument9 pagesPneumoniaRSNo ratings yet
- Cases For Post Prelims Conference 2009-2010Document7 pagesCases For Post Prelims Conference 2009-2010chocoholic potchi100% (1)
- 3f - 1 (Division of Task)Document33 pages3f - 1 (Division of Task)Trisha ArtosNo ratings yet
- Case Studies HemaDocument6 pagesCase Studies HemaJuan Andre' MarquinezNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY 11 411 5 and 12 2 12 3Document6 pagesCASE STUDY 11 411 5 and 12 2 12 3Florenz JoyNo ratings yet
- CasesDocument4 pagesCasesDarryl John Pasamba67% (3)
- Regañon - Rle Case # 1Document22 pagesRegañon - Rle Case # 1Darla Janyll RegañonNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in CC1Document12 pagesCase Studies in CC1Kayne Viernes67% (18)
- Urine Analysis and BiuretDocument30 pagesUrine Analysis and BiuretTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Lab Policies Urinalysis - Clinetek Status and Visual Lab 1583Document17 pagesLab Policies Urinalysis - Clinetek Status and Visual Lab 1583hunnylandNo ratings yet
- ProstateDocument7 pagesProstateGabriela ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- UrinsryDocument10 pagesUrinsryAzizan HakimNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument27 pagesCase PresentationKate ArañezNo ratings yet
- Protein Case SummaryDocument2 pagesProtein Case SummaryGlydenne Glaire Poncardas Gayam100% (2)
- Mega Lo 1Document3 pagesMega Lo 1Sagar JethwaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DR EldaDocument3 pagesCase Study - DR EldaShashi KumarNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Saint James AcademyDocument20 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Saint James AcademyYna Marie GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Data and Results: Include Demographic Information 2 PtsDocument2 pagesData and Results: Include Demographic Information 2 PtsKhairyl RubioNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument6 pagesUrinalysisAsmadayana HasimNo ratings yet
- 2b Case StudyDocument5 pages2b Case StudyCkaye MontilNo ratings yet
- URINALYSISDocument4 pagesURINALYSISsheila_01No ratings yet
- Activity 8 - HERCE - BSMT1BDocument3 pagesActivity 8 - HERCE - BSMT1BJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis in A 9 Year OldDocument4 pagesNephrolithiasis in A 9 Year OldJasmin Kae SistosoNo ratings yet
- LABORATORYDocument4 pagesLABORATORYSharies ArgelNo ratings yet
- Case 5Document14 pagesCase 5Mary Grace TirolNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document4 pagesCase 2Kim Ruiz100% (1)
- Studi KasusDocument9 pagesStudi KasusWina YustisiaNo ratings yet
- Gilbert2021 Article A17-year-oldBoyWithProgressiveDocument2 pagesGilbert2021 Article A17-year-oldBoyWithProgressivefatinarmiantoNo ratings yet
- Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityDocument4 pagesWestern Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityEzra LambarteNo ratings yet
- RAD RLE MCN 6 Case StudyDocument9 pagesRAD RLE MCN 6 Case StudyCathleen Nasis Forrosuelo100% (2)
- Recurrent Nephrolithiasis in A 9-Year-Old Child: (University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC)Document4 pagesRecurrent Nephrolithiasis in A 9-Year-Old Child: (University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC)Shaysta KhanNo ratings yet
- Complementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 6: Liver and GallbladderFrom EverandComplementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 6: Liver and GallbladderNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi: Per una maggiore sensibilizzazione su questa rara malattia geneticaFrom EverandFast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi: Per una maggiore sensibilizzazione su questa rara malattia geneticaNo ratings yet
- The Squeezing Potential of Rocks Around Tunnels Theory and PredictionDocument27 pagesThe Squeezing Potential of Rocks Around Tunnels Theory and PredictionprazNo ratings yet
- Reflection IntouchablesDocument2 pagesReflection IntouchablesVictoria ElazarNo ratings yet
- The American New CriticsDocument5 pagesThe American New CriticsSattigul KharakozhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Case StudyDocument56 pagesIntroduction, Case StudyLeanna Cantanero67% (3)
- Food Corporation of India Zonal Office (N) A-2A, 2B, SECTOR-24, NOIDADocument34 pagesFood Corporation of India Zonal Office (N) A-2A, 2B, SECTOR-24, NOIDAEpaper awaazNo ratings yet
- Dexter Quilisadio-Tanzo BSA-2 Unit-1 Quiz-1: OPMATQM-490Document1 pageDexter Quilisadio-Tanzo BSA-2 Unit-1 Quiz-1: OPMATQM-490Red AriesNo ratings yet
- I. Title: "REPAINTING: Streetlight Caution Signs"Document5 pagesI. Title: "REPAINTING: Streetlight Caution Signs"Ziegfred AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Corporation Essay ChecklistDocument5 pagesCorporation Essay ChecklistCamille2221No ratings yet
- Walmart Assignment1Document13 pagesWalmart Assignment1kingkammyNo ratings yet
- Call Option Agreement Free SampleDocument2 pagesCall Option Agreement Free Sampleapi-235666177No ratings yet
- A Re Ection On The Dominant Learning Theories: Behaviourism, Cognitivism and ConstructivismDocument13 pagesA Re Ection On The Dominant Learning Theories: Behaviourism, Cognitivism and Constructivismchill protocolNo ratings yet
- What Is ForexDocument8 pagesWhat Is ForexnurzuriatyNo ratings yet
- gtg60 Cervicalcerclage PDFDocument21 pagesgtg60 Cervicalcerclage PDFLijoeliyas100% (1)
- Neuralink DocumentationDocument25 pagesNeuralink DocumentationVAIDIK Kasoju100% (6)
- ContinentalDocument61 pagesContinentalSuganya RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Novel Synthesis of BarbituratesDocument3 pagesNovel Synthesis of BarbituratesRafaella Ferreira100% (2)
- LRL Rudy Acuna On Neftali DeLeon - I Am Proud To Be The Grandson Son and Husband of Immigrants.Document9 pagesLRL Rudy Acuna On Neftali DeLeon - I Am Proud To Be The Grandson Son and Husband of Immigrants.EditorNo ratings yet
- Ulf Hannerz - Being There and ThereDocument17 pagesUlf Hannerz - Being There and ThereThomás MeiraNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer To Suspensions of Small ParticlesDocument13 pagesMass Transfer To Suspensions of Small ParticlesrushdiNo ratings yet
- A Palace in TimeDocument6 pagesA Palace in TimeSonkheNo ratings yet
- Virulence: Factors in Escherichia Coli Urinary Tract InfectionDocument49 pagesVirulence: Factors in Escherichia Coli Urinary Tract Infectionfajar nugrahaNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Hot Mix Training ManualDocument91 pagesAsphalt Hot Mix Training Manualyazqa50% (2)
- MNT-Notes Pt. 2Document58 pagesMNT-Notes Pt. 2leemon.mary.alipao8695No ratings yet
- Keir 1-2Document3 pagesKeir 1-2Keir Joey Taleon CravajalNo ratings yet
- Battle of The ChoirDocument3 pagesBattle of The Choirkoizume_reiNo ratings yet
- EchoDocument11 pagesEchoapi-394733232100% (3)
- ADDICTED (The Novel) Book 1 - The Original English TranslationDocument1,788 pagesADDICTED (The Novel) Book 1 - The Original English TranslationMónica M. Giraldo100% (7)
- PSYCHODYNAMICS AND JUDAISM The Jewish in Uences in Psychoanalysis and Psychodynamic TheoriesDocument33 pagesPSYCHODYNAMICS AND JUDAISM The Jewish in Uences in Psychoanalysis and Psychodynamic TheoriesCarla MissionaNo ratings yet
- A Terence McKenna Audio Archive - Part 1Document203 pagesA Terence McKenna Audio Archive - Part 1BabaYagaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base AnswersDocument4 pagesAcid Base Answersapi-232466940No ratings yet