Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic IV Fluid Solution: Isotonic Solutions: Contains Approximately The Same
Uploaded by
mim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageOriginal Title
FLUIDS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageIsotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic IV Fluid Solution: Isotonic Solutions: Contains Approximately The Same
Uploaded by
mimCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
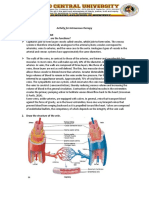
Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic IV 0.
25% normal saline (¼ NS)
2.5% dextrose in water and 5% dextrose in water (D5W)
Fluid Solution
Balance of fluids and electrolytes mostly refers to the
Isotonic in the bag but hypotonic in the body after the
volume and concentration of solutes inside the cell
cells consume the glucose
referred to as intracellular fluid (ICF) and the volume and
Should be used with caution for clients with
concentration outside the cell called extracellular fluid
hyperglycemia (e.g. diabetics)
(ECF). Clients may have too much or too little water in
Should not be use in clients with high intracranial
either of these parts of the body. When practitioners are
pressure (ICP)
diagnosing the imbalance, they generally are looking at
the levels of the ECF where their labs are assessed. If
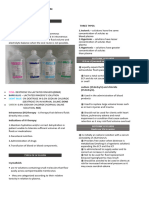
Isotonic solutions: Contains approximately the same
fluid levels in the ECF are high it is called hypervolemic
percentage of solute to solution as in the human body.
and if the levels are low, it is called hypovolemic. If fluid
These are used in situations where fluid levels need to
levels are balanced it is called isovolumic.
be replenished without shifting the fluids in or out of the
cell. Isotonic solutions are very commonly used as these
Hypertonic solutions: higher concentrations of solutes
are effective at rehydrating clients. Examples of isotonic
than what is observed in the body. These solutions are
solutions includes...
generally utilized when clients have low lab values (e.g.
Normal saline (0.9% NS)
low sodium, low glucose, etc.) Hypertonic solutions can
Lactated ringers
also draw water from the ICF to the ECF which can be
Use with caution in renal impairment
useful for clients with edema. These solutions may also
Contains potassium (can affect ECG)
be used for clients with heat exhaustion (where too
Contraindicated in liver impairment (cirrhosis, hepatitis)
many electrolytes were wasted) or peritonitis
as the liver is needed to metabolize lactate
(inflammation of the peritoneal cavity. Examples of
D5W
hypertonic solutions includes...
Isotonic in the bag but hypotonic in the body
3% normal saline (3% NS)
5% normal saline (5% NS)
10% dextrose in water (D10W)
5% dextrose in water with ½ normal saline (D5 ½ NS)
5% dextrose with lactated ringers (D5LR)
50% dextrose in water (D50W)
Hypotonic solutions: lower concentrations of solutes
relative to the water in the bag. Hypotonic solution are
used when clients already have high values of
electrolytes especially hypernatremia (serum sodium >
145 mEq/L). Clients with elevated sodium and are given
an isotonic or hypertonic solution this can exacerbate
their hypernatremia and cause serious side effects. The
main function of hypotonic solutions are to treat cellular
dehydration which results from hyperosmolar conditions
(e.g. hypernatremia, hyperkalemia, hyperglycemia, etc.)
Diabetic clients may require this therapy in the event of
uncontrolled blood sugar as the body will increase the
excretion of glucose and water as a result. Clients with
HHNS or diabetic ketoacidosis are prime examples of
situations where hypotonic solutions may be
administered. of Examples of hypotonic solutions
includes...
0.45% normal saline (½ NS)
0.33% normal saline (½ NS)
You might also like
- Fluids Electrolytes and Acid Base ImbalancesDocument8 pagesFluids Electrolytes and Acid Base ImbalancesSamantha Bernardo UndaNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids ExplainedDocument10 pagesIV Fluids ExplainedMarinill SolimanNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids and Solutions GuideDocument16 pagesIV Fluids and Solutions GuideMostafa MahmoudNo ratings yet
- DISS - Mod7 - Dominant Approaches and Ideas of Social Sciences - Psychoanalysis and Rational ChoiceDocument22 pagesDISS - Mod7 - Dominant Approaches and Ideas of Social Sciences - Psychoanalysis and Rational ChoiceRichard FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids ExplainedDocument5 pagesIV Fluids ExplainedRegine Mae Encinada100% (1)
- Iv Fluids and Solutions With Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument33 pagesIv Fluids and Solutions With Nursing ResponsibilitiesJennie JalemNo ratings yet
- 100 Beats Per Minute. Many DifferentDocument4 pages100 Beats Per Minute. Many Differentjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsMehdi SabeiNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answer Key: 1 Where Are You From?Document16 pagesWorkbook Answer Key: 1 Where Are You From?JuniOr Samuel De Los Santos100% (1)
- Normal ValuesDocument1 pageNormal ValuesmimNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Pathway For Complete Immediate Denture TherapyDocument18 pagesA Clinical Pathway For Complete Immediate Denture TherapyPragya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Fluid Management: Presented by Murad Satary Moderator:Dr - Ibrahim QudaisatDocument80 pagesPerioperative Fluid Management: Presented by Murad Satary Moderator:Dr - Ibrahim QudaisatMorad SatariNo ratings yet
- IV Cheatsheet Monochrome PDFDocument2 pagesIV Cheatsheet Monochrome PDFElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- 10 Worst Foods of All TimeDocument8 pages10 Worst Foods of All TimeMary Ann SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Metacognitive Therapy Hjemdal 2013Document13 pagesMetacognitive Therapy Hjemdal 2013rnuevo2No ratings yet
- I.V Fluid: PathologyDocument7 pagesI.V Fluid: PathologyruchikaNo ratings yet
- IV FluidsDocument7 pagesIV FluidsAmy LalringhluaniNo ratings yet
- Isotonic, HypotDocument4 pagesIsotonic, HypotSannyjale BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Programs: Lactated Ringers (Also Known As LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL)Document5 pagesNursing Programs: Lactated Ringers (Also Known As LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL)KiaBlancheTahud100% (1)
- Common Neonatal DisordersDocument71 pagesCommon Neonatal DisordersRANJIT GOGOI100% (2)
- Narrative Report On Guidelines On The Enhance School Improvement Planning (Sip) Process and The School Report Card (SRC)Document3 pagesNarrative Report On Guidelines On The Enhance School Improvement Planning (Sip) Process and The School Report Card (SRC)Anjo Revatoris Renoballes50% (2)
- IV Infusion SolutionDocument8 pagesIV Infusion SolutionmohammedNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Therapy Options and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument16 pagesIV Fluid Therapy Options and Nursing ConsiderationsRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- IV SolutionsDocument8 pagesIV SolutionsAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Zerrudo IVDocument3 pagesZerrudo IVGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- Isotonic, Hypotonic & Hypertonic Solutions ExplainedDocument2 pagesIsotonic, Hypotonic & Hypertonic Solutions ExplainedJuliene Hannah FloresNo ratings yet
- Understanding Tonicity: Hypotonic, Isotonic and Hypertonic IV Solutions Explained in 40 CharactersDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Tonicity: Hypotonic, Isotonic and Hypertonic IV Solutions Explained in 40 CharactersImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fluid TherapyDocument36 pagesFluid TherapyAmin MasromNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Types and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesIV Fluid Types and Nursing ConsiderationsnicoleNo ratings yet
- SAS 9 Parenteral TherapyDocument41 pagesSAS 9 Parenteral Therapyjenet soleilNo ratings yet
- Smith L (2017) Nursing Times 113: 12, 20-23Document59 pagesSmith L (2017) Nursing Times 113: 12, 20-23Derick RanaNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Ivf InsertionDocument76 pagesAssisting in Ivf Insertionrechelle mae legaspiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1Document25 pagesPharmacology 1Gul NazNo ratings yet
- IV CheatsheetDocument2 pagesIV CheatsheetDWIGHT LESTER O. MANGILANo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- IV Cheatsheet Bgnocolor PDFDocument2 pagesIV Cheatsheet Bgnocolor PDFHermiie Joii Galang MaglaquiiNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsJamil KhanNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsEsarpy (Nana)No ratings yet
- PHAR635 Parenteral Dosage Forms: Instructors: Dr. Tarek Jenani Dr. Faten HamedDocument29 pagesPHAR635 Parenteral Dosage Forms: Instructors: Dr. Tarek Jenani Dr. Faten HamedundeadrebornNo ratings yet
- Smith L (2017) Nursing Times 113: 12, 20-23Document59 pagesSmith L (2017) Nursing Times 113: 12, 20-23Derick RanaNo ratings yet
- What Are IV FluidsDocument7 pagesWhat Are IV FluidsKATHLEEN MARIE MONTA�ONo ratings yet
- Isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic IV solutionsDocument3 pagesIsotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic IV solutionsVivian Beth A. NaragNo ratings yet
- IV SolutionsDocument7 pagesIV SolutionsJeg B. Israel Jr.No ratings yet
- IV Fluid Lecturette for Nursing StudentsDocument16 pagesIV Fluid Lecturette for Nursing StudentsbabiNo ratings yet
- IV FluidDocument49 pagesIV Fluidibrahimadnan040No ratings yet
- Refreshing " Fluid Therapy"Document28 pagesRefreshing " Fluid Therapy"Bangun Cholifa nusantaraNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Fluid Therapy: Types of Intravenous SolutionDocument18 pagesParenteral Fluid Therapy: Types of Intravenous SolutionKathleen Joy Costales Magtanong100% (1)
- Three Main Types of IVF: Isotonic Fluids Hypotonic Fluids Hypertonic FluidsDocument9 pagesThree Main Types of IVF: Isotonic Fluids Hypotonic Fluids Hypertonic FluidsIrina Luciana DumitriuNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid ProtocolDocument4 pagesIV Fluid ProtocolAhmad AfghanNo ratings yet
- Aquino, Christian Jufers G. BSN3-NCA2: IsotonicDocument2 pagesAquino, Christian Jufers G. BSN3-NCA2: IsotonicJuf's Aquino IINo ratings yet
- FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE THERAPY GUIDEDocument41 pagesFLUID AND ELECTROLYTE THERAPY GUIDEsyafiqahNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids TheoryDocument13 pagesIV Fluids TheoryFRESY TRI SUGIANTONo ratings yet
- Iv SolutionsDocument12 pagesIv SolutionsRinalyn BalderramaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Intravenous Fluid?Document11 pagesWhat Is An Intravenous Fluid?Arianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy For Critically Ill Dogs and Cats - WSAVA2005 - VINDocument14 pagesFluid Therapy For Critically Ill Dogs and Cats - WSAVA2005 - VINHament KumarNo ratings yet
- IV Solutions: Isotonic, Hypotonic, HypertonicDocument4 pagesIV Solutions: Isotonic, Hypotonic, HypertonicJhade RelletaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills: Intravenous Fluid and Setting Up A DripDocument30 pagesClinical Skills: Intravenous Fluid and Setting Up A DripNabhan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Intravenous FluidsDocument19 pagesIntravenous Fluidsnicolinna2000yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- IV Infusion Preparations Fluid and Electrolytes: DR Anita JanadriDocument22 pagesIV Infusion Preparations Fluid and Electrolytes: DR Anita JanadriMohamed RasoolNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy: Types and UsesDocument11 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy: Types and UsesHayashi Breads MaaNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy GuideDocument6 pagesIV Therapy GuideDexie James Ventenilla DizonNo ratings yet
- Pocket Card - IV Fluids - September 2021Document6 pagesPocket Card - IV Fluids - September 2021NeweeJoonYowNo ratings yet
- Isotonic, Hypotonic, & Hypertonic FluidsDocument3 pagesIsotonic, Hypotonic, & Hypertonic FluidsNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Hospitalized Patient Intravenous Fluid TherapyDocument6 pagesHospitalized Patient Intravenous Fluid TherapyAnaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Skills ReviewerDocument4 pagesMaternal Skills ReviewerLorel Faith ToradaNo ratings yet
- The Spectrum of Amniotic Fluid Embolism: Is Intralipid the solution ?From EverandThe Spectrum of Amniotic Fluid Embolism: Is Intralipid the solution ?No ratings yet
- Practice Q NursingDocument17 pagesPractice Q NursingmimNo ratings yet
- When Can I Register For The NCLEX-RN Exam?Document3 pagesWhen Can I Register For The NCLEX-RN Exam?mimNo ratings yet
- When Can I Register For The NCLEX-RN Exam?Document3 pagesWhen Can I Register For The NCLEX-RN Exam?mimNo ratings yet
- Enhanced MEA Template for CARAYMAN Elementary SchoolDocument6 pagesEnhanced MEA Template for CARAYMAN Elementary SchoolHermis Rivera CequiñaNo ratings yet
- CV Heo Jungyeong 04232017 Without Transcript CompressedDocument4 pagesCV Heo Jungyeong 04232017 Without Transcript Compressedapi-355596464No ratings yet
- Islamda MutlulukDocument7 pagesIslamda MutlulukAhmet HanikoğluNo ratings yet
- Organ System OverviewDocument3 pagesOrgan System OverviewVan DajayNo ratings yet
- Medical Image Processing G R SinhaDocument3 pagesMedical Image Processing G R SinhaDr.MANIVEL K MEC-ASP/ECENo ratings yet
- Shell Advance 4T Ultra 10W-40Document2 pagesShell Advance 4T Ultra 10W-40Anonymous oAbjbl4HNo ratings yet
- The Humanistic School of PsychologyDocument17 pagesThe Humanistic School of PsychologyJohnNo ratings yet
- Class X - Artificial Intelligence - Evaluation - Question BankDocument8 pagesClass X - Artificial Intelligence - Evaluation - Question Bankrenudevi198725No ratings yet
- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Aphthous UlcersDocument17 pagesCauses, Symptoms and Treatment of Aphthous Ulcerssyarifah naziraNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 4Document20 pagesNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 4Firas Muhammad100% (3)
- Ginkgo Biloba: One of the Oldest Trees on EarthDocument12 pagesGinkgo Biloba: One of the Oldest Trees on EarthlucaspadialNo ratings yet
- Gender Differences in Exercise Habits and Quality of Life Reports - Assessing The Moderating Effects of Reasons For ExerciseDocument15 pagesGender Differences in Exercise Habits and Quality of Life Reports - Assessing The Moderating Effects of Reasons For ExerciseArischo MardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Buah Pepaya Terhadap Nafsu Makan Anak Berumur 2-5 Tahun Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas KuranjiDocument16 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Buah Pepaya Terhadap Nafsu Makan Anak Berumur 2-5 Tahun Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas KuranjiRiza IrmasariNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Life EventsDocument30 pagesCOVID-19 Life EventsJess PeltraNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Are Professional Profilers Better - EnglishDocument5 pages1.3 Are Professional Profilers Better - EnglishsmacujaNo ratings yet
- Aviva 4Document4 pagesAviva 4Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- The Lung Meridian Acu-PointsDocument1 pageThe Lung Meridian Acu-PointsVicaas VSNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Transtibial Amputation: Burgess Technique Versus Modified Bru Ckner ProcedureDocument5 pagesConcepts of Transtibial Amputation: Burgess Technique Versus Modified Bru Ckner ProcedureSanjay NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Ed Psych NotesDocument3 pagesEd Psych NotesJorge GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Prentice9e Im Chap17Document5 pagesPrentice9e Im Chap17api-281340024100% (1)
- Siemens Mammomat Nova 3000 ProspektDocument8 pagesSiemens Mammomat Nova 3000 Prospektbancodesangre688No ratings yet
- HRM (Career Planning)Document21 pagesHRM (Career Planning)pradeep3673No ratings yet
- 12 Lead ECG Interpretation: The Basics and Beyond: ObjectivesDocument35 pages12 Lead ECG Interpretation: The Basics and Beyond: ObjectivesEeqNo ratings yet