Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TSG C 012+pretreatment+ +Dechlorination+Using+Sodium+Metabisulfite+RevB
TSG C 012+pretreatment+ +Dechlorination+Using+Sodium+Metabisulfite+RevB
Uploaded by
JendayiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TSG C 012+pretreatment+ +Dechlorination+Using+Sodium+Metabisulfite+RevB
TSG C 012+pretreatment+ +Dechlorination+Using+Sodium+Metabisulfite+RevB
Uploaded by
JendayiCopyright:
Available Formats
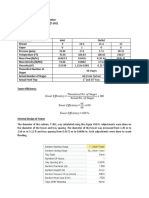
Technical Service Guide
Pretreatment
Dechlorination Using Sodium Metabisulfate
TRISEP® RO & NF thin-film composite membranes require the complete removal of free chlorine from the
feed water. Sodium Metabisulfite (SMBS) is often used as pretreatment to large RO systems for free
chlorine removal and as a biostatic. Carbon filters are a common alternative for small systems, but SMBS
has an advantage for larger systems due to a lower risk of bacteria growth that can cause biological fouling.
Importance of Dechlorination
Feed water to an RO/NF system using TRISEP thin-film composite membranes must have all free chlorine
removed to prevent membrane oxidation. Chlorine oxidation of the membrane surface can cause increased
flux through the membrane and decreased salt rejection. MICRODYN-NADIR recommends total removal
of chlorine during operation of the RO/NF system. A common rule of thumb is that degradation can occur
from about 1,000 to 2,000 ppm-hours of chlorine exposure, although the rate of membrane oxidation will
vary for different feed waters. Higher temperatures and heavy metals such as iron can catalyze membrane
oxidation and significantly reduce the membranes resistance to chlorine degradation.
Dosing SMBS Solution
SMBS is commercially available as a solid in various % purities, typically up to 99%. Food-grade quality
SMBS that is free from impurities is preferred. Under dry, cool storage conditions, solid SMBS can be
stored for about 5 months. SMBS solutions generally have a short shelf life, as it reacts with oxygen as
well as chlorine, with a shelf life of only about 5 days for a 2% solution and about 1 month for a 20%
solution. While theoretically about 0.75 ppm SMBS (equivalent to about 1.5 ppm sodium bisulfite (SBS))
will neutralize 1.0 ppm chlorine, typically 1.0-1.5 ppm SMBS (2-3 ppm SBS) per 1.0 ppm chlorine is used
to account for incomplete mixing. The SMBS should be dosed downstream of cartridge filters so that the
cartridges can still be disinfected by the chlorine. A separate cartridge should be used on the SMBS
solution before dosing into the RO/NF feed water. The SMBS solution should be dosed well enough in
advance of the RO system to allow for about 25 seconds of reaction time. A static mixer is recommended
for enhanced in-line mixing.
SMBS Dechlorination Reaction
Sodium metabisulfite (SMBS) initially reacts with water to form sodium bisulfite (SBS):
Na2S2O5 + H2O → 2 NaHSO3
Next, SBS reacts with hypochlorous acid to form byproducts free from free chlorines:
2 NaHSO3 + 2 HOCl → H2SO4 + 2 HCl + Na2SO4
These byproducts are all readily removed by the RO system.
Chlorine Monitoring
Chlorine levels in the RO/NF feed should be monitored continuously to prevent chlorine passing into the
RO/NF system. An oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) electrode is recommended to be used downstream
of the dosing plant to monitor the presence of chlorine or other oxidants. If the ORP meter reading exceeds
300 mV, a warning should notify operators to take action to reduce the chlorine levels in the feed water. If
the ORP meter exceeds 350 mV, the electrode signal should disable the high pressure pump until a safe
oxidant concentration can be reached.
Europe Americas Asia
Germany: +49 611 962 6001 USA: +1 805 964 8003 China: + 86 592 677 5500
Italy: +39 0721 1796201 Brazil: +55 11 3378 7500 Singapore: +65 6457 7533
info@microdyn-nadir.de info@microdyn-nadir.com infochina@microdyn-nadir.cn
Solving
A MANN Unmet
+ HUMMEL Needs
Company with Customized Products
Form No: TSG-C-011 // Revision: B // Date: April 21, 2017
Form No: TSG-C-012 // Revision: B // Date: April 21, 2017
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Comparative Study of Physical and Bacteriological Analysis of Borehole Water in Kogi StateDocument8 pagesComparative Study of Physical and Bacteriological Analysis of Borehole Water in Kogi StateIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Soil Thermal Stability Thermal Resistivity and Underground Cable Ampacity PDFDocument12 pagesMeasurement of Soil Thermal Stability Thermal Resistivity and Underground Cable Ampacity PDFJayabalan R KNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Sci-NotesDocument17 pagesClass 6 Sci-NotesZoyaNo ratings yet
- Tds Masterroc MP 355 1k DW v2.0Document2 pagesTds Masterroc MP 355 1k DW v2.0DNo ratings yet
- Graphite Purification Al2o3Document2 pagesGraphite Purification Al2o3Narayana Murthy GadiNo ratings yet
- The Draught Requirement of Disc Plough On Lithosols Soils of Adamawa State, NigeriaDocument10 pagesThe Draught Requirement of Disc Plough On Lithosols Soils of Adamawa State, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument24 pagesMetals and Non MetalsSrinivas VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Musa 2009Document288 pagesMusa 2009MogadNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XDocument14 pagesSection-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- GATE COACHchemical Engineering Thermodynamics Sample Chapter PDFDocument41 pagesGATE COACHchemical Engineering Thermodynamics Sample Chapter PDFKanchan NandeshwarNo ratings yet
- GarrettDocument2 pagesGarrettAndrey MarviantoNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Process Condition For Extraction of Gelatin From Red TilapiaDocument8 pagesOptimization of Process Condition For Extraction of Gelatin From Red TilapiaRND GelatinNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument1 pageBiologyMikaylaNo ratings yet
- IISER Admission Test Question Paper 2Document2 pagesIISER Admission Test Question Paper 2Abhishek Abh-iNo ratings yet
- Soil Consolidation - R1Document95 pagesSoil Consolidation - R1estardo123No ratings yet
- Polycaprolactone: Synthesis, Properties, and ApplicationsDocument36 pagesPolycaprolactone: Synthesis, Properties, and ApplicationsFrench Sarah Nera100% (1)
- Charles LawDocument17 pagesCharles Lawkarijsd08No ratings yet
- 13e Chap 05 Solution Manual Engineering Mechanics PDFDocument94 pages13e Chap 05 Solution Manual Engineering Mechanics PDFJohnLesterLaurelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document13 pagesExperiment 2Jerome OlgadoNo ratings yet
- Lignan Dicarboxylates and Terpenoids From The Flower Buds of Cananga Odorata and Their Inhibitory E Ffects On MelanogenesisDocument10 pagesLignan Dicarboxylates and Terpenoids From The Flower Buds of Cananga Odorata and Their Inhibitory E Ffects On MelanogenesisIrene Yuni FaridaNo ratings yet
- Zongping Shao, Xiaomin Xu - Zinc-Air Batteries - Introduction, Design Principles and Emerging Technologies-Wiley-VCH (2022)Document295 pagesZongping Shao, Xiaomin Xu - Zinc-Air Batteries - Introduction, Design Principles and Emerging Technologies-Wiley-VCH (2022)Martin EkiyorNo ratings yet
- VpCI 368DDocument8 pagesVpCI 368DMUHAMMAD UZAIRNo ratings yet
- Moisture and Total Solids Analysis: Importance of Moisture AssayDocument7 pagesMoisture and Total Solids Analysis: Importance of Moisture AssayNaveed Ul HasanNo ratings yet
- Project I Oxalate Ions in GuavaDocument14 pagesProject I Oxalate Ions in Guavaaeriel judsonNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Exercise 2 Circular MotionDocument5 pagesAnswer Key Exercise 2 Circular MotionDamiana BetsyNo ratings yet
- L 23-28 Wave Mechanics AMP 19Document172 pagesL 23-28 Wave Mechanics AMP 19Anindya BiswasNo ratings yet
- Example Shell-and-Tube Exchanger Using The Kern, Bell-Delaware, Wills-Johnston PDFDocument9 pagesExample Shell-and-Tube Exchanger Using The Kern, Bell-Delaware, Wills-Johnston PDFcyclon2010No ratings yet
- T 202 ACETONE COLUMN DESIGN - v2Document7 pagesT 202 ACETONE COLUMN DESIGN - v2Jewls HatudNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Zetag DATA Magnasol 4620 G - 0410Document2 pagesChemicals Zetag DATA Magnasol 4620 G - 0410PromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- LP Grade-8 Procedure in Cleaning Front Office Tools and Equipmentjj.Document6 pagesLP Grade-8 Procedure in Cleaning Front Office Tools and Equipmentjj.Mira BagayNo ratings yet