Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EN 1371-1 Eng
Uploaded by
dface_0310 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views24 pagesOriginal Title
EN 1371-1 eng
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views24 pagesEN 1371-1 Eng
Uploaded by
dface_031Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
eo
pasau dhe, CLBCO degrees
EUROPEAN STANDARD EN 1371-1
i a C9
NORME EUROPEENNE UA RIC@, ptt. ~U Yy
EUROPAISCHE NORM ne
18 77.140.80; 77,150.99
Descriptor
English version
Founding - Liquid penetrant inspection - Part 1:
Sand, gravity die and Tow pressure die castings,
Forderle = contrdte par ressuage - partie 1; Gletereivesen: - Ei ‘fing "= Teil 42
Pitces. mauler au, cable, en coquittes pat Sand)" schwertrafttor tens und
gravité et basse pression Niederdruckkokillengutstucke
‘This European Standard was approved by CEN on 1997-06-02. CEN menbers
Regulations shich stipulate the conditions for giv
any alteration.
Up-to-date Ui bibliographical references concerning such national standards may be obtained on application to
the Central Secretariat or to eny CEW menber.
bound to comply with the CEN/CENELEC Internal
this European Standard the status of a natlonel standard ui thout
The European Standards extet in three official versions (English, French, German). A version In any other Language
ade by eranatation under ‘the responsibility of a CEN member Into Ite ‘own Canguage and notified £oshe Coneeat
Secretariat hos the sane status se the official versions "
CEN menbera are the natfonal standards bodies of Austr!
Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Luxenbourg, Nether(
Kingdon.
lelgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland,
iorway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerla
CEN
European Comittee for Standardization
Comité Européen de Hormal {sation
Europbisches Koaltee fOr Normung
nee, Germany,
“Gnd Uni red
Central secretariat: rue de Stasuart,36 8-1050 Brussels
AU rfohte of exploftation in any form and by any neane reserved worlvide for OfW nat Tonal
Menbers
Ref. WO. EN 1371-1:1997 €
wa Ke
"Page 2
EN 1371-1:1997
Fiore page
Contents
' Page Page
cc seveveresees 3 Table 1: Noture of discontinuities and types
of corresponding liquid penetrant
Introduction. senee 4 Inspection indications ............. 9
1 Scope . sss++ 4 Table 2: Severity levels for liquid penetrant
Inspection ~ Non-linear indications
2 Normative references 5 4 Isolated (SP) or clustered (CP)
3. Conditions for liquid penetrant Table 3: Severity levels for quid penetrant
Inspection ..... eee 4 Inspection ~ Linear (LP) and aligned (AP)
Indleatlons. 6... . ee ee eee eeee eee WY
4” Method of inspection re 5
4.1. Operating mode testsssses 5 Table 4: Recommendad surface finish for liquid
4.2. Qualification of the operator vB penetrant inspection ...........04. 12
4.3. Surface preparation ; Sooo)
4.4 Conditions of inspe iiitees 8. Annex A informative) Bibliography
) 5 Acceptance crite seseeseess 6 Annex B finformative) Reference figur
5.1. Indications of discontinuities... : 6 ‘Non-linear isolated indications
5.2, Definition of liquid penetrant inspection designated SP ........ vee 13
indications ....seeeeeeeeeeev ees
5.3 Severity levels... sess 8 Annex € (informative) Reference figures ~
Non-linear indications designated SP
6 Classification of the Indications and and GP sisscssceeee arente)
Interpretation of results ...... 7
‘Annex D informative) Reference figures —
7 Ordering ers Linear end aligned indications designated
UP and AP eee cscs
8 Retesting . oaeeene)
‘Annex E informative) Model of a liquid
8 8 ppenetrant inspection document +22
Foreword
‘This European Standard has been prepared by Technical Committee CEN/TC 190 “Foundry technology”, the
secretariat of which is held by DIN.
This European Standard shall be given the status of a national stendard, either by publication of an identical text
or by endorsement, at the latest by December 1997, and conflicting national standards shall be withdrawn at
the latest by December 1997.
Within its programme of work, Technical Committee CEN/TC 190 requested CEN/TC 190/WG 4.20 "Surface
ingpection™ to prepare the following standard:
—N1371-1 '
Founding ~ Liquid penetrant inspection ~ Part 1: Sand, gravity die and low pressure die castings
‘This is one of two European Standards for liquid penetrant inspection. The other stendard
prEN 1371-2
;pection ~ Part 2: Investment castings
DB econting tine cENCENELEC InrlReulos, he nana andr ergenieatons of te ftowing
‘countries are bound to implement this European Standard: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland,
France, Germeny, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden,
‘Switzerland and the United Kingdom.
ea
Page 4 =
EN 1371-1:1997
Introduction oe
‘This European Standard complements the general principles of liquid penetrant Inspection given InEN B74 for +
the additional requirements of the foundry industry.
Liquid penetrant inspection as well as any other non destructive examination method Is pert of # genersl or
specific assessment of the quality of a casting to be agreed between the manufacturer and the purchaser at the
time of acceptance of the order.
Poneirant testing examination of castings is stenderdized in two parts: \ eee ase
— EN 1971-1; Sand, gravity die and low pressure die castings
= prEN 1371-2: Investment castings rs
1 Scope
‘This European Standard applies to the liquid penetrant testing of all castings {except copper-tin and/or copper-
tin-lead alloy castings, where copper is the major constituent) produced in conventionel sand moulds, by gravity
and low-pressure die casting whatever their grade and the casting procedure used to produce ther
This stendard doeg not apply to investment and pressure
2 Normative references
‘This standard incorporates, by dated or undated reference, provisions from other publications. These normative
references are cited ét the appropriate places in the text and the publications are listed hereafter. For dated
teferences, subsequent amendments to or revisions of any of these publications apply to this standard only
when incorporated in it by amendment or revision. For undated references, the latest edition of the publici
referred to applies.
EN 473
Qualification and certification of NDT personnel - General principles
Non-destructive testing - Penetrant testing ~ Part 1: General principles .
ED e
Founding - Liquid penetrant inspection ~ Part 2: Investment castings
prEN 1956
Non-destructive te:
19 ~ Penetrant testing and magnetic particle testing - Viewing conditions
nd cited at the
NOTE: Informative reference to documents used in the pr
appropriate places in the text, are listed in a bibliography, se
ation of this standard,
inex A.
3. Conditions for liquid penetrant inspection
‘The manufacturing stage(s) when liquid penetrant inspection is to be performed shall be clearly. defined by
agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser.
Page 5
EN 1971-1:1997
Inspection shall be carried out only on those areas of the castings and on the percentage of castings agreed.
Inspection requirements shall be clearly stated in the call for tender, in the request for prices and, mor
particularly, in the order sent to the manufacturer and accepted by him, so that the manufacturer can assess
the costs of manfacturing to satisfy the required severity level and the costs of additional inspections and
operations, and the manufacturing risks involved. .
For
ich agreed area of the casting to be inspected, the following shall be indicated:
~ type of discontinuity;
verity level.
Sensitivity can differ depending on the method of liquid penetrant inspection selecte
levels required shall be selected as a function of the liquid pene!
manufacturer and the purchaser.
Therefore the severity
ints v'3ed and the method agreed between the
The type of discontinuity and the severity level can vary depending on the area of the casting inspected (see
tables 1 to 3).
4 Method of inspection
4.1 Operating mode
Inspection shall be carried out as described in EN 671-1. The characteri
checked in accordance with spe
he penetrant materials shall be
fications to be agreed between the manufacturer and the purchaser.
4.2 Qualification of the operators
Inspection shall be pérformed by personnel, qualified in accordance with EN 473 or by a certification scheme
which is. considered to be equivalent. The qi ion level of the personnel shall be agreed between the
manufacturer and the purchaser at the time of acceptance of the order.
4.3 Surface preparation
The surface to’be inspected shall
contaminant which could inter
inspection test results.
lean and free from oil, grease, moulding and coating residues or any other
fe with the correct implementation and interpretation of the penetrant
The surface finish of the casting in the area to be tested shall have sufficient brightness and contrast of colour
shape to determine the required severity level. Unless otherwise specified at the time of ordering,
finish shall be selected from table 4.
NOTE: It is recommended that the assessment of surface finish is ca
roughness comparator.
sd out using a visual cast-surface
it inspection shall be performed on castings in the as-delivered conditon. If sand blasting or shot
blasting’) is required, it shall be as light as possible, in order to avoid sealing or closing up possible dis-
continuities. If the tisk of sealing or closing up possible discontinuities is unacceptable then blasting shall be
followed by chemical etching in ofder to enable detection of discontinuities. The chemical composition of the
‘stching bath and other parameters such as concentration, temperature, immersion time neutralizing and rinsing,
4.4 Conditions of inspection
The inspection shall be carried out with the naked eye or at a maximum magnification of 3 and viewing
conditions in conformity with prEN 1966,
') Shot blasting is not recommended prior to liquid penetrant testing.
ee ¥
j
997
5 Acceptance criteria
5.1. Indications of discontinuities
5.1.1 General
‘The indication of discontinuities can be non-linear (isolated or clustered),
penetrant inspection cannot generally be used to determine the size of
discontinuities to be assessed by measurement of the length L of the indic
+ it allows
. In the following clauses
= L_ indicates length;
- W indicates width:
1 indicates section thickness;
= SP indicates non-linear isolated indicat
~ CP indicates non-linear clustered indication;
~ AP indicates aligned indication;
= LP indicates linear indication.
5.1.2 Criteria a
i 3
tc.) shown in table 1.
‘The various types of penetrant indication can correspond to the discontinuities (A, B, C,
jled in table 1 shall give either a non-linear, linear or aligned liquid penetrant
5.2. Definition of liquid penetrant inspection indications
al linear indication (LP). An indication with a largest dimension three or more times its smallest dimension
fie. L = 3; :
b) non-linear indication. An indication with largest dimension less then three times its smallest dimension
fie. L< 3M 5
~ Isolated (SPI;
= clustered {CP}: area of multiple indict
= {they seem to form only one indication!
ions, the distance between the indications cannot be measured
©) sligned indication (API. Indications that are either
= liner: the distance between two indications is smaller than the length of the longest discontinuity i
the alignment;
indications is !éss than 2 mm and at least three indications ar
r; the distance between two
5.3. Severity levels
5.3.1 General
Several severity levels are recognized in accordance with tables 2 and 3. It is necessary to carry out the test
on a surface coiresponding to 8 given degree of finish (see table 4) depending on the severity level desired.
‘The liquid penetrant inspection for each type of indication and its severity levels shall be specified at the time
of ordering, by the purchaser, depending on the use of the castings. The manufacturer shall give his agreement.
by
we
Page 7
EN 1371-1:1997
The penetrant indications to be taken into account shall have dimensions in accordance with the severity level.
The required séverity level shall be
‘manufacturer and the purchaser.
ected accordingly and specified in the order by agreement between the
5.3.2 Criteria
The maximum permissible length for linear or aligned indications vari
Section thickness types are specified (see table 3):
with the section thickness . Three
~ type
1s 16 mm;
= type b: 16 mm < 1s 60 mm;
~ type cf > 50 mm,
Tables 2 and 3 show the largest dimensions of the siallest indications to be considered in the severity level
concerned.
5.3.3 Tables
Table 2 corresponds to non-lin
isolated or non-linear clustered indications.
Examples of non-linear indications are shown in annexes B and C. These have been established in accordance
with table 2; the reference figures are given to and shall be interpreted against a scale of ir
Table 3 corresponds to linear or aligned indications.
Tables. 2 and 3 a
independent (differing severity lavels may be selected from these tables)
6 Classification of the indications and interpretation of results
In order to classify an indication of discontinuity, a ) should be placed in
the most unfavourable location. The observed indications shall be in relation to the referenc, severity levels as
described in this standard and compared to the equival ely better severity level.
inalettions shall be considered to be equivalent when the same number of non-linear spots andlor the same
length of linear indications of similar appearance are detected. Maximum permissible digeerth ug may appear
‘simultaneously on the area of 105 mmx 148 mm:
ion type, the observed
be considered to be in non-conformanc
indard when the observed
Verity level is worse than that specitied in the order, the casting shall
with this standard. It shall be considered as conforming with t
verity level is equal to or better than that specified in the order, :
For Severity levels 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6, classification shall be made by comparison with reference figures. For
Band ayes 001. 01. 02 nd 03, and in the event of dispute in the interpretation of severity levels 1, 2, 3,
4 and 6, reference shall be made to the values in tables 2 and 3.
NOTE 1: Reference figures corresponding to non-linear, aligned and clustered indications in accordance
with tables 2 and 3 are repre annexes B, C and D for guidance only, drawn to a scele of 1: 1.
ions in total are smaller than 105 mmx 148 mm, then the
‘and agreed between the manufacturer and the put
Poge 8
EN 1371-1:1997
The requirements deteiled in the order or in the specifications shall be writ
used in this standard:
-Extiniples of j.ow the requirements shall be specified are as follows:
= non-linear indications level 2 (sbbreviated as SP 2);
= linear and aligned indications level 5 (ab: evieted as LP Sc and AP Bc).
NOTE 2: "c* in LP 6c means: The section thickness type r is greater than 50 mm,
NOTE 3: Severity level references are arbitrary. They cannot be considered in the same progression from
‘one table to the other nor from one kind of indication to another.
NOTE 4: Provided that on the casting surf contains discontinuities which exceed the
agreed geverity level, theré is no limit to the acceptability of discontinuities.
7 Ordering
‘The enquiry and/or order shall specify the following points:
8} the area(s) of the castingis) and percentage of castings to be inspected (
e clause 3);
b) the manufacturing stage or stages when the inspection is to be carried out, as agreed between the parties
(see clause 3);
Cc) the type of discontinuity indications and the severity level for each area of the casting(s) to be inspected
{see clause 3 and 6.2).
8 Retesting
Retesting shall be in accordance with EN 671-1 %
9 Post-exemination cleaning procedures
Post-examination cleaning procedures shall be in accordance with EN 571-1.
J Inspection documentation
Inspection documentation shall be in accordance with EN 571~
is shown in annex E.
A model of a trilingual inspection document
Page 3
EN 1971-1:1997
‘Table 1: Nature of discontinuities and types of corresponding liquid penetrant Inspection indications.
symbol non-linear
isolated
SP Lp ap
(Gas porosity A x = x
jand and/or slag inclusions A z = x
{other than alumina)
Shrinkage defects due to
nitrogen’) G x x x
Cracks. D = x x
Hot tears E = x x
—
Inserts F x x x
—-
©) [ters and cold shuts H = x x
Presence of alumina’) J = x x
Graphite flotation’) K
*) For non-ferrous alloys only
For cast iron only
Page 10
EN 1371-1:1997
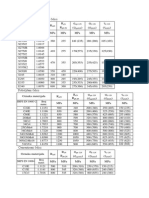
‘Tobie 2: Severity levels for quid penstrant inspection - Non-inear Incleations')
Isolated (SP) or clustered (CP) Ty
Severity levels
C1 spor) | spo2 | spos | sp1 | sP2 | sP3|°o.4 | gpg
. cp.o1) | cpoz | cpos | cp1 | cp2 | ce3
magnifying
Inspection means glass or eye
eye
Magnification for observation | 1 H
of penetrant indication
Diametér of smallest indication
to be considered in mm a ud 1 Ww] 2] o-[+6 u
Maximum number of non-linear|
indications allowed a ie a . S| 12 | 20 | a2
Maximum size of discontinuity
indcnton AB, Cand F ®
allowed in mm
~ isolated indications SP 1 1 1s | 3 6 }.9 | 14 |oa
~ clustered indications CP 3 4 6 |1 | 1 | 2 | - | -
{for aluminium alloys only,
‘with @ maximum of 2 per
ares)
) Such that L < 3 W where Z is the length and Wis the width of the indication.
2) Severity level to be reserved for particular us
NOTE 1: Only, values expressed in this table are valid. Reference figures are for information only (see
annexes # and C).
NOTE 2: The sensitivity can differ, depending on the method of penetrant inspection
ected.
NOTE 3: The penetrant indications may grow over a period of time and this should be taken into account. | @
Page 11
EN 1371-1:1997
Table 3: Severity levels for liquid penetrant inspection ~ Linear (LP) and aligned (AP) indications")
Severity te
wpoor furor | upi [| we2 | ips [ ups | ws
apooi | apoi| ap1 | AP2 | ap3 | apa | APE
a ‘magnifying glass
Inepecton meane ing oe
Maghiiation for observation of za 7
pert indeation :
Length of smallest indication to be
considered in mm O38 18 2 a 8 5
“Arrangomert of indications - |
isolated (I) or cumulative (C) bod Hyeyryeyiyeyryeyrye
Masur
ection thickness
lve pend ofa aol off [roe |repfee
wrth | PES
tigned
im section thickness
inloations ‘ype ° a lA] oa} ofe |rat4r |27 Ho
tllowed | 16 mm <1 60mm |
depending
jon the" | section thickness Z| lp
a ‘ypee of | 2/) 5 Ko] 10 }40 |18 }4o | 20 [4s | 45 Yo
in ment pee 1 {P| BL |S
figure figure figure
D2) D3 De
Following
annex D
figure figure
D6 DT
1) The length L of an aligned indication is the distence between the
land the opposite end of the last discontinuity iL = 3 W)
ing point of the first discontinuity
2) No functional relationship exists betwaen range of wall thickness and maximum crack length, relative to
fracture mechanics study. However, this table is # useful guide where no relevant fracture mechanics
parameters presently exist.
NOTE 1; Only values expre
annex 0),
this table are valid. Reference figures or
for information only (see
NOTE 2: The severity levels 001, 01 and 1 are di
NOTE 3: Tho sensitivity can differ, depending on the method of pene
NOTE 4: The penetrant indications may grow over a period of time and this should be taken into account.
Page 12
EN 1371-1:1997
‘Table 4: Recommended surface finish for liquid penetrant inspection, rel
Dimension of smallest
indication
tors!)
SCRATA)
2/081 ~ 1/081
182-282
AG 181-281 AY ;
oo i 382-452 Ht ‘
5 281-381 A2 H
482-552 H2 iH
noni specified A3-A4 i
(rough surface) H3
) See EN 1370
*) See annex A
Page 13
EN 1971-1:1997
Annex A (informative) 4
Bibliography
{In the preparation of this European Standard, use was made of a number of documents for reference purposes.
‘These informative references are cited at the appropriate places in the text and the publications are listed
hereafter.
180 4987
Stoel castings ~ Penetrant inspection
Iso 9916
Aluminium alloy and magnesium alloy castings - Liquid penetrant inspection
"SCRATA comparators for the definition of surface quality of steel castings", available from The Castings
Development Centre Ltd., 7 East Bank Road, Sheffield, S2 3PT, United Kingdom.
“BNIF 359 Recommandation technique du Bureaus de Normalisation des Industries de la Fonderie. Caractérisation
d’états de surface des pidces moulées ~ Utilisation des échantillons types de 110 x 160 mm*, available from
Editions Techniques des Industries de la Fonderie, 44 avenue de la Division Leclerc, 92310 Sévres, France.
Annex B (informative) -
Reference figures - Non-linear isolated indications designated SP
Valid for all cast alloys éxcept cast aluminium and magnesium alloys
NOTE: All re
rence figures shown in this annex are for guidance only and are drawn and shall be used
at a scale of
Figure B.1: Severity level SP t
Page 14
EN 1971-1:1997
Figure B.2: Severity level SP 2
a)
Le Se
Figure B.3: Severity level SP 3 hPa
Page 18
EN 1971-1:1997
Figure B.4: Severity level SP 4
.® . 0: |
’ e ® °
@ . oo.
8
oe O 7 ® °
@ » 40
Figure B.6: Severity level SP 5
Page 16 s
EN 1371-1:1997
Annex C (informative) i
Reference figures - Non-linear indications designated SP and CP
Valid only for aluminium and magnesium cast alloys. i
NOTE: All reference figures shown in this annex are for guidance only and are drawn and shall be used
at a scale of 1: 1. i
Figure C.1: Severity level SP'1 - CP 1
Page 17
EN 1371-1:1997
Figure C.2: Severity level SP 2 - CP 2
Figure C.3: Severity level SP 3 ~ CP'S
Page 18
EN 1371-1:1997
Annex D (informative)
Reference figures — Linear and aligned indications designated LP and AP
Valid for all cast alloys
NOTE: All reference figures shown in this annex are for guidance only and are drawn and shall be uséd
at a scale of 1: 1.
Figure D.1: Severity level LP 1a - AP 1a
=e
Page 19
EN 1971-1:1997
Figure D.3: Severity level LP 1¢ - AP 1c ILP 2b*) ~ AP 2b *) or LP 3a *) - AP 3a*)]
") Approximately comparable at these severity levels |
Page 20
EN 1371-1:1997
Figure D.4: Severity level LP 2c ~ AP 2c [LP 3b*) — AP 3b*) of LP 4a*) ~ AP.4
jt Severity level LP 3c - AP 3c [LP 4b*) - AP 4b*) or LP 6
- AP 6a)]
"| Approximately comparable at these severity levels
Page 21
EN 1971-1:1997
an :
Bot Figure D.6: Severity level LP 4c - AP 4c [LP 6b*) ~ AP Sb*i]
Figure D.7: Severity level LP Sc - AP 6c
|
|
1
|
| +) Approximately comparable at these severity lovelé
bpd
&
Annex E (informative)
Model of a liquid penetrant Inspection document
Company Liquid-penetrant inspection document
Société Document de contréle
Firma Prafbescheinigung zur Eindringprofung
Customer Order No.
Client Commande n*
Kunde Bestell-Nr.
Specltication Material
Spécification Nuance
Vorschrift Werkstoft Schmelze Nr.
Taenitication | Guanity | Casting designation Tot No, Brewing No;
Marquege Quantité |- Désignstion des pitces | n° du lot Plan n*
Kennzeichnung Menge | GuBstdckbezeichnung | _Los Nr. Zeichnung Nr.
Tapa exnrined = Fone ContTelee = PruTbersich
0 100 %
Ci testing scheme - plan de contréle ~ Prifplan
C. cavity root ~ fonds atfouillements ~. Avsmuldung fOr Schweitung
Stage - stede — Zustand
CO. after heat treatment - apras traitement thermique — nach Wirmebehendlung
O betore stress relieving
avant détensionnement - vor Spnnungsarmglihen
Dye-penetrant ~ pénétrant — Eindringmittel
Trademark ~ marque ~ Handelsmarke ...
Excess penetrant remover ~ produit de lavage - Spilmittel
Trademark ~ marque ~ Handelsmarke’...ssssseeres
Developer - révélateur ~ Entwickler
Trademark - marque - Handelsmarke
(continued)
a
Model (continued)
Page 23,
EN 1371-1:1997
Testing conditions — conditions Wexamen = Prifbedingungen
jurface condition ~ état de surface - Oberflchenzustand
‘shot blasted - grensillé ~ gestrahit
D ground - meuté - geschitten
TD machined — usiné - mechanisch b
Casting temperature — température de la pidce moulée - Guisticktemperatur
D5 ‘Cup tofjusqu'amis 14 °C
0116 ‘cup tojusqu'anis 36 *c
D 36 ‘Cup tojusqu'abis 55 *C
oO os mELe
Pre-cleaning ~ nettoyage préslable - Vorreinigung 7
D yes - oui -
Ono + non - nein
Penetrant application — application du pénétrant — Auftragan des Pritmittels
O brush - pinceau - Pinsel
D spray - pulvérisation - Sprihen
D aiip - immersion - Tauchen
Penetration time — temps d’imprégnation - Eindringdauer ++ min
Penetration removal ~ elimination du péndtrant ~ Entforen des Eindringmivele
D cleaning with water - lavage a eau - Abspiilen mit Wasser
CO solvent - solvant ~ Losemittel
Drying time'~ durée de séchage = Tracknungsdauer min
Drying temperature ~ température de séchage - Trocknungstemperatur
Developer epplication — pplication du révélateur - Anwendung des Entwickle
C2. brush - pinceau - Pinsel
CO spray - pulvérisation - Sprohen
wet - humide ~ nas
D dry - sec - trocken
Developing time ~ temps de révélation ~ Entwicklungsdaue
Mlumination - éclairage - Beleuchtung
CO naturel - naturel - Tagesiicht
D artiticial - artiticiel - kanstlich
D uttraviolet ~ ultraviolet ~ ultraviolett
Testing results - résultats de l'examen — Prifergebnisse
‘According to - conforme a - entsprechend
‘Accepted - accepté - abgenommen
Oy
Dino - non - nein
oul - ja
(continued)
Page 24
EN 1371-1:1997
Model (concluded)
Won-conformance note - fiche d’enomalie — Beanstendung
Continuation sheet ~ annexe - Fortsetzungsblett
13 Yes = out - je
C no - non ~ nein
Tnepection authority ~ organieme de controle = Abnahmegesellachaft
‘Quality sasurance section ~ service assurance qualité - Abteilung Qualitétssicherung
nature de Tihepscteur/contrOleur ~ Unterschrit des Letters der
| Stanatare srnapectaraperator=
fetolle/Prifers
ick the relevant box.
Hf applicable,
Suivant le cas, cocher le case correspondante.
Fells zutreffend, Entsprechendes ankreuzen.
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- 2000-2004 Renault Twingo I Fuse Box DiagramDocument3 pages2000-2004 Renault Twingo I Fuse Box Diagramdface_031No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Norme ISODocument1 pageNorme ISOFolpoNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Praktikum Mašinskih ElemenataDocument115 pagesPraktikum Mašinskih Elemenatadface_031100% (1)
- EN 12680-3 EngDocument15 pagesEN 12680-3 Engdface_031No ratings yet
- Definicije I Oznake Na CrtezimaDocument4 pagesDefinicije I Oznake Na Crtezimadface_031No ratings yet
- Industrial Vibrators: The Worldwide Leader in Vibration TechnologyDocument41 pagesIndustrial Vibrators: The Worldwide Leader in Vibration Technologydface_031No ratings yet
- d7f PDFDocument202 pagesd7f PDFdface_031No ratings yet
- VibrodijagnostikaDocument13 pagesVibrodijagnostikadface_031No ratings yet
- Introduction To FEADocument55 pagesIntroduction To FEAdface_031No ratings yet
- Tabela Emisivnosti Materijala PDFDocument3 pagesTabela Emisivnosti Materijala PDFdface_031No ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Lightweight Clutch DiskDocument62 pagesThermal Analysis of Lightweight Clutch Diskdface_031No ratings yet
- Poly V Belt SpecsDocument6 pagesPoly V Belt Specsdface_031No ratings yet