Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EFA - Module 1
EFA - Module 1
Uploaded by
calvin AliaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EFA - Module 1
EFA - Module 1
Uploaded by
calvin AliaCopyright:
Available Formats
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
This course covers the
mandatory competences
and the required
knowledge, understanding
and proficiencies
prescribed in Table A-VI/1-3
of the STCW Code as
amended.
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
• An immediate help
provided to a sick or
injured person until
professional assistance
arrives
• Includes self-help or
home care if medical
assistance is not
available or delayed
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Bridge that fills the gap
between injured crew or
passenger and the medical
officer
Immediate Care Only
Endorse Victim to Medical
Officer upon arrival
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
1 2 3
To alleviate To prevent
To Prolong
pain and further
Life
sufferings injury
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Safety
Consciousness
Breathing
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Radial Pulse Brachial Pulse Carotid Pulse
Femoral Pulse Posterior Dorsalis Pedis
Tibial Pulse Pulse
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
PROCEDURE
1. Determines safety of the scene
2. Checks for consciousness
3. Checks for breathing
4. Activates medical assistance
5. Checks for pulse
FIRE PREVENTION AND FIRE FIGHTING
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord
to various parts of the body.
Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=44B0ms3XPKU
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon
dioxide
Parts of the respiratory system
• Nose
• Cilia
• Trachea
• Bronchi
• Bronchiole
• Alveoli
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zRv5tNCMpyY
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
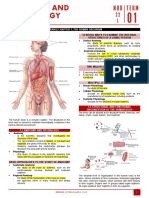
Responsible for the flow of blood, nutrients, hormones,
oxygen and other gases to and from cells
Basic Components
Heart Blood Vessels Blood
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
The Heart
• Muscular organ with four
chambers
• Located behind and slightly
left of the chest
• Pumps blood through
network of blood vessels
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Blood Vessels
• Measures about 60,000
miles (96,560 kms.
• Transports oxygenated
blood from the heart
• Delivers oxygen and
nutrients to the cells
• Return deoxygenated
blood back to heart
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Blood
• Average adult has 5 to
6 liters of blood
• Made up of red blood
cells, white blood cells,
plasma, platelet
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CWFyxn0qDEU
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Waterproof, cushion and protect the body from
infection
The Skin
• Largest organ of the human body
• Includes the skin, hair, nails,
glands and nerve receptors.
• Weighs about 6 lbs. (2.7
kilograms)
• Sheds itself about once every 27
days
• In adults, skin covers a surface
area of 18 square feet (1.7
square meters),
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Layers of the Skin
Epidermis – barrier to
infection
Dermis – contains
nerves, hair roots, sweat
and oil glands and blood
vessels
Hypodermis – contains
fat, blood vessels,
connective tissues that
helps maintain body
temperature
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OxPlCkTKhzY
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Responsible for the movement of the human body,
maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the
body
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Three Types of Muscle Tissue
Visceral Muscle
• Found inside of organs like the stomach, intestines,
and blood vessels
• The weakest of all muscle tissues
• Makes organs contract to move substances through
the organ
• Controlled by the unconscious part of the brain, it is
known as involuntary muscle
• Smooth muscle
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Three Types of Muscle Tissue
Cardiac Muscle
• Found only in the heart
• Responsible for pumping blood throughout the body
• Involuntary muscle
• Stimulates itself to contract
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Three Types of Muscle Tissue
Skeletal
• The only voluntary muscle tissue in the human body
• 80% to 90% of the muscles are skeletal muscles
• Every physical action that a person consciously
performs (e.g. speaking, walking, or writing) requires
skeletal muscle.
• Most skeletal muscles are attached to two bones
across a joint.
• The function of skeletal muscle is move parts of the
body
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMcg9YzNSEs
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aLoY1wjmVvg&t
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
The action or process of reviving someone from
unconsciousness or apparent death.
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
No Breathing With Pulse
Respiratory
Arrest
Rescue Breathing
(12 breaths per minute for 2 minutes)
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Head-Tilt-Chin Lift
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cPaV8GP3Yjc
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
PROCEDURE
1. Identifies victim's condition as no breathing but
with pulse
2. Opens the airway using head-tilt-chin-lift
maneuver
3. Seals the nose and the mouth prior to ventilation
4. Provides 1 ventilation every 5 seconds up to 24
cycles
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
No Breathing No Pulse
Cardiac
Arrest
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation
(30 compressions and 2 breaths,
5 cycles in 2 minutes)
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
COMPRESSION SITE
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TbyV6Z_WQJQ
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
PROCEDURE
1. Identifies victim's condition as breathless and
pulseless
2. Places heel of one hand over the center lower half
of the chest
3. Interlocks fingers of both hand, with one hand on
top of the other
4. Delivers 30 compression at the rate of 100/min
5. Compresses the chest at the depth of at least 2
inches
6. Compresses the chest with arms perpendicular to
victim's chest at all times
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
PROCEDURE
7. Observes complete chest recoil during compressions
8. Compresses the chest without jerking, bouncing,
bending or massaging
9. Opens the airway using head-tilt-chin-lift maneuver
10. Provides 2 ventilations at 1 sec each after 30
compressions
11.Ventilates with victim's nose and mouth sealed to
avoid leaks
12. Completes five cycles correctly
13. Rechecks pulse and breathing for not more than 10
secs ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hTWefylIY2E
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
PROCEDURE
1. Lifts the hand farther next to the head with palms
up
2. Places the other hand on victim's side
3. Bends up the farther knee of the victim
4. Supports the head, shoulder and hips of victim
5. Rolls the victim to side in a smooth motion
6. Bends the other knee on top of the other
7. Slides the hand from the side to victim's face
palms down
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
3. Stand
1. Attach Pad
Clear
2. Plug 4. Analyze/
Connector Shock
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Please click here to watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wAa_C0SIqiE
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
• With good airway exchange
• With poor airway exchange
• Complete obstruction
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
HEIMLICH MANEUVER
Abdominal Thrust
Chest Thrust
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Interview A.M.P.L.E.
Check Vital Signs T.P.R.B.P
Head to Toe Exam D.C.A.P.B.T.L.S
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
1. Allergies
2. Medications,
3. Past illness/Pregnancy
4. Last oral intake
5. Events/Environment
relating to injury
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Body Temperature Pulse Rate
(36.5 – 37.5 Celcius) (60 – 100 beats/min)
Respiratory Rate Blood Pressure
(12 – 20 breathes/min) (90 – 130/60 – 90 mmHg)
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
Impaled
Objects
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
ELEMENTARY FIRST AID
You might also like
- The Ultimate BLS CheatsheetDocument30 pagesThe Ultimate BLS CheatsheetAimee Eichler67% (3)
- BLS Skills Lab For SimulationDocument116 pagesBLS Skills Lab For Simulationczeremar chan100% (1)
- CPR SeminarDocument76 pagesCPR SeminarAmy Lalringhluani Chhakchhuak100% (3)
- First Aid Level 1 Power Point PresentationDocument79 pagesFirst Aid Level 1 Power Point PresentationDeon Venter100% (7)
- CPR SeminarDocument73 pagesCPR SeminarAmy Lalringhluani Chhakchhuak100% (6)
- EFA - Module 2 r1Document57 pagesEFA - Module 2 r1Jerry CañeroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-ONE-FOURDocument34 pagesCHAPTER-ONE-FOURPrincess Raysel BaticbaticNo ratings yet
- Principles & Practice of First AidDocument298 pagesPrinciples & Practice of First AidJoshua100% (2)
- Marteja, Katrina Mendoza, Alexis Jason Molano, JosephDocument26 pagesMarteja, Katrina Mendoza, Alexis Jason Molano, JosephNdor BariboloNo ratings yet
- Horn Internional University: Chapter TwoDocument35 pagesHorn Internional University: Chapter TwoAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Im Deftac211Document72 pagesIm Deftac211Gerome DariaNo ratings yet
- Efaw NDocument410 pagesEfaw NBuba JawnehNo ratings yet
- Bls - Fbao - First AidDocument172 pagesBls - Fbao - First AidMaria Regina Castro Gabriel100% (1)
- Bls For Healthcare WorkerDocument67 pagesBls For Healthcare WorkerJop PayNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument28 pagesBasic Life SupportMhar T. MasongsongNo ratings yet
- Mod 3.1 - 4.1 - First AidDocument72 pagesMod 3.1 - 4.1 - First Aidabhishek sudheerNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument43 pagesBasic Life SupportNguyen Anh Tung100% (3)
- Pediatric Basic Life Support: Philippine Heart Association Council On Cardio-Pulmonary ResuscitationDocument106 pagesPediatric Basic Life Support: Philippine Heart Association Council On Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitationjitendra magar100% (1)
- Basic Concept of BLS: Muhammad SaleemDocument27 pagesBasic Concept of BLS: Muhammad Saleemms khanNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support (BLS)Document36 pagesBasic Life Support (BLS)Hero MondaresNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument36 pagesBasic Life SupportycccaNo ratings yet
- Bls Power Point2Document64 pagesBls Power Point2Francis Emman SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 14 CPR PDFDocument75 pages14 CPR PDFBlessy Susan100% (1)
- 6 - BLS HandoutDocument18 pages6 - BLS HandoutEastern SamarNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support: Dr. Aatir Fayyaz Nishtar Medical University MultanDocument42 pagesBasic Life Support: Dr. Aatir Fayyaz Nishtar Medical University MultanShahzeb KhanNo ratings yet
- BLS HandoutsDocument27 pagesBLS HandoutsFroilan Ferrer100% (2)
- CPR and First Aid Guidelines: Presentation Prepared By: Randy G. Tabaog, LPT AMA Computer College Santiago CampusDocument24 pagesCPR and First Aid Guidelines: Presentation Prepared By: Randy G. Tabaog, LPT AMA Computer College Santiago CampussunshineNo ratings yet
- Iap CprdayDocument33 pagesIap CprdayRabi KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument77 pagesBasic Life SupportNiel John Recones CanoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support (BLS) : Franklin O. Que, BSN-RNDocument90 pagesBasic Life Support (BLS) : Franklin O. Que, BSN-RNfrank_1785No ratings yet
- Basic Life Support For Healthcare Providers (BLS) : Presented By: Youssef Youssef RT Respiratory Therapy DepartementDocument43 pagesBasic Life Support For Healthcare Providers (BLS) : Presented By: Youssef Youssef RT Respiratory Therapy Departementkurt94764No ratings yet
- Cardio Pulmonary ResuscitationDocument98 pagesCardio Pulmonary ResuscitationjekolfindoNo ratings yet
- Emergency NursingDocument27 pagesEmergency Nursingcrisa_sarte2906No ratings yet
- BLS - CopyDocument26 pagesBLS - CopyadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Firstaidbyessamsidqi 210313230642Document80 pagesFirstaidbyessamsidqi 210313230642Ni Cho LayyNo ratings yet
- W4-Basic Life SupportDocument28 pagesW4-Basic Life SupportaefgNo ratings yet
- Handout-Elementary First AideDocument27 pagesHandout-Elementary First AideTerrinz BuensalidaNo ratings yet
- BLS Ahmad Hafiz 01Document31 pagesBLS Ahmad Hafiz 01Fahad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- LA Union: PDRRM ODocument32 pagesLA Union: PDRRM OEnash RidNo ratings yet
- BLS and First Aid ReportDocument4 pagesBLS and First Aid ReportAriane Joyce AgkisNo ratings yet
- CRI 089 PrelimsDocument74 pagesCRI 089 Prelimsdebroah280No ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitati On (CPR) : 2.1 HistoryDocument34 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitati On (CPR) : 2.1 HistoryGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Module ContentDocument8 pagesModule Contenttelsaaru31No ratings yet
- Cardio ResuscitationDocument38 pagesCardio ResuscitationBhakti WashilkarNo ratings yet
- Bls Dewasa PKDJB 2022Document74 pagesBls Dewasa PKDJB 2022Halawatul ImanNo ratings yet
- Occupational First AidDocument12 pagesOccupational First AidEddie Bulwayan Endeken Jr.No ratings yet
- Introduction To First Aid & Basic Life SupportDocument34 pagesIntroduction To First Aid & Basic Life SupportRO Chiel Kjskjs100% (1)
- First AidDocument44 pagesFirst AidHarish SurendrakurupNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 A Basic Life SupportDocument49 pagesLesson 4 A Basic Life SupportJames Artajo ViajedorNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid and Basic Life Support Training For 701st RRIBN Reservists 2022Document88 pagesBasic First Aid and Basic Life Support Training For 701st RRIBN Reservists 2022kerwinjohnaliporoNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation PresentationDocument29 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation PresentationolelNo ratings yet
- CPR SioDocument38 pagesCPR SioGerry OshNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation: College of Nursing Madras Medical CollegeDocument48 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation: College of Nursing Madras Medical CollegeNithin ManlyNo ratings yet
- Prof - Dr. Ruswan Dachlan, SP An KIC Dept - of Anaesthesiology & Intensive Care FKUIDocument71 pagesProf - Dr. Ruswan Dachlan, SP An KIC Dept - of Anaesthesiology & Intensive Care FKUIFerdy ErawanNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument33 pagesBasic Life SupportJoshi Thomas John JikkuNo ratings yet
- 2M-Cardio-Pulmonary-ResuscitationDocument19 pages2M-Cardio-Pulmonary-ResuscitationJason Matthew ImpasNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Victim at The Accident SiteDocument64 pagesAssessment of Victim at The Accident SiteGerald Limo Arap ChebiiNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Firtst AidDocument73 pagesThe Basics of Firtst Aidjenjang yannieNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument14 pagesBasic Life SupportSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Body Mass Index (A Brief Introduction) :: By: Mehreen Saleem MSC Biochemistry (Ku)Document8 pagesBody Mass Index (A Brief Introduction) :: By: Mehreen Saleem MSC Biochemistry (Ku)Aamir AliNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Test Review Body System Function Major Organs/Structures & Their Functions Specialized Cells (If Any)Document8 pagesHuman Body Systems Test Review Body System Function Major Organs/Structures & Their Functions Specialized Cells (If Any)Christine Megan YoungNo ratings yet
- Buku Menu Bening'sDocument57 pagesBuku Menu Bening'sAlfina AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Las Science4 q2w2Document2 pagesLas Science4 q2w2Annabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Packing Method Approval - T-ShirtsDocument8 pagesPacking Method Approval - T-ShirtsPraneeth MallikaarachchiNo ratings yet
- Portfolio: Medical University - PlevenDocument11 pagesPortfolio: Medical University - PlevennoyNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory SystemIshan Jacob PiadocheNo ratings yet
- Children'S Alternative Conceptions in Science: 1. EnergyDocument11 pagesChildren'S Alternative Conceptions in Science: 1. EnergyKurtis HarperNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Physical Fitness ActivitiesDocument27 pagesPhysical Education: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Physical Fitness ActivitiesKeith Tristan RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document11 pagesChapter 11christian anchetaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument28 pagesPlant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsJohn Michael Lopez100% (1)
- Natural Science Syllabus (p1-3), Jan 2012 - FinalDocument36 pagesNatural Science Syllabus (p1-3), Jan 2012 - FinalNanaleoNo ratings yet
- DA 5501 - Body Fat Content Worksheet (Female)Document1 pageDA 5501 - Body Fat Content Worksheet (Female)Kam 87No ratings yet
- 06 - 11 - 2020 (Jumma Bayan Mohamed H) 55: மிக்க (Surah 55:Ar-Rahman) IntroDocument10 pages06 - 11 - 2020 (Jumma Bayan Mohamed H) 55: மிக்க (Surah 55:Ar-Rahman) IntroMohamed HNo ratings yet
- AutopsyDocument26 pagesAutopsyOmar JamilNo ratings yet
- Oopnik FashionDocument9 pagesOopnik FashionoopnikNo ratings yet
- Weapons and ArmorDocument5 pagesWeapons and ArmorVault in The ForestNo ratings yet
- Adjectives To Describe A Person in EnglishDocument19 pagesAdjectives To Describe A Person in EnglishUSWATUN KHASANAHNo ratings yet
- Skirts: A Woman's Outer Garment Fastened Around The Waist and Hanging Around The LegsDocument39 pagesSkirts: A Woman's Outer Garment Fastened Around The Waist and Hanging Around The Legsjross martinesNo ratings yet
- Eight-Week Indoor PlanDocument2 pagesEight-Week Indoor PlanThe GuardianNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support (BLS) : Franklin O. Que, BSN-RNDocument90 pagesBasic Life Support (BLS) : Franklin O. Que, BSN-RNfrank_1785No ratings yet
- Master List Beneficiaries For School-Based Feeding Program (SBFP)Document12 pagesMaster List Beneficiaries For School-Based Feeding Program (SBFP)Elvin Manjares100% (1)
- Laboratory Exercise No. 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 10 Endocrine SystemJamesanne DemetriaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TransesDocument5 pagesAnaphy TransesScyrah Allana RiegoNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument13 pagesFormulasKaren SabaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Nervous SystemHans Festin-DiazNo ratings yet
- Ketogains Calculator Reddit v1.9Document4 pagesKetogains Calculator Reddit v1.9nial69No ratings yet
- What Am I? A Human Body Riddle Book: Resource ID#: 28851 Primary Type: Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesWhat Am I? A Human Body Riddle Book: Resource ID#: 28851 Primary Type: Lesson PlanGrade2 CanaryschoolNo ratings yet
- The Lost Secret of Ab Training - Don AlessiDocument3 pagesThe Lost Secret of Ab Training - Don AlessiJTB01No ratings yet
- BLS Manual For Online - Clerks PDFDocument41 pagesBLS Manual For Online - Clerks PDFMiko Vargas100% (2)