0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views16 pagesTransformer Construction Overview
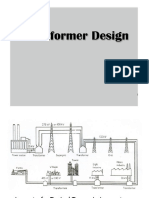
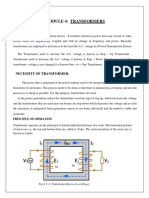
The document discusses transformer construction. It describes the main elements as two windings (primary and secondary) and a laminated core made of silicon steel. Transformers are classified as core type or shell type depending on how the windings are placed around the core. Core type transformers have half of each winding around each core limb, while shell type transformers place both windings around a central limb. Three phase transformers are required to step up and step down voltages in power systems.
Uploaded by
Kailash PandeyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views16 pagesTransformer Construction Overview
The document discusses transformer construction. It describes the main elements as two windings (primary and secondary) and a laminated core made of silicon steel. Transformers are classified as core type or shell type depending on how the windings are placed around the core. Core type transformers have half of each winding around each core limb, while shell type transformers place both windings around a central limb. Three phase transformers are required to step up and step down voltages in power systems.
Uploaded by
Kailash PandeyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd