Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Applying Cardiac Monitor Procedure
Uploaded by
Swillight meCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Applying Cardiac Monitor Procedure
Uploaded by
Swillight meCopyright:
Available Formats
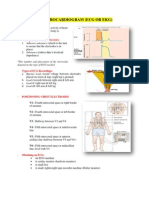
APPLYING A CARDIAC MONITOR
Cardiac monitoring is used for patients with conduction disturbances and for those at risk for
life-threatening arrythmias, such as post-operative patients and patients who are sedated.
EQUIPMENT:
Lead wires
Pregelled (gel foam) electrodes (number varies from 3 to 5)
Alcohol pads
Patient cable for hardwire cardiac monitor
Transmitter, transmitter pouch, and telemetry battery pack for telemetry
PPE, as indicated.
PROCEDURE:
1. Verify the order for cardiac monitoring on the patient’s medical record.
2. Gather all equipment and bring to bedside.
3. Perform hand hygiene and put on PPE, if indicated.
4. Identify the patient.
5. Close curtains around bed and close the door to the room, if possible. Explain the procedure to
the patient. Tell the patient that the monitoring records the heart’s electrical activity. Emphasize
that no electrical current will enter his or her body. Ask the patient about allergies to adhesive,
as appropriate.
6. For hardwire monitoring, plug the cardiac monitor into an electrical outlet and turn it on to warm
up the unit while preparing the equipment and the patient. For telemetry monitoring, insert a
new battery into the transmitter. Match the poles on the battery with the polar markings on the
transmitter case. Press the button at the top of the unit, test the unit to ensure that the battery
is operational.
7. Insert the cable into the appropriate socket in the monitor.
8. Connect the lead wires to the cable. In some systems, the lead wires are permanently secured
to the cable. For telemetry, if the lead wires are not permanently affixed to the telemetry unit,
attach them securely. If they must be attached individually, connect each one of the correct
outlet.
9. Connect an electrode to each of the lead wires, carefully checking that each lead wire is in its
correct outlet.
10. If the bed is adjustable, raise it to comfortable working height, usually elbow height of the
caregiver.
11. Expose the patient’s chest and determine electrode positions, based on which system and
leads are being used. If necessary, clip the hair from an area about 10cm in diameter around
each electrode site. Clean the area with soap and water and dry it completely to remove skin
secretions that may interfere with electrode function.
12. Remove the backing from the pregelled electrode. Check the gel for moistness. If the gel is
dry, discard it and replace it with a fresh electrode. Apply the electrode to the site and press
firmly to ensure a tight seal. Repeat with remaining electrodes to complete the three-lead or
five lead system.
13. When all the electrodes are in place, connect the appropriate lead wire to each electrode.
Check waveform for clarity, position, and size. To verify that the monitor is detecting each beat,
compare the digital heart rate display with an auscultated count of the patient’s heart rate. If
necessary, use the gain control to adjust the size of the rhythm tracing, and use the position
control to adjust the waveform position on the monitor.
14. Set the upper and lower limits of the rate alarm, based on the patient’s condition or unit policy.
15. For telemetry, place the transmitter in the pouch in the hospital gown. If not available in gown,
use a portable pouch. Tie the pouch strings around the patient’s neck and waist, making sure
that the pouch fits snugly without causing discomfort. If no pouch is available, place the
transmitter in the patient’s bathrobe pocket.
16. To obtain a rhythm strip, press the RECORD key either at the bedside for monitoring or at the
central station for telemetry. Label the strip with the patient’s name and room number, date,
time, and rhythm identification. Analyze the strips, as appropriate. Place the rhythm strip in the
appropriate location in the patient’s chart.
17. Return the patient to a comfortable position. Lower bed height and adjust head of bed to a
comfortable position.
18. Remove the additional PPE, if used. Perform hand hygiene.
You might also like
- Applying Cardiac Monitor ProcedureDocument1 pageApplying Cardiac Monitor ProcedureSwillight meNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MonitorDocument2 pagesCardiac MonitorNasrah TalusobNo ratings yet
- Obtaining An ECG ChecklistDocument2 pagesObtaining An ECG ChecklistSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Performance Checklist For Obtaining An ElectrocardiogramDocument2 pagesPerformance Checklist For Obtaining An ElectrocardiogramNasrah TalusobNo ratings yet
- Obtaining Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Clinical Nursng SkillsDocument2 pagesObtaining Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Clinical Nursng SkillsSwillight meNo ratings yet
- Obtaining Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Clinical Nursing SkillsDocument2 pagesObtaining Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Clinical Nursing SkillsSwillight meNo ratings yet
- Institute of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesDocument4 pagesInstitute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciencesshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Perform 12 Lead ECGDocument2 pagesPerform 12 Lead ECGKim Kristine D. GuillenNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg or Ekg) : - 2 Components of ELECTRODESDocument4 pagesElectrocardiogram (Ecg or Ekg) : - 2 Components of ELECTRODESDhanNie CenitaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY StudentDocument7 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY StudentSuzanne AndresNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Rle Skills Lab Performance Checklist Obtaining An ElectrocardiogramDocument3 pagesNCM 112 - Rle Skills Lab Performance Checklist Obtaining An ElectrocardiogramDominicManlutacNo ratings yet
- Obtaining An Electrocardiogram (ECG) : Goal: A Cardiac Electrical Tracing Is Obtained Without AnyDocument4 pagesObtaining An Electrocardiogram (ECG) : Goal: A Cardiac Electrical Tracing Is Obtained Without AnyAirrahMaeCutangNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg)Document6 pagesElectrocardiogram (Ecg)rnrmmanphd100% (1)
- Ecg Placement RetdemDocument3 pagesEcg Placement RetdemDianne Erika MeguinesNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument17 pagesElectrocardiogramvinnu kalyanNo ratings yet
- Ecg CiDocument5 pagesEcg CirnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- The CardiacDocument7 pagesThe CardiacCake ManNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) : Danilyn R. Cenita Paula M. PauloDocument41 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) : Danilyn R. Cenita Paula M. PauloDhanNie CenitaNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - PacemakersDocument23 pagesGroup 7 - PacemakersKimberly Abella CabreraNo ratings yet
- Administering Oxygen by Nasal CannulaDocument2 pagesAdministering Oxygen by Nasal CannulaStephanie ToribioNo ratings yet
- Jasmine Ouseph F.Y.Msc Nursing Dr.D.Y.Patil ConDocument68 pagesJasmine Ouseph F.Y.Msc Nursing Dr.D.Y.Patil ConJASMINE JOY100% (1)
- Electrocardiogram Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument28 pagesElectrocardiogram Nursing ResponsibilitiesKristine Jade Rojas100% (1)
- ECG2Document2 pagesECG2Pollen Siega BunalNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Cardiac MonitoringDocument6 pagesPurpose: Cardiac Monitoringpramod kumawatNo ratings yet
- Continuous Cardiac MonitoringDocument4 pagesContinuous Cardiac MonitoringPoova RagavanNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: Measuring Oral Temperature, Radial Pulse, Respiratory Rate, and Blood PressureDocument4 pagesVital Signs: Measuring Oral Temperature, Radial Pulse, Respiratory Rate, and Blood PressureellithNo ratings yet
- ECG Procedural Cheklist With RationaleDocument3 pagesECG Procedural Cheklist With RationaleCzarina Rachel RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker ImplantationDocument17 pagesPacemaker ImplantationKaku ManishaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals ChecklistsDocument143 pagesFundamentals ChecklistsParimala Pavan100% (1)
- 7.assignment On PacemakerDocument8 pages7.assignment On Pacemakersantosh kumarNo ratings yet
- MANUAL. Electroestimulador - AGF-3E - DriveDocument48 pagesMANUAL. Electroestimulador - AGF-3E - Drivebiomedicos.bogotaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills Output (Nso) : Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDocument2 pagesNursing Skills Output (Nso) : Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityJaiton Pagayonan100% (1)
- Cardiacmonitoring 221217173812 306f7eddDocument18 pagesCardiacmonitoring 221217173812 306f7eddNaseem Bin YoosafNo ratings yet
- CP 150 12-Manual EletrocardiografoDocument24 pagesCP 150 12-Manual EletrocardiografoAndreaNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Proc GuideDocument20 pagesVital Signs Proc GuideKrish Lorrie100% (1)
- Electrocardiogram Return Demonstration ScriptDocument3 pagesElectrocardiogram Return Demonstration ScriptRio Dante100% (1)
- Protocol On Transcutaneous PacingDocument7 pagesProtocol On Transcutaneous PacingAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Cpms College of Nursing: Assignment ON Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document6 pagesCpms College of Nursing: Assignment ON Electrocardiogram (ECG)Amy Lalringhluani ChhakchhuakNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MonitoringDocument5 pagesCardiac MonitoringAmit Kl100% (1)
- PacemakerDocument15 pagesPacemakermariet abraham100% (4)
- 420 20081015 01 Major Proc ApneamonitorDocument8 pages420 20081015 01 Major Proc ApneamonitorsantiNo ratings yet
- Script For EcgDocument14 pagesScript For EcgMonesa Badil LingasaNo ratings yet
- Administering An ECGDocument4 pagesAdministering An ECGSupnet QueeneeNo ratings yet
- BHS Standard Operating Procedure For ABPMDocument3 pagesBHS Standard Operating Procedure For ABPMYohanes SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Monitoring ChecklistDocument6 pagesCardiac Monitoring Checklistdigdag100% (1)
- NCM 118L ReviewerDocument10 pagesNCM 118L ReviewerGRACIEL MERS FONTAMILLASNo ratings yet
- Holter Test PolicyDocument8 pagesHolter Test PolicykNo ratings yet
- (ECG) ElectrocardiogramDocument3 pages(ECG) Electrocardiogramjanna mae patriarca67% (3)
- NAME: - YEAR AND BLOCK: - Recording An ECGDocument3 pagesNAME: - YEAR AND BLOCK: - Recording An ECGmyqs4d7rmxNo ratings yet
- Crash CartDocument55 pagesCrash Carthatem alsrour100% (4)
- 418RLE M2 SL1 Basic ECGDocument8 pages418RLE M2 SL1 Basic ECGCamille Neypes CarreraNo ratings yet
- 418rle m2 Sl1+Basic+EcgDocument8 pages418rle m2 Sl1+Basic+EcgPaul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Clinical Lab Skills Assignment 2Document9 pagesClinical Lab Skills Assignment 2Daniel WoodardNo ratings yet
- ECG Monitor and RhythmDocument9 pagesECG Monitor and Rhythmboxed juiceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Journal EcgDocument2 pagesNursing Journal EcgCharlene Jacobe CornistaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MonitoringDocument6 pagesCardiac MonitoringAIMNo ratings yet
- 7mosby's EMT-Basic Textbook - Revised Reprint, 2nd EditionDocument22 pages7mosby's EMT-Basic Textbook - Revised Reprint, 2nd EditionKathrina AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MonitorDocument5 pagesCardiac MonitorhumbertolgeNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography Method (ECG/EKG): A Primary Guideline for Starters to Understand about Arrhythmias & EKG InterpretationFrom EverandElectrocardiography Method (ECG/EKG): A Primary Guideline for Starters to Understand about Arrhythmias & EKG InterpretationNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Nurse Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesOperating Room Nurse Job DescriptionSwillight meNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Nurse Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesOperating Room Nurse Job DescriptionSwillight meNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Nurse Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesOperating Room Nurse Job DescriptionSwillight meNo ratings yet
- Abdullahi Vs PfizerDocument76 pagesAbdullahi Vs PfizerSwillight meNo ratings yet
- Obtaining Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Clinical Nursing SkillsDocument2 pagesObtaining Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Clinical Nursing SkillsSwillight meNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitati0on (CPR)Document3 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitati0on (CPR)Swillight meNo ratings yet
- Vol07 1 PDFDocument275 pagesVol07 1 PDFRurintana Nalendra WarnaNo ratings yet
- TA1515VDocument4 pagesTA1515VLeo LeiNo ratings yet
- Varactor AssignmentDocument9 pagesVaractor Assignmentjawad_h89No ratings yet
- VAM Must Sumitomo 1209 PDFDocument4 pagesVAM Must Sumitomo 1209 PDFnwohapeterNo ratings yet
- General Anaesthesia MCQsDocument5 pagesGeneral Anaesthesia MCQsWasi Khan100% (3)
- Article Unleashing The Power of Your StoryDocument17 pagesArticle Unleashing The Power of Your StoryAnkit ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of Dragon FruitDocument6 pagesProduction Technology of Dragon FruitAbhinash MoirangthemNo ratings yet
- TOP233YDocument24 pagesTOP233YJose BenavidesNo ratings yet
- 2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual RSUDocument12 pages2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual RSUAndy Dellinger100% (1)
- 1 28701-FGC+101+3441+Router+6471+Datasheet+Rev+FDocument2 pages1 28701-FGC+101+3441+Router+6471+Datasheet+Rev+FВладимир ЕгоровNo ratings yet
- Under Pass Wing Wall (4.1m)Document12 pagesUnder Pass Wing Wall (4.1m)Naveed NazNo ratings yet
- Notice: Environmental Statements Notice of Intent: Eldorado National Forest, CADocument2 pagesNotice: Environmental Statements Notice of Intent: Eldorado National Forest, CAJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Vertical Isolation VCBEnglishDocument1 pageVertical Isolation VCBEnglishdip461No ratings yet
- Bluforest, Inc. (OTC: BLUF) InvestigationDocument5 pagesBluforest, Inc. (OTC: BLUF) Investigationfraudinstitute100% (1)
- Most Important One Liner Questions and Answers May 2022Document15 pagesMost Important One Liner Questions and Answers May 2022pradeepNo ratings yet
- IsdettaDocument2 pagesIsdettaHa Phuoc HoaNo ratings yet
- Progress Report Week#9 UlubeluDocument6 pagesProgress Report Week#9 UlubelutiantaufikNo ratings yet
- Marriage HalldocxDocument50 pagesMarriage HalldocxBalaji Kamalakannan100% (2)
- Thesis 1-15Document15 pagesThesis 1-15hewelirNo ratings yet
- Med Chem Exam 2Document24 pagesMed Chem Exam 2cNo ratings yet
- +chapter 6 Binomial CoefficientsDocument34 pages+chapter 6 Binomial CoefficientsArash RastiNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous ChipsDocument27 pagesAsynchronous ChipsSai TejaNo ratings yet
- Smart Locker - A Sustainable Urban Last-Mile Delivery Solution: Benefits and Challenges in Implementing in VietnamDocument14 pagesSmart Locker - A Sustainable Urban Last-Mile Delivery Solution: Benefits and Challenges in Implementing in VietnamQuynh LeNo ratings yet
- Ac 521 007Document10 pagesAc 521 007JacquesNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Definition:: Economic Infrastructure Includes BroadlyDocument3 pagesInfrastructure Definition:: Economic Infrastructure Includes Broadlyabraha gebruNo ratings yet
- Electric Bike Monitoring and Controlling System Based On Internet of ThingsDocument8 pagesElectric Bike Monitoring and Controlling System Based On Internet of ThingsEarl PhamtonhiveNo ratings yet
- IMS Institute BelgradeDocument10 pagesIMS Institute BelgradeBoško JanjuševićNo ratings yet
- Visedo FPC-2016Document13 pagesVisedo FPC-2016Probonogoya Erawan SastroredjoNo ratings yet
- 2UEB000487 v1 Drive On GeneratorDocument19 pages2UEB000487 v1 Drive On GeneratorSherifNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Microsoft VirtualizationDocument36 pages1 Introduction To Microsoft VirtualizationRavinder KantNo ratings yet