Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Sultana KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Sultana KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1.
Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
AL WADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, JEDDAH
I – Term Notes
Name: ____________________________ Date: _________________
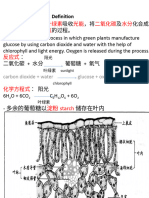
PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
❖ Animals eat food to get their energy. But green plants do not. Instead, they
make their own food-glucose, by a process called photosynthesis. So, we call
plants as Autotrophs.
❖ ‘Photo’ means to do with light. ‘Synthesis’ means ‘making’. So Photosynthesis
is a process by which plants make food, using energy from light.
✓ These are the requirements plants need for photosynthesis:
1. Carbon dioxide
2. Water
3. Light
✓ These are the products plants make by photosynthesis:
1. glucose
2. oxygen
❖ We can show photosynthesis in a word equation, where light energy is shown
in brackets because it is not a substance:
Carbon dioxide + Water (+ light energy) → Glucose + Oxygen + Water
❖ Definition: Photosynthesis is a process where plants use carbon dioxide and
water in the presence of sunlight to give glucose, oxygen and water.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 1
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
A. WHERE DO PLANTS GET RAW MATERIALS FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS?
❖ Plants get carbon dioxide from the air through stomata by diffusion into their
leaves and water from the ground through their roots by osmosis. Light energy
comes from the sun.
❖ The oxygen produced is released into the air from the leaves through stomata.
❖ Plants use the food- glucose that they made in photosynthesis to make new
cells and tissues which forms the Biomass of plant. They also use it to produce
energy by Respiration.
B. WHERE DOES PHOTOSYNTHESIS TAKES PLACE?
❖ Photosynthesis takes place in structures (cell organelles) called Chloroplasts,
present inside leaf cells of plants.
❖ Chloroplasts contain a green substance pigment called chlorophyll, which
absorbs the light energy for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll gives green colour to
the leaves.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 2
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
C. THE STRUCTURE OF A LEAF
Waxy Cuticle A waxy layer on the leaf surface stops the leaf cells from
drying out and prevents entry of microorganisms into
leaf.
Upper Epidermis It protects the cells inside the leaf.
Palisade layer It is a layer of cells that do most of the photosynthesis.
Spongy mesophyll This later has lots of air spaces. The cells in spongy layer
layer do small amount of photosynthesis.
Vascular bundles They carry water, minerals and nutrients to the cells in a
leaf.
Lower epidermis It also protects the cells inside the leaf.
Stomata These are tiny holes present on the surface of leaf in the
lower epidermis. These holes let carbon dioxide from the
air get into the leaf.
Transverse section (T.S.) of a leaf
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 3
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
D. ADAPTATIONS OF A LEAF FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
ADAPTATION FUNCTION
To expose to the light
Large surface area
To absorb as much sunlight as possible.
Waxy cuticle Protection.
Thin structure To allow sunlight to penetrate easily.
To allow sunlight to penetrate easily.
Transparent upper epidermis (Presence of chloroplast would make it difficult
for sunlight to pass efficiently.)
Palisade cells oblong shaped Allow many cells to fit and perform
with lots of chloroplast Photosynthesis at a maximum rate.
Many Stomata on lower Exchange gases from air by diffusion.
epidermis Control rate of transpiration (loss of water).
Dense network of veins Carry water to every cell in the leaf.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 4
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
E. FATE (USES) OF GLUCOSE:
Glucose made in photosynthesis is used in several ways such as:
→ It can be converted into chemicals, such as cellulose for growth of plant cells.
→ It can be converted into storage molecules such as starch, oils, and fats.
→ It can be broken down during respiration, to release energy.
→ It makes proteins for growth and repair.
Uses of Glucose
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 5
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
F. MINERALS:
Plants need a number of minerals to live healthy. Plants absorb these minerals
from the soil as salts along with water.
DEFICIENCY OF
ELEMENT WHY IT IS NEEDED
ELEMENT
Nitrogen To make proteins Poor growth, yellow leaves.
Sulphur To make proteins Poor growth, yellow leaves.
To make DNA and chemicals involved Poor growth, especially in
Phosphorus
in respiration roots.
Yellowing between veins of
Magnesium To make chlorophyll leaves.
(Chlorosis)
Potassium To keep correct salt balance for cells Mottled leaves
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 6
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
G. THE UPTAKE OF MINERALS AND WATER:
• The function of the roots is to absorb water and minerals from soil. Water gets
into root hairs by osmosis.
• Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules, from a region of higher
concentration to a region of lower concentration, through a partially permeable
membrane
• Transpiration is a process of removal of excess water from the surface of leaf
through stomata.
• Water is absorbed by the root hair moves up to the leaf through the xylem
vessels due to transpiration pull, so it is called as transpiration stream.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 7
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
H. INVESTIGATING PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
1. TEST FOR STARCH:
1. Take a leaf from a healthy plant; put it in boiling water taken in a beaker.
Leave for about 30 seconds. This will break cell wall.
2. Remove the leaf and put it into a boiling tube of alcohol kept in beaker with hot
water. This will remove all the chlorophyll out of the leaf. The leaf will now be
brittle.
3. Remove it from the alcohol and dip it into hot water to soften it.
4. Place the leaf in a white tile and cover it with iodine solution to detect starch. If
blue-black colour appears, it means the leaf contains starch.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 8
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
2. TEST: CHLOROPHYLL IS ESSENTIAL FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
1. Take a potted plant with variegated (green and white/pale yellow) leaves.
2. Destarch the plant by keeping it in complete darkness for about 48 hours.
3. After that expose, the plant to the sunlight for a few hours.
4. Test one of the leaves for starch with iodine solution.
5. Areas with green patches test positive (turn blue black).
6. Areas (without green) pale yellow patches test negative (remain brown).
3. TEST: LIGHT IS ESSENTIAL FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
1. Take a potted plant.
2. Destarch the plant by keeping it in complete dark for about 48 hours.
3. Fix one leaf of this plant in between two strips of a thick black
paper/aluminum foil as shown in the diagram below.
4. Place the plant in light for a few hours to let it photosynthesize.
5. Pluck out the leaf, remove the black paper from the leaf and do starch test.
6. The portion of the leaf exposed to light only will give positive starch test and
turns into blue/black colour.
Note:
The control for this experiment:
The other uncovered leaves of same
plant will be the control of this
experiment which will show positive
test for starch, and all the
Leaf turns blue/black.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 9
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
4. TEST: CARBON DIOXIDE IS ESSENTIAL FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
1. Take two destarched potted plants.
(You can destarch a plant by keeping it in dark for about 48 hours)
2. Cover both the plants with bell jars and label them as a and b as shown below.
3. Inside Set-up a, keep KOH (Potassium hydroxide) and cover it with bell jars.
KOH absorbs and removes CO2 produced by respiration of plants.
4. Keep Set-up b it as it is without lid so CO2 gas can enter.
5. Keep both the set-ups in sunlight at least for 6-8 hours.
6. Finally pluck one leaf from each plant and perform the starch test on both
separately and compare.
7. Leaf from the plant kept with KOH will give negative test for starch meaning
blue/black colour does not appear.
The control for this experiment:
The setup “b” without KOH will be the control of this experiment. The leaf from this
plant will give positive test for starch and blue/black colour will appear.
Finally, it is concluded that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 10
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
5. TEST: OXYGEN IS MADE IN PHOTOSYNTHESIS.
How can we tell if a leaf is photosynthesising?
One of the simplest ways is to check if it is giving (releasing) oxygen gas. This is
easiest to do if the leaf is under water, because the oxygen gas makes bubbles in
water.
1. Take a beaker, fill it with water. Take a funnel and put a water plant in it and
invert it in the beaker.
2. Take a test tube filled completely with water and invert it on the funnel as
shown in the figure.
3. Leave the apparatus near a warm, sunny place for few hours.
4. You will see gas bubbles collecting in the test tube. When you have collected
about half a test tube of gas, you can test it to see if it is oxygen, as follows:
5. Carefully remove the test tube by putting your thumb over the opening,
allowing the water to run out, but not the gas.
6. Introduce a glowing splint into the tube.
7. If the gas is oxygen, it will make the glowing splint more vigorous.
The control for this experiment:
Set up the same experiment in a dark cupboard, for the same length of time. No gas
collects in the test tube which means plant did not photosynthesize.
Finally, it is concluded that oxygen is evolved during photosynthesis.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 11
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
I. LIMITING FACTORS IN PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
❖ Limiting factor is something present in the environment in such short supply
that it restricts life processes. Three factors that limit the rate of
photosynthesis are:
1. Light intensity
2. Carbon dioxide concentration
3. Temperature.
Maximizing growth
• Farmers use their knowledge of these limiting factors to increase crop
growth in greenhouses.
• They may use artificial light so that photosynthesis can continue beyond
daylight hours, or in a higher-than-normal light intensity.
• They use of paraffin lamps inside a greenhouse to increase the rate of
photosynthesis because the burning paraffin produces carbon dioxide, and
heat too.
1. EFFECT OF LIGHT INTENSITY ON THE RATE
OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
• Plants need light energy to carryout
photosynthesis to make the chemicals needed
to synthesize carbohydrates.
• Increasing the light intensity will increase the
speed of photosynthesis.
• However, after certain limit the rate of
photosynthesis remains constant even if light
intensity is increased as shown in the graph.
Experiment
• Following setup was made using pond weed Elodea
keeping constant temperature and constant supply of
CO2 (NaHCO3 was added for this).
• Light intensity was changed by changing distance of
the lamp from plant.
• As the distance decreased number of oxygen bubbles
formed per minute increased, but after a limit they
remained constant, showing rate of photosynthesis was also constant.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 12
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
2. EFFECT OF CARBON DIOXIDE ON THE RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
When the concentration of CO2 is low the rate of photosynthesis will also be slow.
Increasing the concentration of CO2 increases the rate of photosynthesis. However,
after certain limit the rate of photosynthesis becomes constant even if the
concentration of CO2 increases as shown in the graph.
Experiment:
• Following setup was made using pond weed Elodea keeping constant
temperature and constant light intensity from a lamp.
• Supply of CO2 was changed by changing concentration of CO2 this was done by
adding different amounts of NaHCO3.
As the concentration of CO2 was increased number of oxygen bubbles formed per
minute also increased, but after a limit number of oxygen bubbles made per
minute remained constant, showing rate of photosynthesis was also constant.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 13
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
3. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
As the temperature rises the rate of photosynthesis also rises. Anyhow, there is
an optimum temperature at which the rate of photosynthesis is maximum.
Beyond this temperature, the reaction starts decreasing and photosynthesis
eventually stops. Optimum temperature is usually around 40o C. Above this
temperature, the photosynthesis will decrease because enzymes denature.
Experiment
• Following setup was made using pond weed Elodea keeping constant light
intensity and constant supply of CO2.
• Temperature was changed by placing a heat shield around the plant.
• As the temperature increased number of oxygen bubbles formed per minute
also increased, but after a limit, number of oxygen bubbles started to
decrease and finally release of oxygen stopped.
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 14
BIOLOGY Gr-8 1. Photosynthesis [2021 – 2022]
CONCEPT MAP FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS
ALWADI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Page | 15
You might also like
- Gardening by The Moon 2009Document6 pagesGardening by The Moon 2009decabob100% (6)
- SCIENCE9 Q1 WEEK6 (LESSONS 17-18) - Photosynthesis (22 Pages)Document22 pagesSCIENCE9 Q1 WEEK6 (LESSONS 17-18) - Photosynthesis (22 Pages)Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutNo ratings yet
- Botany and TaxonomyDocument25 pagesBotany and TaxonomyDennard Dacumos100% (1)
- Combined Science Notes-1Document258 pagesCombined Science Notes-1Premier Car Sales67% (3)
- Jerusalem ArtichokeDocument16 pagesJerusalem ArtichokeceramickurtNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes - BiologyDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes - Biologythe lillyNo ratings yet
- PREPARE LAND PREPARATIONvegetables GardenDocument52 pagesPREPARE LAND PREPARATIONvegetables GardenRayge HarbskyNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science NotesDocument115 pagesIntegrated Science Notesserene munga100% (1)
- Cambridge Checkpoint Science 3 Chapter 1, Photosynthesis NotesDocument5 pagesCambridge Checkpoint Science 3 Chapter 1, Photosynthesis NotesMujtaba Aamir50% (2)
- Biology Notes PDFDocument79 pagesBiology Notes PDFSaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab ReportDocument5 pagesBio Lab ReportNrl MysrhNo ratings yet
- CROP SCIENCE - Exam - ARC-1Document24 pagesCROP SCIENCE - Exam - ARC-1juliet udaundoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 7 S9LT-Ig-j-31: PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 7 S9LT-Ig-j-31: PhotosynthesisJulia Clarisse Alanza BallonNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDocument50 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wDocument5 pagesTopic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wSeve ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PhotosynthesisDocument99 pagesChapter 6 Photosynthesisjzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 06Document8 pagesBiology Chapter 06Aabisha Sharmin KhanNo ratings yet
- Broad Topics Biology CXC Exam 2022Document22 pagesBroad Topics Biology CXC Exam 2022tonk staryNo ratings yet
- BIO PRACTICAL 10 Class CBSE IndiaDocument12 pagesBIO PRACTICAL 10 Class CBSE Indiaroshni.ahmadNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition 2021Document8 pagesPlant Nutrition 2021lowkeydeadNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic Nutrition and Photosynthesis A LevelDocument62 pagesAutotrophic Nutrition and Photosynthesis A Levelnatukundajoshua42No ratings yet
- This Chapter Looks at PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesThis Chapter Looks at PhotosynthesisGiuseppe CondelloNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument43 pagesPlant NutritionSubaashNairNo ratings yet
- Notes Grade 8 - Chapter 6Document7 pagesNotes Grade 8 - Chapter 6qasimzebest2010No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument36 pagesLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- Bio PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesBio PhotosynthesisDoreth BridgemanNo ratings yet
- 植物的营养Document51 pages植物的营养2375606245No ratings yet
- NUTRITION - PlantDocument8 pagesNUTRITION - PlantKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition.Document16 pagesPlant Nutrition.zena mohamedNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument7 pagesPlant NutritionVedant SinghNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument28 pagesPDF Documentkaleb.kgzlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 How Green Plants FeedDocument41 pagesChapter 5 How Green Plants FeedAnonymous s5veYTCyWHNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition (Photosynthesis)Document45 pagesPlant Nutrition (Photosynthesis)Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - Ch10 - Plants and Food - Students' NotesDocument24 pagesUNIT 3 - Ch10 - Plants and Food - Students' NotesMostafa A MansiNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument18 pagesPlant Nutritionayman.hazem66No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument92 pagesLife ProcessesPrasanna DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition NoteDocument5 pagesPlant Nutrition NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 NotesDocument52 pagesBio 1 NotesTadala NsaliwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document4 pagesChapter 10Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1SashankNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants: 2 (G) 2 (L) 6 12 6(s) 2 (G)Document7 pagesNutrition in Plants: 2 (G) 2 (L) 6 12 6(s) 2 (G)John Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument59 pagesPhotosynthesisAima AzharNo ratings yet
- Combined Science NotesDocument61 pagesCombined Science NotesShawn ChimbwandaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Plant Responses#3Document29 pagesPhotosynthesis and Plant Responses#3BALQIS NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 Plants&Food REVIEW QUESTION AnswersDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 10 Plants&Food REVIEW QUESTION AnswersMostafa A MansiNo ratings yet
- Unit One Plantpart TwoDocument8 pagesUnit One Plantpart TwoAdmi BraccNo ratings yet
- Pamuzinda Science Notes in PDFDocument113 pagesPamuzinda Science Notes in PDFSillolwazi BroughNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Nutrition QB - 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesLife Processes - Nutrition QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Structure of A LeafDocument82 pagesStructure of A Leaflevie agacerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants: Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pagesChapter 10 - Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutition - 230204 - 212736 PDFDocument10 pagesPlant Nutition - 230204 - 212736 PDFashraf alaqilyNo ratings yet
- BWA L4 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesBWA L4 PhotosynthesisAghaanaa JaiganeshNo ratings yet
- 2.4 (A) Main Organ For PhotosynthesisDocument22 pages2.4 (A) Main Organ For PhotosynthesisVERNESS CHIA XIN THONG MoeNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Mastery BookletDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1Cheong JkNo ratings yet
- Notes ON PLANT NUTITION FOR GR 9Document5 pagesNotes ON PLANT NUTITION FOR GR 9PranatiNo ratings yet
- Notes PDFDocument38 pagesNotes PDFAbigail SachNo ratings yet
- Grade 08 English Medium Science - Copy (53114Document12 pagesGrade 08 English Medium Science - Copy (53114onmd2435No ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument50 pagesNutrition in PlantsAbigail SachNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapt 2Document11 pagesBio Chapt 2legaiansNo ratings yet
- Biology SQ3RDocument68 pagesBiology SQ3RJay JustNo ratings yet
- Preig Point 8 Unit1Document30 pagesPreig Point 8 Unit1myatthirisan2010No ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Delgado Et Al (2008) Propagacion Vegetativa de Taique y Tepa Con Fines OrnamentalesDocument7 pagesDelgado Et Al (2008) Propagacion Vegetativa de Taique y Tepa Con Fines OrnamentalesJoaquín Eduardo Sepúlveda AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Department of Agriculture Regional Field Office No. 02 Cagayan Valley Research CenterDocument7 pagesDepartment of Agriculture Regional Field Office No. 02 Cagayan Valley Research CenterAdonis CristobalNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Jenis Mulsa Organik Dan Sistem Tanam Jajar Legowo Terhadap Pertumbuhan Dan Hasil Tanaman Nilam Pogostemon Cablin BenthDocument8 pagesPengaruh Jenis Mulsa Organik Dan Sistem Tanam Jajar Legowo Terhadap Pertumbuhan Dan Hasil Tanaman Nilam Pogostemon Cablin BenthLAILATUL BADRIYAHNo ratings yet
- Soil Water RelationshipDocument34 pagesSoil Water RelationshipraghurmiNo ratings yet
- 18 Artikel 33 1 10 20200619Document6 pages18 Artikel 33 1 10 20200619Dirajati Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Indoor Herb Garden Outline - EditedDocument2 pagesIndoor Herb Garden Outline - EditedRuselleNo ratings yet
- New Species of Ruellia (Acanthaceae) From Southern South AmericaDocument5 pagesNew Species of Ruellia (Acanthaceae) From Southern South AmericabioandreyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Temperate VegetablessDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank - Temperate Vegetablesspradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument7 pagesTransport in PlantsRiya SharanNo ratings yet
- Insect Pest of CottonDocument4 pagesInsect Pest of CottonUmair FaheemNo ratings yet
- The R-Values of Honey: Pollen CoefficientsDocument24 pagesThe R-Values of Honey: Pollen Coefficientspppswing9320No ratings yet
- Orchid BooksDocument4 pagesOrchid BooksDr-Pranit SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Landscape ArchitectureDocument36 pagesLandscape ArchitectureMariz Aina LoberianoNo ratings yet
- Keragaman Dan Analisis Kekerabatan 30 Jenis Begonia Berdasarkan Karakter MorfologiDocument13 pagesKeragaman Dan Analisis Kekerabatan 30 Jenis Begonia Berdasarkan Karakter MorfologiNurmawadha LaemboNo ratings yet
- Silara - Issue 02 (Latest)Document61 pagesSilara - Issue 02 (Latest)J&A Partners JANNo ratings yet
- Plants Ouir Green Friends Worksheet LEAVESDocument3 pagesPlants Ouir Green Friends Worksheet LEAVESMeofcourseNo ratings yet
- Heritage Trees of Coimbatore DistrictDocument4 pagesHeritage Trees of Coimbatore DistrictV.SUNDARARAJUNo ratings yet
- PJJ B Inggris For Grade IXDocument2 pagesPJJ B Inggris For Grade IXErna HamidahNo ratings yet
- Agric Cucumber VarietyDocument33 pagesAgric Cucumber VarietyGabriel HarunaNo ratings yet
- Kandungan Hara BlotongDocument13 pagesKandungan Hara BlotongM. Abiyyu NaufalNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Production Technology of Safed MusliDocument63 pagesPresentation On: Production Technology of Safed MuslijagatividyasagarNo ratings yet
- MeristemDocument25 pagesMeristemhazizi100% (3)
- Plant NamesDocument484 pagesPlant NamesStalloneStallone50% (2)
- About The Course: VHSE CurriculumDocument61 pagesAbout The Course: VHSE CurriculumAneesha AK100% (1)
- Can You Identify The Parts of A Full Size Corn Plant?Document9 pagesCan You Identify The Parts of A Full Size Corn Plant?Mohamad Fitri Mustafa100% (1)