Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 3
Uploaded by
Bibek GajmerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 3
Uploaded by
Bibek GajmerCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Bibek Biswakarma Date: 30 th Sep 2021
Student no. 19-2-02646 Course: BS BIO 4-1
Immunology
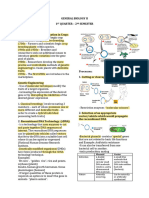
Assignment 3: Antigen Capture and presentation to lymphocytes
1. When antigens enter through the skin, in what organs are they
concentrated? What cell type(s) play important roles in this process of antigen
capture?
Antigens that enter through the skin are captured by dendritic cells that
reside in the epidermis and dermis and transported to skin draining lymph
nodes, where the antigens are concentrated and displayed to
lymphocytes.
2. What are MHC molecules? What are human MHC molecules called? How
were they discovered, and what is their function?
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules are cell surface
proteins that present antigenic peptides to T cells. Human MHC proteins
are called HLA molecules. They were initially discovered as products of
polymorphic genes that mediate transplant rejection. Their physiologic
function is antigen presentation.
3. What are the differences between the antigens that are displayed by class I
and class II MHC molecules?
Proteins that are produced in or enter the cytosol are presented by MHC
class I molecules. Proteins internalized into vesicles by endocytosis are
presented by MHC class II molecules.
4. Describe the sequence of events by which class I and class II MHC
molecules acquire antigens for display.
MHC class II α and β chains are produced in the endoplasmic reticulum,
where they assemble with each other and with an invariant chain that
occludes the antigen binding cleft. The MHC class II-invariant chain
complex is transported to a late endosomal/lysosomal compartment
where the invariant chain is degraded, leaving a peptide called CLIP in the
cleft. Proteins internalized by the endocytic pathway are degraded in late
endosomes and lysosomes into peptides. Specific peptides displace CLIP
and bind tightly to the cleft of the MHC class II molecule, which is then
transported to the cell surface.
5. Which functional subsets of T cells recognize antigens presented by class I
and class II MHC molecules?
CD4+ helper T cells recognize antigens displayed by class II molecules,
and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize MHC class I-peptide
complexes.
6. What molecules on T cells contribute to their specificity for either class I or
class II MHC–associated peptide antigens?
The CD4 co-receptor of helper T cells can bind to MHC class II molecules,
and the CD8 co-receptor of cytotoxic T cells binds to MHC class I
molecules.
You might also like
- Abdomen - Esophagus To ColonDocument42 pagesAbdomen - Esophagus To ColonBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- 17 Accessory Organs and The Portal SystemDocument103 pages17 Accessory Organs and The Portal SystemBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument62 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- 3d. Triangles of The NeckDocument82 pages3d. Triangles of The NeckBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pelvis: Fernando J. Peraldo, MD, MPHDocument67 pagesAnatomy of The Pelvis: Fernando J. Peraldo, MD, MPHBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear EACDocument29 pagesAnatomy of The Ear EACBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Anterior Eye and AdnexaeDocument66 pagesAnterior Eye and AdnexaeBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy: Abdomen 4 Kidneys, Ureter and Urinary BladderDocument74 pagesGross Anatomy: Abdomen 4 Kidneys, Ureter and Urinary BladderBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- 20 RectumDocument125 pages20 RectumBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The EarBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exercise AnalysisDocument1 pageBreathing Exercise AnalysisBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- 08 Female Reproductive SystemDocument70 pages08 Female Reproductive SystemBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Cellular Size and Components, Virus and ViroidsDocument52 pagesCellular Size and Components, Virus and ViroidsBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Lab 16Document4 pagesLab 16Bibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Biswakarma Bibek Reflection PaperDocument1 pageBiswakarma Bibek Reflection PaperBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Employee MotivatioDocument19 pagesEmployee MotivatioBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Analysis BreathingDocument2 pagesAnalysis BreathingBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Exercise Proteins and EnzymesDocument4 pagesExercise Proteins and EnzymesBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Running Head: Motivation in The WorkplaceDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Running Head: Motivation in The WorkplaceBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Module 1 BiochemDocument40 pagesModule 1 BiochemAlyssa PachecoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Transes (Week 4)Document6 pagesBiochem Lec Transes (Week 4)Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan in Science Grade Level: 9 Quarter: 1Document14 pagesLearning Plan in Science Grade Level: 9 Quarter: 1Chin CustodioNo ratings yet
- Bio. ReviewerDocument20 pagesBio. ReviewerdanglapenmaryjayNo ratings yet
- Charlie Gard Ethics, Conflict and Medical Treatment For ChildrenDocument15 pagesCharlie Gard Ethics, Conflict and Medical Treatment For ChildrenNurudeen AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Notes: Independent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticsDocument22 pagesGenetics Notes: Independent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticsTevfik DoğanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Quiz 4Document1 pageAnswer Key Quiz 4Coronacion, Earl Vin T.No ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension LatihanDocument3 pagesReading Comprehension LatihanlolatrhesiaNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument5 pagesGram StainingDavid WolfyNo ratings yet
- What Is MitosisDocument3 pagesWhat Is MitosisJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education: St. Joseph Village, Cogon, Bogo City, CebuDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education: St. Joseph Village, Cogon, Bogo City, CebuSaiza BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument10 pagesLab ReportJeevikaGoyal100% (1)
- Nakita Harris - VIRUS READING (LYTIC & LYSOGENIC)Document2 pagesNakita Harris - VIRUS READING (LYTIC & LYSOGENIC)Nakita HarrisNo ratings yet
- Questions Based On AllenDocument24 pagesQuestions Based On AllenSanvi VjNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismsDocument46 pagesGenetically Modified OrganismsVann BanastaoNo ratings yet
- Cells: Hap - Cell BiologyDocument8 pagesCells: Hap - Cell BiologyKyle LumingkitNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1687157X12000376 Main PDFDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S1687157X12000376 Main PDFJonathan RedricoNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Pathophysiology andDocument15 pagesPreeclampsia Pathophysiology andYojhaida Zarate CasachahuaNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 Significance or Applications of Mitosis and MeiosisDocument7 pagesActivity 8 Significance or Applications of Mitosis and Meiosissarah jane lomaNo ratings yet
- Clsi MM12 PDocument118 pagesClsi MM12 PCristian Gutiérrez VeraNo ratings yet
- Articulo 1Document14 pagesArticulo 1MARIA KATHERINE MORANTES PORRASNo ratings yet
- GB2 LAS Q3 W2 Evol of Life On EarthDocument14 pagesGB2 LAS Q3 W2 Evol of Life On EarthAnn Clarisse Ondiano100% (1)
- Biotechnology Guide Grade 8Document30 pagesBiotechnology Guide Grade 8Mary Celky Espinosa100% (1)
- Glofish AmericaDocument43 pagesGlofish Americastreliza1No ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 2019Document26 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 2019Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- SIGNIFICANCE OR APPLICATIONS OF MITOSIS and MEIOSIS - EllaDocument8 pagesSIGNIFICANCE OR APPLICATIONS OF MITOSIS and MEIOSIS - EllaKennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- Topic 11-Application FUGABAN SHEINA MAE E. BSBA MM 1ADocument3 pagesTopic 11-Application FUGABAN SHEINA MAE E. BSBA MM 1ASheina FugabanNo ratings yet
- Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Biosignaling: Prof. Yong Tae KwonDocument86 pagesMolecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Biosignaling: Prof. Yong Tae KwonJon QNo ratings yet
- Bone Development Andbone Growth-0Document28 pagesBone Development Andbone Growth-0Aruli AruliNo ratings yet
- STS Filipino ScientistDocument2 pagesSTS Filipino Scientistmico bautistaNo ratings yet