Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemistry Lecture Exercises
Uploaded by
Reina JeanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrochemistry Lecture Exercises
Uploaded by
Reina JeanCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|9960545
Electrochemistry Lecture with Exercises (General Chemistry)
Senior High School (Pontifical and Royal University of Santo Tomas, The Catholic
University of the Philippines)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by REINA JEAN PEPITO (rj.plouise17@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9960545
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Rules in Oxidation Number
ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Free Elements (uncombined state) have an
- Branch of chemistry that deals with the oxidation number of zero.
interconversion of electrical energy and chemical Na, Be, K, Pb, H2, O2, P4= 0
energy 2. In monatomic ions, the oxidation number is
equal to the charge on the ion.
Electrochemical processes are oxidation- reduction Li+,Li=+1;Fe3+,Fe=+3; O2-,O=-2
reactions in which: 3. The oxidation number of oxygen is usually –2.
● the energy released by a spontaneous In H2O2 and O22-it is –1.
reaction is converted to electricity or 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 except
● electrical energy is used to cause a when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds.
nonspontaneous reaction to occur In these cases, its oxidation number is –1.
5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and
Batteries are the most familiar devices for fluorine is always –1.
converting between electrical and chemical 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the
energies. Laptops and other gadgets rely on atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to the charge on
batteries to provide the electricity needed for the molecule or ion.
operation.
OXIDATION-REDUCTION (REDOX) REACTIONS
- involves transfer of electrons and is made up of
two half - reactions (oxidation and reduction):
Oxidation - loss of electrons
Reduction – gain of electrons
(Since, electrons are negatively charged, an
atom that is oxidized (losses electrons) will
have an increase in its oxidation number (more
+) and an atom that is reduced (gains electrons)
will have a decrease in its oxidation number
(more -)
2Mg(s) + O2 (g) → 2MgO(S)
In the reaction:
Mg lost electrons. We say Mg was oxidized.
HIGHER ELECTRONEGATIVITY,
O gained electrons. It was reduced.
HIGHER MASS.
Each of the two half-processes cannot happen
Oxidation: Loss of electrons, ON ↑
independently without the other half- process.
Reduction: Gain of electrons, ON ↓
Hence, when one reads phrases like “the
oxidation of magnesium”, there is emphasis
placed on what is happening to the magnesium
metal, but there is always an accompanying
reduction process.
Downloaded by REINA JEAN PEPITO (rj.plouise17@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9960545
Oxidizing agent (oxidant) Zn electrode (anode): Zn(s) Zn2+ (aq) + 2e-
- the reactant that carries the atom or element that Cu electrode (cathode): Cu2+(aq) + 2e-
is reduced - substance that acquires electrons, Cu(s)
thereby causing another substance to be oxidized
and so is reduced in the process Salt bridge
- an inverted U tube containing an inert
Reducing agent (reductant) electrolyte solution, such as NaCl, KCl or
- the reactant that carries the atom or element that NH4NO3 (whose ions will not react with other
is oxidized - substance that gives up electrons, ions in solution or with the electrodes) that
thereby causing another substance to be reduced. prevents build up of positive charge in anode
and so is oxidized in the process compartment (due to the formation of Zn2+
ions) and negative charge in the cathode
compartment (created when some of the Cu2+
ions are reduced to Cu) which would stop the
cell from operating.
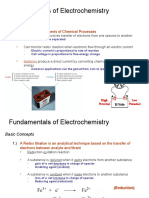
Cell Notation (a.k.a Cell Diagram)
- is a shorthand form of a galvanic cell (rather
than drawing a complete set-up)
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
Spontaneous
- The energy released by a spontaneous redox
reaction is converted to electricity or
- conducted in a galvanic cell Cell Potential
- (a.k.a. voltaic cell) - the difference in electrical potential between the
anode and cathode
Non-Spontaneous - electromotive force, or cell voltage
- Electrical energy is used to cause a - Cell Potential (Ecell)
nonspontaneous reaction to occur
- also known as electrolysis Electromotive Force (EMF)
- conducted in an electrolytic cell - because it provides the driving force that
pushes electrons through the external circuit
GALVANIC CELLS Cell Voltage
- an experimental apparatus for generating - because it is measured in volts
electricity through the use of a spontaneous
redox reaction “An Ox”: anode where oxidation happens
- a device in which the transfer of electrons (from “Red cat”: reduction happens in the cathode
a spontaneous redox reaction) takes place
through an external pathway rather than
directly between reactants present in the same
reaction vessel.
Anode - electrode at which oxidation occurs
Cathode - electrode at which reduction occurs
Downloaded by REINA JEAN PEPITO (rj.plouise17@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9960545
ELECTROLYSIS
- is the process in which electrical energy is used
to cause a non spontaneous chemical reaction to
occur.
Electrolytic Cell
- is an apparatus for carrying out electrolysis.
The same principles underlie electrolysis
and the processes that take place in galvanic
cells.
The external battery supplies the electrons.
They enter through the cathode and come out
through the anode:
Anode – is the positive electrode
Cathode – is the negative electrode
“PANIC”: Positive in Anode, Negative in
Cathode
--------------------------------------------------------------------
TRIVIAS
1. Furan in canned tuna
- furan is a toxin categorized as possible
carcinogen
- tuna contains omega-3 fatty acid (unsaturated
fatty acid)
Downloaded by REINA JEAN PEPITO (rj.plouise17@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9960545
Downloaded by REINA JEAN PEPITO (rj.plouise17@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9960545
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT smallest whole-number coefficients, the coefficient
of S is _____.
1. Complete and balance the following redox
H2S + HNO3 → S + NO (acidic solution)
equation. What is the coefficient of H2O when the
equation is balanced with the set of smallest
whole-number coefficients?
– – – (basic) Ans: 3
H2O + MnO4 + I → MnO2 + IO3
3H2S + 2HNO3 → 3S + 2NO + 4H2O
Ans: 1
5. Consider an electrochemical cell constructed from
H2O + 2MnO4- + I- → 2MnO2 + IO3- + 2OH-
the following half cells, linked by a KCl salt bridge.
2. A balanced redox equation must have which of the - a Fe electrode in 1.0 M FeCl 2 solution
following: - a Sn electrode in 1.0 M Sn(NO 3) 2 solution
I. The same number of each type of atom on
both sides of the equation. When the cell is running spontaneously, which
II. The total number electrons lost in the choice includes only true statements and no false
oxidation equal to the total number of ones? Sn is more electronegative than Sn.
electrons gained in the reduction. A. The tin electrode gains mass and the tin
III. The same total charge of all ionic species electrode is the cathode.
on both sides of the reaction. B. The iron electrode loses mass and the iron
IV. H2O present as a product or a reactant. electrode is the cathode.
C. The iron electrode gains mass and the iron
Ans: I, II, III electrode is the anode.
D. The tin electrode loses mass and the tin
3. In an electrolytic cell, electrical energy is used to electrode is the cathode.
cause a chemical reaction to occur that would
otherwise be nonspontaneous. Ans: The tin electrode gains mass and the tin
electrode is the cathode.
Ans: TRUE HIGHER ELECTRONEGATIVITY,
HIGHER MAS
4. Complete and balance the following redox
equation. When properly balanced using the
Downloaded by REINA JEAN PEPITO (rj.plouise17@gmail.com)
You might also like
- 11 ElectrochemistryDocument26 pages11 ElectrochemistryKEVIN PALMERONo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrochemistry NotesDocument21 pagesBasics of Electrochemistry NotesErianne ReyesNo ratings yet
- CTSC Matric Masterclasses Electrochemistry 2020-1Document17 pagesCTSC Matric Masterclasses Electrochemistry 2020-1Nika ReleniNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry GuideDocument78 pagesElectrochemistry GuideNik Muhammad Firdaus100% (1)
- (18530) Sheet 1 Electrochemistry B PDFDocument99 pages(18530) Sheet 1 Electrochemistry B PDFAnuragPandey100% (1)
- Electrochemistry GuideDocument56 pagesElectrochemistry GuideSuyash BuchkeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Introduction To Electroanalytical ChemistryDocument16 pagesChapter Five Introduction To Electroanalytical ChemistryZekarias LibenaNo ratings yet
- Notes ElectroDocument15 pagesNotes ElectrodasdwasdwadNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument56 pagesElectrochemistry NotesAnusha PanchumarthiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Electrochemistry StudentsDocument53 pagesChapter 8 Electrochemistry Studentsnur hashimahNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument30 pagesElectro ChemistryPower booster100% (1)
- Electrochemistry GuideDocument59 pagesElectrochemistry GuideSwayam Tejas PadhyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15-4811-ElectroanalyticalmethodsDocument137 pagesChapter 15-4811-ElectroanalyticalmethodsMustafa KamalNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry GuideDocument67 pagesElectrochemistry GuideShyam KiranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 DatedDocument16 pagesLecture 02 Datedجعلی اکاؤنٹNo ratings yet
- Lecture-02 DatedDocument16 pagesLecture-02 Datedجعلی اکاؤنٹNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes Merged MergedDocument721 pagesChem Notes Merged Mergedmaxrenson2002No ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument51 pagesElectrochemistryhelloNo ratings yet
- Chemi G 10 Chap 3 HanoutDocument5 pagesChemi G 10 Chap 3 HanoutYISHAK ABRHAMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Electro ChemistryDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Electro ChemistryKritika MishraNo ratings yet
- CH.3.14Document135 pagesCH.3.14active learning educationNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument40 pagesElectrochemical CellsMohosin MahmudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document59 pagesChapter 2Kiran RajNo ratings yet
- Electrochem 1Document77 pagesElectrochem 1koustubhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Engineering ChemistryDocument56 pagesLecture Notes - Engineering ChemistryadamjosephNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument27 pagesElectrochemistrymanishaNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Cells - Chemistry LibreTexts PDFDocument5 pagesElectrolytic Cells - Chemistry LibreTexts PDFPahe DriveNo ratings yet
- CW 37Document13 pagesCW 37lgguillen20No ratings yet
- Electrochemical Energy: Unit 2. Matter and Energy: CDocument43 pagesElectrochemical Energy: Unit 2. Matter and Energy: CMayNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Chy2018Document48 pagesElectrochemistry Chy2018DubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry FundamentalsDocument26 pagesElectrochemistry FundamentalsJayden WangNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Class 12 - Chemistry Chapter 3:electrochemistryDocument9 pagesDelhi Public School Class 12 - Chemistry Chapter 3:electrochemistryAvishi OjNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Electrochemical CellsDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Electrochemical CellsNieva Aldiano LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: An Introduction to Batteries and CellsDocument54 pagesElectrochemistry: An Introduction to Batteries and CellsLala LalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ElectrochemistryDocument51 pagesUnit 3 Electrochemistrysukaina fatimaNo ratings yet
- Study of Electrochemical Energy ConversionDocument13 pagesStudy of Electrochemical Energy Conversionilias1973No ratings yet
- Electrochemical cells explainedDocument21 pagesElectrochemical cells explaineddanishNo ratings yet
- Week 3 and 4 Electrochemical EnergyDocument59 pagesWeek 3 and 4 Electrochemical EnergyB - DAPO, John Michael Q.No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 1Document17 pagesElectrochemistry 1dwijsaidwhatNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument35 pagesElectrolysisericbattyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Electro ChemistryDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Electro ChemistryKritika MishraNo ratings yet
- Chem 17Document9 pagesChem 17Adi SoNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument153 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYSTUDY GRINDNo ratings yet
- 2 e Lech Tro ChemistryDocument39 pages2 e Lech Tro ChemistryrahmaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument54 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYMaria OzaoNo ratings yet
- BS MME 2024 Lec#9Document20 pagesBS MME 2024 Lec#9maqsood3982No ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesIntroduction To ElectrochemistryKharylle Ann IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument9 pagesTerm PaperKojo PappoeNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument5 pagesElectro ChemistryPRanavNo ratings yet
- Plating 3Document60 pagesPlating 3Muthu AravindNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus in Nat. Sci. 1L - Chemistry For EngineersDocument14 pagesCourse Syllabus in Nat. Sci. 1L - Chemistry For EngineersVincent BaguioNo ratings yet
- II Semester/Unit 1/electrochemistryDocument25 pagesII Semester/Unit 1/electrochemistryapi-26041653100% (1)
- CHE 111 - Lecture 15 Electrochemistry PDFDocument62 pagesCHE 111 - Lecture 15 Electrochemistry PDFElisa MuntangaNo ratings yet
- Electromotiveforcefinal 200727 135128Document15 pagesElectromotiveforcefinal 200727 135128Mohit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectrochemistryDocument36 pagesBasics of ElectrochemistryNaveed JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Matter and Energy Electrochemical Energy: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - Matter and Energy Electrochemical Energy: Learning ObjectivesNiña Viaña BinayNo ratings yet
- Electro Chemistry IIDocument6 pagesElectro Chemistry IIPavan PavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document27 pagesChapter 14Louise RaphaelleNo ratings yet
- PCC 3300 PDFDocument6 pagesPCC 3300 PDFdelangenico4No ratings yet
- Buckley V UkDocument12 pagesBuckley V UkShriya ChandankarNo ratings yet
- Fasader I TraDocument56 pagesFasader I TraChristina HanssonNo ratings yet
- Tsu m7 Practice Problems Integral CalculusDocument1 pageTsu m7 Practice Problems Integral CalculusJAMNo ratings yet
- PRAGMATISMDocument22 pagesPRAGMATISMChristian Jay A MoralesNo ratings yet
- Communication Strategy Target AudienceDocument47 pagesCommunication Strategy Target Audienceguille simariNo ratings yet
- 6 Fsiqiatria-1524041346Document48 pages6 Fsiqiatria-1524041346მირანდა გიორგაშვილიNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Consolation Orchestra InstrumentsDocument2 pagesOur Lady of Consolation Orchestra InstrumentsCelestian Valensario PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal HaDocument3 pagesResearch Proposal Haapi-446904695No ratings yet
- Diagrama RSAG7.820.7977Document14 pagesDiagrama RSAG7.820.7977Manuel Medina100% (4)
- Motor-Catalog English 2013 PDFDocument80 pagesMotor-Catalog English 2013 PDFILham Dwi PutraNo ratings yet
- Architecture Floor Plan Abbreviations AnDocument11 pagesArchitecture Floor Plan Abbreviations AnGraphitti Koncepts and DesignsNo ratings yet
- CV HannahDocument3 pagesCV HannahRoxan DosdosNo ratings yet
- SD NEGERI PASURUHAN PEMERINTAH KABUPATEN TEMANGGUNGDocument5 pagesSD NEGERI PASURUHAN PEMERINTAH KABUPATEN TEMANGGUNGSatria Ieea Henggar VergonantoNo ratings yet
- Global Internship for Language TeachersDocument5 pagesGlobal Internship for Language TeachersCarlos ChamorroNo ratings yet
- Contrastive Study of English and Romanian Legal TerminologyDocument39 pagesContrastive Study of English and Romanian Legal TerminologyVictorNo ratings yet
- Surveying 2 Practical 3Document15 pagesSurveying 2 Practical 3Huzefa AliNo ratings yet
- A Text-Book of Colloquial Japanese, Based On The Lehrbuch Der Japanischen Umgangssprache by Dr. Rudolf Lange (1907)Document634 pagesA Text-Book of Colloquial Japanese, Based On The Lehrbuch Der Japanischen Umgangssprache by Dr. Rudolf Lange (1907)asdf123123100% (1)
- The Definition and Unit of Ionic StrengthDocument2 pagesThe Definition and Unit of Ionic StrengthDiego ZapataNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Manufacturing ProcessesDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Manufacturing Processesnauman khanNo ratings yet
- Ky203817 PSRPT 2022-05-17 14.39.33Document8 pagesKy203817 PSRPT 2022-05-17 14.39.33Thuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Inducting - Orientation, Socialisation & Placing New HiresDocument17 pagesInducting - Orientation, Socialisation & Placing New HiresJaskiran KaurNo ratings yet
- Anne Frank Halloween Costume 2Document5 pagesAnne Frank Halloween Costume 2ive14_No ratings yet
- Dasakam 31-40Document16 pagesDasakam 31-40Puducode Rama Iyer RamachanderNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Unit IDocument14 pagesAbnormal Psychology Unit IMahadevan K V100% (1)
- KluberDocument20 pagesKluberJako MishyNo ratings yet
- UTH homework template for English exercisesDocument8 pagesUTH homework template for English exercisesCinthya Peña de MezaNo ratings yet
- Json Cache 1Document5 pagesJson Cache 1Emmanuel AmoahNo ratings yet
- Titanium Plates and Screws For Open Wedge HtoDocument6 pagesTitanium Plates and Screws For Open Wedge HtoDaniel Quijada LucarioNo ratings yet
- Form of SpesDocument2 pagesForm of SpesMark Dave SambranoNo ratings yet