0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views5 pagesWrapper Class
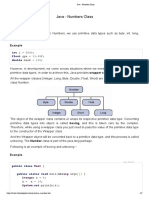
The document contains 4 questions that demonstrate the use of wrapper classes in Java. Question 1 prints the minimum and maximum values for various primitive wrapper types like Integer, Double, etc. Question 2 converts an integer to its binary, octal, and hexadecimal equivalents. Question 3 formats a binary string for an integer entered by the user. Question 4 demonstrates cloning an Employee object that overrides the clone method.
Uploaded by
RaghuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views5 pagesWrapper Class
The document contains 4 questions that demonstrate the use of wrapper classes in Java. Question 1 prints the minimum and maximum values for various primitive wrapper types like Integer, Double, etc. Question 2 converts an integer to its binary, octal, and hexadecimal equivalents. Question 3 formats a binary string for an integer entered by the user. Question 4 demonstrates cloning an Employee object that overrides the clone method.
Uploaded by
RaghuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd