Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soil Investigation Report (Gawadar)
Uploaded by
Shergul Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views10 pagesghjkloi
Original Title
Soil Investigation Report (Gawadar) - Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentghjkloi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views10 pagesSoil Investigation Report (Gawadar)
Uploaded by
Shergul Khanghjkloi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
SOIL INVESTIGATION
REPORT
Gwadar Bay
st Mets aero (Greco hor )
eX [NED Universit of Engineering nd Technology
, Department of Chl Engineering
wes Soil Mechanics Laboratory
No, NEDICIVTSML 20926 Dat: 26092020
rein <8 Seaplane
Quasi Associates Architect Engineers Interior
‘Consultancontractor
Project Name | Echo Resort Construction
Projcct Location | Geer Bay
Type of Testing | Denied So iniesinia
Date of Testing | 264072020,
‘ASTM D 1452 ~ 7a StandattPrsetice for Soil Investigation
sg Sumping
ape ae
'D2487 -I7el Standard Practice for Casification of Soils for
Engineering Purposes Unified Soil Cisification System)
1 1194 ~94 Standéra Test Method for Bearing Capacity of Soil
Standard Test Method
1) Resuks petinng to the disturbed samples collected and
Supplied the abort) py the lent,
2) The ess were condusted based onthe avaiable quantity of
the material provided
23) Theseus slong with pbs ar nloed
PREPARED & VERIFIED IT
LE
Dr: Amaneilah Marri
Professor
DRAMANULLA MARR
Solace
Ce
Tn On apr BED i ang Tans Rao PaR TST
fetches tora cen zd &
‘TABLE OF CONTENTS
(GEOTECHNICAL SITE INVESTIGATION REPORT. 3
1. Introduction 3
2, Seopeof work 3
3. Shallow foundations. 3
4, Raft foundation. = 3
5. Borehole location. = 4
6, Soil profile 5
7, Bearing capacity 8
8. Seismic profil of Gwadar Bay. 9
| 9 Resommendaons = 0
|
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure | Borehole location map. 4
Figure § Pitre of site Guring investigation 5
| Figure 2 Bearing capacity along she depth Gwader Bay BH Nod 3
| bse) wera cacy sng ide Grad BHNo2.. 9
[les re Gro Assen (Gn) map of Fain MD). 10
1 LIST OF TABLES
| Tle} Qeae may BH Nod 6
‘Table? Gwadar Bay BH No2. : 5
| Table 3 Guadar Bay BH No. a - 8
“Table 4 Gwadat Bay BH NO ooo : 9
Sp TE Fag TED pe Eee ech Rae PTS
con ae (ouch god @
(GEOTECHNICAL SITE INVESTIGATION REPORT
1. Introduction
‘The geotechnical site investigation ata site at Gwadar Bay Baluchistan was carried out
based on the field and laboratory testing, Feld work consisting of two boreholes drilled up
to a depth of 15m, The samples were brought in core boxes for laboratory investigations,
Allthe tests were conducted as per ASTM standards or otherwise wherever, required, The
laboratory testing consisted of soil gradation (sievehyérometer amlyss), consistency
limits, density of sol samples (from undisturbed/remoulded samples and corelations,
te), strength parameters (@hrough direct shear test), the elastis parameters. were
determined through testing and corelations with the type of sll and elative density, et.
“The results forthe boreholes are given inthe following tables corresponding tothe depth
‘of samples from which the samples were exhumed.
2, Scope of work
The scope of present geotechnical site investigation report compises of the bearing
capacity analysis ofthe borehole samples based on field and lsboratory investigations and
analysis forthe detemmination ofthe necessary sol parameters required for the design of @
foundation
Shallow foundations are usually comprised of isolated foctings, combined footing, spread
footing and raft foundations to offer support 10 the lightweight or one to two story
buildings. The shallow foundations usually draw its load carrying capacity through sol-
foundation interaction based on the soil behaviour and foundation dimensions, Therefore,
the type of soil its elative density ane strength parameters have significant contribution
jn the design of shallow foundations.
4, Raft foundation
A mat foundation isa large concrete slab used to interface one column, or mare than one
‘column in several ines, with the Bae soi, Itmay encompass the entre foundition area or
capacity andlor the column lads are so large that more than SO pacent of the aes it
‘overed by conventional spread footings
5, Borehole locations
‘Borehole locations mep is shown in Figure 1. The pictre of site during investigation is
shown in Figure 2.
Figure | Borehole location map
igure 2 Pictur of site daring investigation
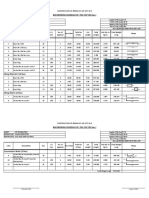
6, Soll profile
The sil onthe sit is mainly consisted of fine sand and silt sand below 7.0 m dept there
isa bed rock consisting of weathered rock of medium hardness. The soil profile for BH
‘No.1 and BH No, 2is shown in Table 1 and Table 2
ee
suc go
Sa Moi Lato
“Table } Guadar Bay BEN
Ta Ese an RreiTaTe ase
ttc torso cin ep) ©)
‘Table? Guadir Bay BH No2
Banaras
‘Table 4 Gwadar Bay BHNO2
Fine sand LS,
Fine sly sand
Fine silty sand
Silty la
Sit la
a
Cis
‘Core samples
‘ore samples
Core samples
Bearing Capacity (9)
00 0s Lo 1s 20
Depth (=)
2
Figue 4 Bearing capi slong the éeph GoadarBay BH No
8, Seismie profile of Gwadar Ba
‘According to the Balochistan Conservation Strategy (BCS) Makean Coast is one of the
-most seismically active regions in Pekistan hati susceptible to earthquakes and tsunamis.
“The cosst sits on e major subduction zone. Seismic records fr the period between 1851
and 1990 indicate the occurence of 193 earthquakes of 4 and shove on the Richter sels
“The epicenter ofthe earthquake was 87 kilometres south-west of Chur in Balochistan, The
towns of Pasr and Ormara were both reportedly underwater afer the tsunami that was
also recorded at Muscat and Gwadar, Tis was the most recent msjortsunami-Beneting
‘earthquake in the Arabian Sea, Several studies wee carried out for the seismic actyite hn
jis region the peak ground acceleration through deterministic and probabilistic analysis
pr determined to be around 0.38 g for Gwadar City
nd; therefore, soil liquefaction factor may be given due consderetion. The
commended bearing capacity forthe foundation is 1.5 tsf for BH No! site and 1.0 tf
hallow foundation depth may be kept within Dy~ 30 m.
You might also like
- Mix Design of ConcreteDocument9 pagesMix Design of ConcreteShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- FT FT in in PSF PSF PSF in FT FT FT FTDocument13 pagesFT FT in in PSF PSF PSF in FT FT FT FTShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Design QADocument2 pagesRetaining Wall Design QAShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- Basement Retaing WallDocument2 pagesBasement Retaing WallShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-09-13 09.46.39Document2 pagesNew Doc 2019-09-13 09.46.39Shergul KhanNo ratings yet
- 49 - All Contractors - Suspention of WorksDocument2 pages49 - All Contractors - Suspention of WorksShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- CV - Neha Shamim - April 2019Document3 pagesCV - Neha Shamim - April 2019Shergul KhanNo ratings yet
- Option 5a PDFDocument13 pagesOption 5a PDFShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- Quote & Invoice For STR & BIMDocument3 pagesQuote & Invoice For STR & BIMShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- Personal DataDocument2 pagesPersonal DataShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- Option 5a PDFDocument13 pagesOption 5a PDFShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- 0 - Title Page-Vol-Ii (DRWGS)Document1 page0 - Title Page-Vol-Ii (DRWGS)Shergul KhanNo ratings yet
- Bar Bending Schedule of Pile Cap (01 Nos.) : Construction of Bridge at Asf City M-9Document2 pagesBar Bending Schedule of Pile Cap (01 Nos.) : Construction of Bridge at Asf City M-9Shergul KhanNo ratings yet
- Syed Ashar Hussain CVDocument3 pagesSyed Ashar Hussain CVShergul KhanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)