0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views8 pagesReproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 9
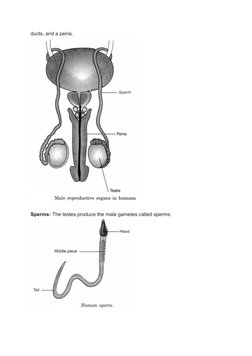
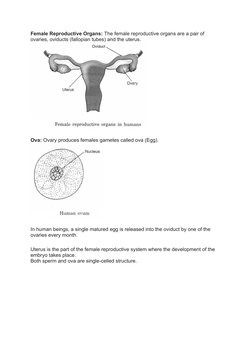
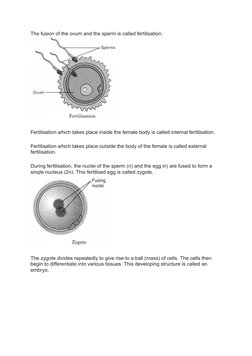
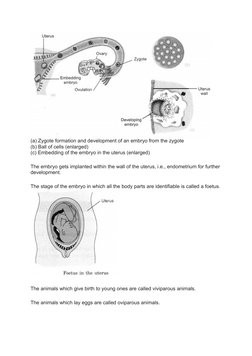
The document provides an overview of reproduction in animals, including the key differences between sexual and asexual reproduction. It outlines the male and female reproductive organs and gametes involved in sexual reproduction, such as testes that produce sperm and ovaries that produce eggs. Fertilization, the process by which sperm and eggs fuse, is also explained. The zygote develops into an embryo, then fetus, with viviparous animals giving birth and oviparous animals laying eggs. Asexual reproduction methods like budding and binary fission are also summarized briefly.
Uploaded by
zodika khiangteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views8 pagesReproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 9
The document provides an overview of reproduction in animals, including the key differences between sexual and asexual reproduction. It outlines the male and female reproductive organs and gametes involved in sexual reproduction, such as testes that produce sperm and ovaries that produce eggs. Fertilization, the process by which sperm and eggs fuse, is also explained. The zygote develops into an embryo, then fetus, with viviparous animals giving birth and oviparous animals laying eggs. Asexual reproduction methods like budding and binary fission are also summarized briefly.
Uploaded by
zodika khiangteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Sexual Reproduction
- Introduction
- Asexual Reproduction
- Reproductive Terminology