Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nadiatul - Summary Week 4
Uploaded by
nadxco 17110 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageOriginal Title
041911333077_Nadiatul_Summary Week 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageNadiatul - Summary Week 4
Uploaded by
nadxco 1711Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Name : Nadiatul Qalbi Amalia Rizqi
Student ID : 041911333077
Process costing is a method of costing used mainly in manufacturing
where units are continuously mass-produced through one or more processes.
Examples of this include the manufacture of erasers, chemicals or processed
food. In process costing it is the process that is costed (unlike job costing
where each job is costed separately). The method used is to take the total cost
of the process and average it over the units of production.
Process costing is used in situations where homogeneous products or services
are produced on a continuous basis. Costs flow through the manufacturing
accounts in basically the same way in both job-order and process costing
systems. A process costing system differs from a job-order system primarily in
that costs are accumulated by department (rather than by job) and the
department production report replaces the job cost sheet.
To compute unit costs in a department, the department's output in terms
of equivalent units must be determined. In the weighted-average method, the
equivalent units for a period are the sum of the units transferred out of the
department during the period and the equivalent units in ending work in
process inventory at the end of the period.
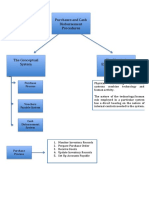
The activity in a department is summarized on a production report. There are
three separate (though highly interrelated) parts to a production report. The
first part is a quantity schedule, which includes a computation of equivalent
units and shows the flow of units through a department during a period. The
second part consists of a computation of costs per equivalent unit, with unit
costs being provided individually for materials, labour, and overhead as well
as in total for the period. The third part consists of a cost reconciliation, which
summarizes all cost flows through a department for a period.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Cost DriverDocument15 pagesCost Drivernadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Tata Starbucks: A Brew For India: Nadiatul Qalbi Amalia RizqiDocument18 pagesTata Starbucks: A Brew For India: Nadiatul Qalbi Amalia Rizqinadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatul Qalbi - Week 11Document10 pagesNadiatul Qalbi - Week 11nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Team 2 - Uber Case - Week 9Document8 pagesTeam 2 - Uber Case - Week 9nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Pixar Case StudyDocument13 pagesPixar Case Studynadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatul - Summary Week 9Document2 pagesNadiatul - Summary Week 9nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Team 2 - Case CHPT 9 - Week 8 (SIM)Document1 pageTeam 2 - Case CHPT 9 - Week 8 (SIM)nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Audit Sampling For Test of Controls and Substantive Tests of TransactionDocument27 pagesAudit Sampling For Test of Controls and Substantive Tests of Transactionnadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Non Attestation ServicesDocument20 pagesNon Attestation Servicesnadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatuk - Summary Week 7 and CaseDocument3 pagesNadiatuk - Summary Week 7 and Casenadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatul - Week 14Document5 pagesNadiatul - Week 14nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatul - Summary Week 5Document4 pagesNadiatul - Summary Week 5nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatul - Summary Chapter 9Document2 pagesNadiatul - Summary Chapter 9nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Units Completed and Transferred Out: Total Units Finished From Beginning Work inDocument2 pagesUnits Completed and Transferred Out: Total Units Finished From Beginning Work innadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Risk Management: Nadiatul Qalbi Amalia Rizqi (04191133307)Document23 pagesChapter 4: Risk Management: Nadiatul Qalbi Amalia Rizqi (04191133307)nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Final PPT Week 13Document32 pagesFinal PPT Week 13nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Database Management System: Nadiatul Qalbi Amalia RizqiDocument23 pagesDatabase Management System: Nadiatul Qalbi Amalia Rizqinadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatul - Resume Chapter 5Document2 pagesNadiatul - Resume Chapter 5nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatul - HW Week 7Document4 pagesNadiatul - HW Week 7nadxco 1711No ratings yet
- Nadiatul - Summary ISA 300Document2 pagesNadiatul - Summary ISA 300nadxco 1711No ratings yet