0% found this document useful (0 votes)
247 views5 pagesTP1 TP2 TP3 Ranking Table PFMEA English 27-06-2019 2
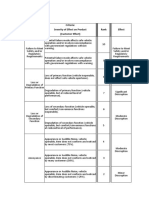
The document provides a process for evaluating the severity of potential failures according to ratings from 1-10. It defines the severity levels and provides examples of how severity would be determined based on the impact to manufacturing plants, end users, and vehicle functions. It also includes a table for rating the occurrence potential of failure causes on a scale of 1-10, which considers prevention controls.
Uploaded by
白子健Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
247 views5 pagesTP1 TP2 TP3 Ranking Table PFMEA English 27-06-2019 2
The document provides a process for evaluating the severity of potential failures according to ratings from 1-10. It defines the severity levels and provides examples of how severity would be determined based on the impact to manufacturing plants, end users, and vehicle functions. It also includes a table for rating the occurrence potential of failure causes on a scale of 1-10, which considers prevention controls.
Uploaded by
白子健Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd